
LondonLife – View down Whitehall…


A rectangular block of pale yellow sandstone decorated with a Latin cross, the Stone of Scone, also known as the Stone of Destiny, long featured in the crowning of Scottish kings. But in 1296, it was seized by King Edward I as a trophy of war.

He brought it back to England (or did he? – it has been suggested the stone captured by Edward was a substitute and the real one was buried or otherwise hidden). In London, it was placed under a wooden chair known as the Coronation Chair or King Edward’s Chair on which most English and later British sovereigns were crowned.
On Christmas Day, 1950, four Scottish nationalist students – Ian Hamilton, Kay Matheson, Gavin Vernon and Alan Stuart – decided to liberate the 152 kilogram stone and return it to Scotland.
The stone broke in two when it was dropped while it was being removed (it was later repaired by a stone mason). The group headed north and, after burying the greater part of it briefly in a field to hide it, the stone was – on 11th April, 1951 – eventually left on the altar of Arbroath Abbey in Scotland.
No charges were ever laid against the students.
It was brought back to the abbey and used in the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II in 1953.
The stone was eventually returned to Scotland in 1996 on the proviso it could be temporarily relocated back to London for coronations and now sits in Edinburgh Castle. It was taken to London temporarily in 2023 for the coronation of King Charles III but has since been returned.
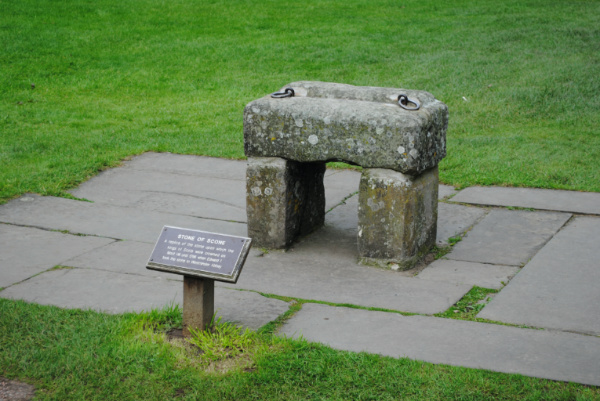

There is a replica of the stone at Scone Castle in Scotland.

• Almost 200 garments from the Royal Ceremonial Dress Collection are able to be explored online thanks to a new collaboration between Historic Royal Palaces, which looks after six royal palaces including Hampton Court Palace and the Tower of London, and Google Arts & Culture. Drawing on ultra-high-resolution photography and 3D scanning, the garments – which include everything from ceremonial uniforms such as those worn by Yeoman Warders and a rare Bristow hat which may have been worn by King Henry VIII to Queen Victoria’s silk shoes, a waistcoat worn by King George III and a dress worn by the future Queen Elizabeth II in 1927 when she was just 18-months-old – can now be viewed in unprecedented detail (a billion pixels per image) without the risk of the damage which can occur thanks to light, humidity, and handling. The Royal Ceremonial Dress Collection comprises over 10,000 pieces of historic dress and related materials spanning the period from the 16th century to the present day and features garments worn by monarchs and key historical figures, including, as well as the aforementioned, Prince Albert, Princess Margaret, and Diana, Princess of Wales. To see the items, head to goo.gle/royalwardrobe.
• Author, politician and artist Victor Hugo’s rarely seen works on paper have gone on show at the Royal Academy of Arts. Astonishing Things: The Drawings of Victor Hugo features around 70 works drawn from European collections and follows his preoccupation with drawing from early caricatures and travel drawings to later landscapes and abstract works. Arranged across four sections, the works on show include everything from Mushroom (1850) – which depicts a giant anthropomorphic toadstool, some of his many works depicting castles such as The cheerful castle (c 1847), and drawings that Hugo created in tandem with writing his 1866 novel The Toilers of the Sea, set in Guernsey in the years following the Napoleonic Wars, as well some relating to his most famous work, Les Misérables. The exhibition, being held in the Jillian and Arthur M Sackler Wing of Galleries, can be seen until 19th June. Admission charge applies. For more, see royalacademy.org.uk.
• A “ground-breaking” exhibition showing the outsized impact British Black music has had on the world stage over the past 100 years has opened at the Barbican Music Library. Black Sound London highlights artists who created their own platforms, audiences, and spaces, often without mainstream support and spans genres including jazz, lovers’ rock, jungle, grime, and drill. Among the objects on show are vintage mixtapes, iconic magazine covers, and fly-posted walls. Runs until 19th July. For more, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/services/libraries/barbican-music-library.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
Located just to the east of the Tower of London, St Katharine Docks were opened in 1828 following the demolition of more than 1,000 houses along with a brewery and what was left of the medieval St Katharine’s Hospital.

This north London district owes its name to the family estate on which it was developed.
The district, one of the first planned residential developments in London, was developed in the early 1770s along what was known as New Road. It can be found to the north of Clerkenwell with King’s Cross to the west and Angel to the east.

Set within rolling fields, it was named for the family who owned the land which it was developed – that of Henry Penton, a Lord of the Admiralty, whose family, who hailed from Winchester, had owned the land for a couple of generations. The suffix “ville” was added to give the land sales appeal (a move which proved less popular after the rise of Napoleon thanks to its associated with French).
The new suburb was laid out mostly in a grid pattern on Islington Hill with the first street, named Penton Street, was completed in 1773. Building of further streets continued sporadically over the ensuing decades until the 1840s.
A church – St James Pentonville – was built halfway up the hill on Pentonville Road; it survived until its demolition in 1984. The burial grounds now form a public park – the Joseph Grimaldi Park (named for the clown who is buried within it). Other notable burials include Henry Penton.
Chapel Market was built as a residential street in 1790 but gradually transformed into a market and shops (it still contains some original properties).
Other landmarks include St Silas Church, Pentonville, which opened in 1863 and still stands in Risinghill Street, and the Church of St Mark the Evangelist, which opened in Myddleton Square in 1855, and was demolished in 1970.
Initially a fashionable place to live, this led to the term ‘Pentonville’ being used to describe an area beyond its original boundaries (Charles Dickens was apparently guilty of doing this). But its reputation began to fade during the mid-19th century as some homes were converted into businesses and others became boarding houses and tenements. By the turn of the century it was one of London’s poorest districts.
The area was partly redeveloped with council housing during the period between the two world wars – this was continued to a greater degree after World War II.
Incorporated into the London Borough of Finsbury in 1899, Pentonville became part of the London Borough of Islington in 1965 (there was Pentonville ward in the borough until 1978).
Famous residents have included philospher and economist John Stuart Mill (born at 13 Rodney Street in 1806) and Vladimir Lenin, who lived with his wife at 30 Holford Square just off Pentonville Road briefly in 1902-03.
Pentonville Road, formerly part of New Road, shares the name and a number of other streets also feature related names including, of course, the aforementioned Penton Street. Interestingly, the (in)famous HM Prison Pentonville, is not located in the area but in Caledonian Road in Barnsbury, some distance to the north.
Of course, Pentonville (in the form of Pentonville Road) can also be found in the pale blue section of properties on the Monopoly board.

This rounded arch in the Church of All Hallows is believed to be oldest surviving arch of the Anglo-Saxon period surviving in the City of London.
The arch can be found at the west end of the nave and dates from an earlier church on the site, possibly built as early as the 7th century (the church was later rebuilt and expanded several times, survived the Great Fire in 1666, and was then largely destroyed during the Blitz before being rebuilt and reconsecrated in 1957).
Roman tiles have been reused in the arch’s construction as well as Kentish ragstone and it doesn’t include a keystone.
The arch was fully revealed after a bombing during the Blitz in 1940 brought down a medieval wall and revealed it.
The arch has given some weight to the idea that the Anglo-Saxon church was founded not long after Erkenwald founded Barking Abbey in the 7th century (he went on to become the Bishop of London in 675).
WHERE: All Hallows by the Tower, Byward Street (nearest Tube station is Tower Hill); WHEN: 8am to 5pm Monday to Friday; 10am to 5pm Saturday and Sunday; COST: Free; WEBSITE: https://www.ahbtt.org.uk/
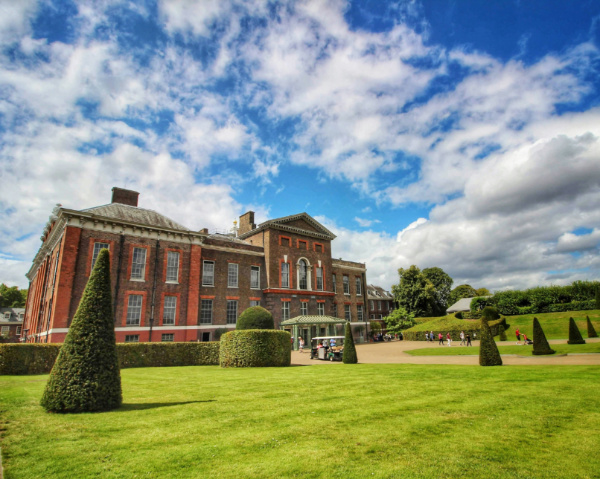

• Never-before-seen royal clothing is going on show at a new exhibition opening at Kensington Palace today. Dress Codes, which includes rarely seen highlights from the Royal Ceremonial Dress Collection, explores the codes and conventions of royal clothing, and the impact fashion can make “when boundaries are pushed and dress codes evolve”. Highlights include two matching Liberty print floral cotton dresses, worn in 1936 by Queen Elizabeth II (then Princess Elizabeth) and her younger sister Princess Margaret, a glittering red Bruce Oldfield gown worn by Diana, Princess of Wales, for a state visit to Saudi Arabia in 1987, and a Catherine Walker green silk velvet tuxedo-style dress which was shared with the world as one of 79 dresses famously auctioned to raise money for HIV/AIDS and cancer charities in 1997. There also two dresses worn by Princess Margaret which are going on show for the first time in the UK – a 1978 Thea Porter evening ensemble and a colourful green embroidered evening gown by the Filipino designer Jose Pitoy Moreno, worn in 1980. Other items include a never-before-displayed black mourning bodice worn by Queen Victoria. Runs until 30th November. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.hrp.org.uk/kensington-palace/whats-on/dress-codes.
• The first ever exhibition of Edvard Munch portraits opens at the National Portrait Gallery. The display, Edvard Munch Portraits, include Munch’s portraits of lawyer Thor Lütken and physicist Felix Auerbach as well as early family portraits such as Evening (1888) which shows his sister Laura on a family holiday and Andreas Munch Studying Anatomy (1886). Other works include The Brooch (1902) and full-length portraits of Jappe Nilssen, the painter Ludvig Karsten and writer Christian Gierløff – all from the group of men he called his ‘Lifeguards’ or ‘Guardians’. Runs until 15th June. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.npg.org.uk.
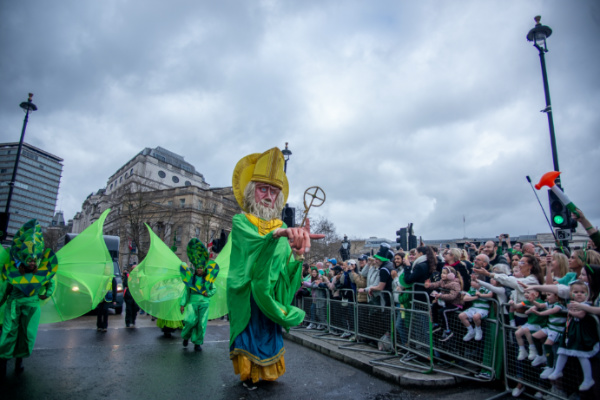

• The St Patrick’s Day Parade and Festival returns to London this Sunday. Irish Paralympic gold medal winning cyclist Katie-George Dunlevy and Olympic gold medal winning boxer Kellie Harrington are serving as this year’s Grand Marshals of the parade which, with more than 50,000 participants, will feature floats, marching bands, and dance troupes. The parade kicks off at noon and will make its way from Hyde Park Corner past Piccadilly and Trafalgar Square and on to Whitehall. Meanwhile, Trafalgar Square will host an afternoon of entertainment hosted by Irish-Indian-Malaysian DJ and broadcaster Tara Kumar and featuring a wide range of family-friendly performances by the likes of Kíla, Irish Women in Harmony and Ragz-CV. Celebrity chef Anna Haugh will provide Irish cooking demonstrations and there will be an exhibition celebrating Ireland’s unsung women heroes as well as the chance to learn Irish dancing and a dedicated zone for kids with free creative workshops. For more, see https://www.london.gov.uk/events/st-patricks-day-2024.
• An audio-led exploration of Hampton Court Palace after dark kicks off next Wednesday to mark
International Women’s History Month. Still The Hours uses a layered soundscape to guide visitors through the palace’s darkened halls as established actors including Kathryn Hunter (Harry Potter, Black Doves, Poor Things) and Miranda Richardson (Harry Potter, Good Omens, The Hours) can be heard alongside up-and-coming female voices to “weave a vivid tapestry” of women’s lives at the palace. The stories explored in the hour long presentation range from a suffragette to a mistress and a queen to a maid. Runs until 30th March. Admission charge applies (for ages 14+, under 16s must be accompanied by an adult). For more, see www.hrp.org.uk.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com
While the oldest dock or harbour in London is found at Queenhithe, we thought we’d take a look at 10 other historic docks.
First up, it’s Billingsgate, which, along with Queenhithe, was one of London’s earliest docks or harbours.

UNESCO’s World Heritage List includes as many as 1223 properties right across the globe which the World Heritage Committee considers as having “outstanding universal value”.
Most of them are cultural sites (952) but they also include some 231 natural sites and 40 which have both qualities.
The UK is actually home to 35 sites on the list, ranging from Stonehenge and the English Lake District to neolithic Orkney and the City of Bath.
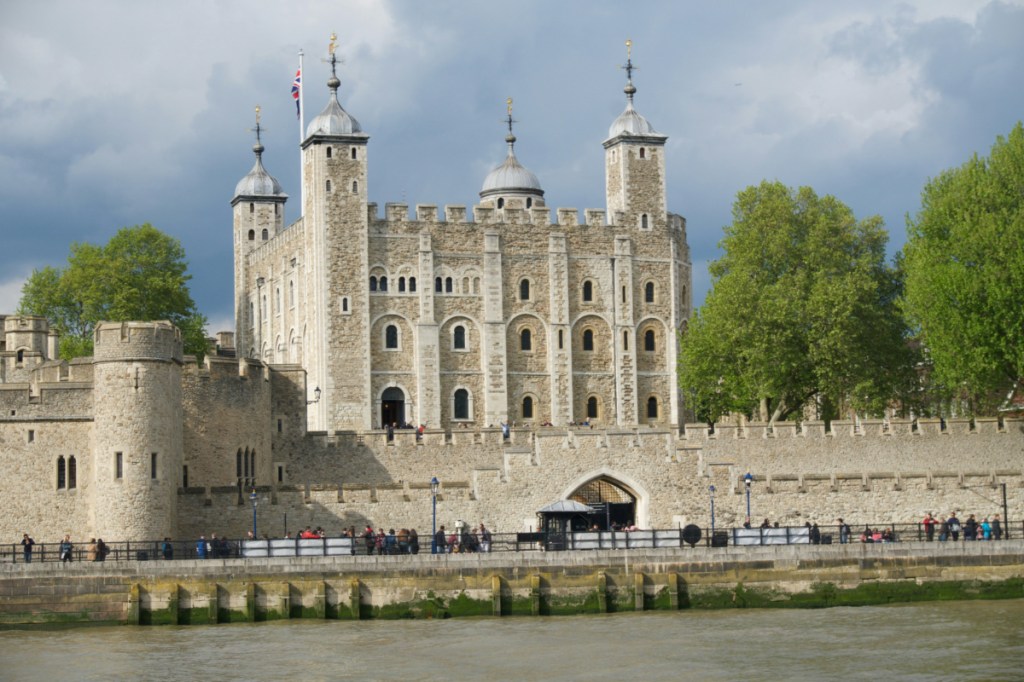

London itself is home to four internationally recognised UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These include the Tower of London, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew, the Palace of Westminster and Westminster Abbey (including the neighbouring St Margaret’s Church), and maritime Greenwich.
The first of the four to be added to the list was the 10 hectare site of Palace of Westminster and Westminster Abbey in 1987 (described as being of “great historic and symbolic significance”). It was followed by the Tower of London in 1988, and the 109 hectare area covering the Queen’s House, Old Royal Naval College and Royal Observatory known as maritime Greenwich in 1997.
The 132 hectare site of the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew was the most recent addition to the list in 2003.
As well as being added to the list, sites can also be removed as happened when Liverpool became the third site to be removed from the list in 2021 due to what the World Heritage Committee said was “the irreversible loss of attributes conveying the outstanding universal value of the property”.
Concerns have been raised over the Tower of London’s future on the list due to surrounding development and, of course, there are always other sites that can be added (we vote for Hampton Court Palace, among others).

• Paintings by some of the greatest Italian artists of the 14th century have been reunited in a new exhibition opening at the National Gallery on Saturday. Siena: The Rise of Painting 1300‒1350, which is being held to mark the gallery’s 200th anniversary, features around 100 works including some of the most innovative in the Western tradition. Highlights include Maestà, painted by Sienese artist Duccio di Buoninsegna (active 1278, died 1319). The first double-sided altarpiece in Western painting, it was dismantled in the 18th century and the National Gallery’s own three panels are now reunited with others from the original ensemble including Christ and the Woman of Samaria from the Museo Thyssen- Bornemisza in Madrid, and The Calling of the Apostles Peter and Andrew from the National Gallery of Art in Washington DC. Another work being reunited for the exhibition is the Orsini Polyptych by Sienese artist Simone Martini (1284‒1344). A folding work of art made for private devotion, probably for Cardinal Napoleone Orsini, it is today divided into six works held by the Louvre, Paris, the Royal Museum of Fine Arts, Antwerp and the Gemäldegalerie, Berlin. All six panels are being brought together for the National Gallery’s exhibition. Two triptychs by Duccio which seem to have been conceived as a single work are also being reunited and the display also features works by Pietro Lorenzetti (active possibly 1306; died probably 1348) and his brother Ambrogio Lorenzetti (active 1319; died 1348/9) as well as Sienese works in a variety of media (metalwork, enamel, gilded glass, wood, marble, and manuscript illumination). The display runs until 22nd June. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.nationalgallery.org.uk.

• An installation featuring new work by artist duo Hylozoic/Desires (Himali Singh Soin & David Soin Tappeser) has opened at Tate Britain. In The Hedge of Halomancy, which runs in parallel with a large-scale new commission by Hylozoic/Desires at Somerset House, the artists excavate the lost archive of the Inland Customs Line, a 4,000 kilometre-longe barrier which comprised 2,500 kilometres of planted hedge and was created by the British Empire in the 19th century to prevent salt smuggling between British-occupied territories and neighbouring independent states. A 23-minute film at the heart of the installation focuses on Mayalee, a character inspired by a courtesan who defied the British Empire’s attempts to cut off her stipends of salt. Alongside it sits an embroidered tapestry, entitled Mokshapat (Snakes and Ladders) which was woven as mashru fabric – cotton on one side and silk on the other. Runs until 25th August. Admission is free. For more, see www.tate.org.uk.
• On Now: Unfolding Time: The Medieval Pocket Calendar. A “remarkable” set of medieval concertina-fold almanacs grappling with the concept of time is on display at the Lambeth Palace library. Less than 30 such manuscripts are known to exist and the display brings a group of the works, in which time is expressed in colourful pictures, poems, tables and devices, together for the first time. Runs until 15th May. For more, see https://www.lambethpalacelibrary.info.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.

• Shrove Tuesday, also known as Pancake Day, takes place this coming Tuesday and to mark the event, representatives from the City of London’s livery companies are coming in their annual Inter-Livery Pancake Race around Guildhall Yard. The event is organised by the Worshipful Company of Poulters while the Worshipful Company of Gunmakers provide the starting gun, the Worshipful Company of Clockmakers time the races and the Worshipful Company of Fruiterers provide lemons to accompany the pancakes. The starter’s gun fires at noon. Entry is free.
• East Enders is celebrating its 40th anniversary and to mark the occasion, the Museum of the Home in Hoxton is featuring props and costumes from the show in its displays. EastEnders at 40: Icons of Home and Drama features props and costumes including the costumes from Syed and Amira’s wedding in 2010, Kat Slater’s leopard print coat and Frank Butcher’s spinning bow tie. Runs until 22nd June. Admission is free. For more, see www.museumofthehome.org.uk.
• The origins of the Hallelujah Chorus and its special connecting to the Foundling Hospital is the subject of a new display at the Foundling Museum in Bloomsbury. Composer George Frideric Handel first held a benefit concert at the venue in 1749 in which he premiered his Foundling Hospital Anthem. He returned the following year to perform the Messiah, which had made its debut in Dublin in 1742, and this event proved so popular it was held annually until the 1770s. The display can be seen until 29th March, 2026. Admission charge applies. For more, see https://foundlingmuseum.org.uk/event/hallelujah-display/.
Send items to exploringlondon@gmail.com

In an article first published on The Conversation, LACEY WALLACE of the University of Lincoln, looks at the recent discovery….
Archaeologists from the Museum of London have discovered a well-preserved part of the ancient city of London’s first Roman basilica underneath the basement of an office block. The basilica was constructed for use as a public building in the 70s or early 80s AD.

In a Roman town, a basilica was a multi-functional civic building. Often paid for by leading local inhabitants, it provided a large indoor space for public gatherings. These ranged from political speeches to judicial proceedings.
Along with the connected forum – an arrangement of buildings that surrounded an open courtyard space – the building formed the centre of administrative and civic life in the ancient Roman city of Londinium.
Other walls of London’s basilica and forum have been known by archaeologists since the early 1880s. But they were only recognised as remains of the social and civic centre of Londinium in 1923.
Peter Marsden, the author of The Roman Forum Site in London (1987), compiled disconnected evidence for the different phases of London’s forum basilica complex.
Referring to the current area of excavations (on Gracechurch Street), he noted that: “More than half of the archaeological deposits still remain, and should be carefully excavated when the opportunity arises, since only then will the history of the site be elucidated.”
Occasional opportunities have arisen to reveal small parts of the forum basilica. For example, during construction of a shaft to install a lift at 85 Gracechurch Street, some important remains from the first century were found. But the excavated area was too small to contribute greatly to our knowledge.
In contrast, the recent work is part of a major redevelopment. It has opened targeted excavation areas where walls of the basilica were expected to be found, exposing substantial parts of the building.
Archaeologists have found one-metre-wide foundations and walls of the interior, some of which probably extend for more than 10 metres in length. The walls are constructed of flint, tile and Kentish ragstone (a type of limestone quarried in Kent), and some stand at four metres high.
Londinium was constructed on an unoccupied site beginning in about AD47 or 48. It began to gain the trappings of a Roman-style town, including a basilica building, in the lead-up to its destruction in the Boudican Revolt in AD60 or 61.
The city did not have a monumental forum and basilica complex until later, however, when a major programme of public and private construction was undertaken in the Flavian period (AD69–96).
London’s Flavian basilica took the plan of a long rectangle (44m x 22.7m) divided into three aisles. There is good evidence from the deeper central aisle (nave) wall foundations that the nave roof was raised to two storeys, to allow for windows to provide internal light.
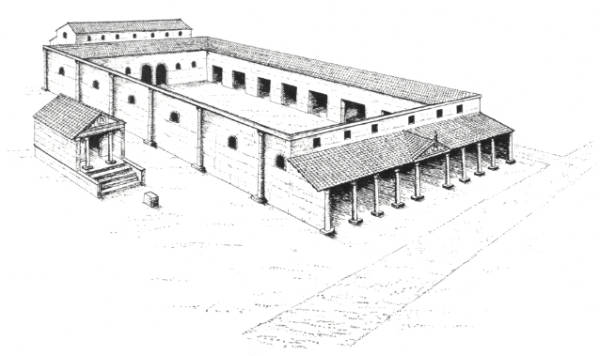
Shallow foundations crossing the nave are evidence of a raised dais or platform at the eastern end. The speaker or judge would sit there, elevated above the crowds, increasing both his visibility and status. This platform, or “tribunal”, is the area that has recently been revealed.
The basilica would have risen above the north side of the buildings that formed the forum courtyard. It would have dominated the high ground of this monumental space at the highly visible crossroads leading straight up from the Roman Thames bridge.
It would have been the largest building in the area and firmly announced that the people of Londinium were constructing a high-status Roman city.
Rebuilding following the British Queen Boudica’s revolt had been swift. The post-Revolt fort that was built only 100 metres or so down the street had likely been decommissioned and the people were ready to embark on a new phase and a major expansion of the urban centre.
The designs of late first century forum basilica complexes varied across the provinces. But generally they combined religious, civic, judicial and mercantile space.

In places like Pompeii, the forum had developed over time. But, when the town was buried by the ash of Vesuvius in AD79 (approximately the same time the forum basilica of London was built), the focus of the elongated monumental space was the Temple of Jupiter, symbol of the Roman state.
Although a classical temple was constructed to the west of the exterior of Londinium’s Flavian forum, it was clearly separate. No forum in Britannia was dominated by a temple, setting the core of urban space in this province apart from most examples in the rest of the empire.
The Flavian forum basilica at Londinium is one of the earliest examples to demonstrate this characteristic, along with that at Verulamium (St Albans). There, an inscription links the circa AD79–81 construction to the governor Agricola, who is well known among historians from the celebratory biography written by his son-in-law, Tacitus.
The Flavian basilica and forum only stood for about 20 or 30 years, however. With increased prosperity in the early second century, they were demolished and replaced by a new structure which was five times larger, leaving the remains of the first basilica underneath the surface of the later courtyard space.
Museum of London Archaeology will now analyse and publish the results of its find, applying modern methods to advance our understanding of the development of the first forum basilica. We can expect refined dating evidence and an improved understanding of the architecture from the post-excavation analyses. An exhibition space to make the remains visible for the public is also planned.
![]()
Lacey Wallace is a senior lecturer in Roman history & material culture at the University of Lincoln. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
• Iconic portraits which featured in the trail-blazing magazine, The Face, have gone on show from today at the National Portrait Gallery off Trafalgar Square. The Face Magazine: Culture Shift features more than 200 prints by more than 80 photographers including Sheila Rock, Stéphane Sednaoui, David LaChappelle, Corinne Day, Elaine Constantine, Juergen Teller and Sølve Sundsbø. The display explores how the cult magazine, which ran from 1980 to 2004 before being relaunched in 2019, impacted culture in the Eighties, Nineties and Noughties and in particular how it shaped the tastes of Britain’s youth. Runs until 18th May. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.npg.org.uk.
• Visitors to the London Transport Museum are being treated to live performances from some of London’s most promising classical and jazz musicians under a new initiative which kicked off earlier this month. The young musicians, from the Guildhall School of Music and Drama, Royal Academy of Music, Royal College of Music, or Trinity Laban, are performing in a programme designed to equip them with real-world performance experience. The music is being performed over various dates until 24th October. For more details, see www.ltmuseum.co.uk/whats-on/music-museum.
• A new exhibition celebrating the work of illustrator Ralph Steadman has opened at the Heath Robinson Museum in Pinner. Ralph Steadman: INKling spans the 70 years of Steadman’s career and covers his literary illustrations, including Steadman’s interpretations of Alice in Wonderland, Animal Farm, and Treasure Island, his illustrations for children’s books such as From Fly Away Peter (1963) and The Ralphabet (2023), and the “Gonzo art” he created in collaboration with Hunter S Thompson. Runs until 10th May. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.heathrobinsonmuseum.org/#whatson.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
Linked to the brutal slayings of at least five women in the later half of 1888, the identity of Jack the Ripper is London’s most infamous mystery and one which continues to fuel speculation – and make headlines – more than 130 years later.
