Now long gone, this central London property was once the residence of the, you guessed it, bishops of Durham.
Tudor
10 London bishop’s palaces, past and present – 2. York Place…
The precursor to Whitehall Palace, York Place was the London residence of the Archbishops of York between the 13th and 16th centuries.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to access all of Exploring London’s content…
What’s in a name?…Upminster…
Known to many as the eastern end of the District Line, Upminster is located some 16.5 miles to the north-east of Charing Cross and is part of the London Borough of Havering.
Historically a rural village in the county of Essex, its name comes from Old English and means a large church or “minster” located on high ground.
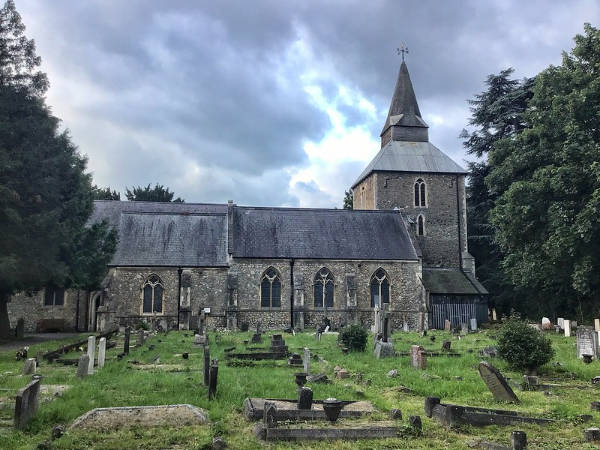

The church is said to have dated at least as far back as the 7th century and to have been one of a number founded by St Cedd, a missionary monk of Lindisfarne, in the area. It was located on the site occupied by the current church of St Laurence (parts of which date back to the 1200).
The nearby bridge over the River Ingrebourne shares the name Upminister and is known to have been in existence since the early 14th century.
Once wooded, the area was taken over for farming (cultivation dates as far back as Roman times) and by the 19th century it came to be known for market gardens as well as for some industry including windmills and a brickworks.
Development was initially centred around the minister and nearby villages of Hacton and Corbets Tey. It received a boost in the 17th century when wealthy London merchants purchased estates in the area.
Improved transportation links also helped in later centuries including the arrival of the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway in 1885 – it was extended from Barking – and the underground in 1902 via the Whitechapel and Bow Railway.
Landmarks include the Church of St Laurence, the redbrick Clock House (dating from about 1775), the 16th century house Great Tomkyns, the Grade II*-listed Upminster Windmill, built in 1803 and considered one of England’s best surviving smock mills, and the 15th century tithe barn (once owned by the monks of Waltham Abbey and now a museum).
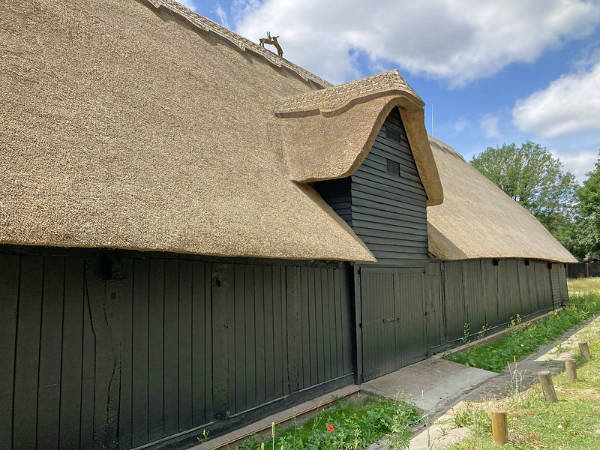

Upminster Hall, which dates back to the 15th and 16th century (and, once the hunting seat of the abbots of Waltham Abbey, was gifted by King Henry VIII to Thomas Cromwell after the Dissolution), is now the clubhouse of the Upminister Golf Club.
Hornchurch Stadium, the home ground of AFC Hornchurch, is located in the west of the area.
It was in Upminster that local rector Rev William Derham first accurately calculated the speed of sound, employing a telescope from the tower of the Church of St Laurence to observe the flash of a distant shotgun as it was fired and then measuring the time before he heard the gunshot using a half second pendulum.
LondonLife – Look up!…
10 London mysteries – 1. The murder of Robert Pakington…
London’s rich layers of history has left its fair share of mysteries and in this series we’re going to take a look at 10, some well-known and others, such as this first one, less so…
First up, it’s a 500-year-old murder mystery. The victim was Robert Pakington, an MP and prominent member of the Worshipful Company of Mercers, who is often said to be the first victim to be murdered with a handgun.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to see all of Exploring London’s content (and the rest of this post). Thanks for your support of our work
10 towers with a history in London – 10. The ‘Lollard’s Tower’, Lambeth Palace…
This 15th century tower can be found at the north-west corner of Lambeth Palace, London residence of the Archbishop of Canterbury.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to gain access to all our stories – that’s less than the price of a cup of coffee!
A Moment in London’s History – The first bananas go on sale…
It’s widely reported that the first banana went on sale in London in the mid-17th century but there is evidence bananas had been in the capital well before that date.
Subscribe for full access for just £3 a month.
10 towers with a history in London – 1. The Bloody Tower…

Carrying rather a gruesome name, this rectangular-shaped tower sits over a gate leading from outer ward into the inner ward in the Tower of London.
The tower, which once controlled the watergate before the outer walls were constructed, was originally known as the Garden Tower due to its location adjoining the Tower Lieutenant’s Garden.
To see the rest of this post (and all of our coverage), subscribe for just £3 a month. This small contribution – less than the cost of a cup of coffee – will help us continue and grow our coverage. We appreciate your support!
Treasures of London – The Abraham Tapestries, Hampton Court Palace…
Hanging in the Tudor Great Hall at Hampton Court Palace, this series of 10 huge tapestries are believed to have been commissioned by King Henry VIII and were first hung in the hall in 1546.
To see the rest of this post (and all of our coverage), subscribe for just £3 a month. This small contribution – less than the cost of a cup of coffee – will help us continue and grow our coverage. We appreciate your support!
This Week in London – West Ham Park celebrates its 150th; rare examples of 17th century paper-cutting; King Henry VIII jousts at Hampton Court; the collection of Elizabeth Legh; and, ‘Horrible Science’…
• West Ham Park celebrates its 150th anniversary this weekend with a festival of music, food, sport, and other activities. On Saturday there will be a free, family-friendly festival with music – including appearances by Australian-born singer-songwriter Celina Sharma and singer-songwriter, Fiaa Hamilton, as well as a DJ set from Ellis – along with arts and crafts, a children’s fun fair and local food stalls. On Sunday, activities are based around the theme of ‘give it a go’ with visitors able try out various sports and health activities, including football, cricket, tennis, athletics, Tai Chi, and long-boarding. There will also be free taster sessions and opportunities to meet local sporting legends. An outdoor exhibition about the park’s history can be seen in Guildhall Yard in the City leading-up to the event after which it will be moved to Aldgate Square. West Ham Park is the largest green space in the London Borough of Newham and has been managed by the City of London Corporation since 1874. Activities on both days start at 12pm. For more, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/westhampark150.
To see the rest of this post (and all of our coverage), subscribe for just £3 a month. This small contribution – less than the cost of a cup of coffee – will help us continue and grow our coverage. We appreciate your support!
10 significant (and historic) London trees…9. The Fulham Palace Oak…

Said to be the oldest of its species in the UK (and a contender for the oldest tree in London), this holm oak (Quercus ilex), also known as a holly leaved oak, is believed to be more than 500-years-old.
The site was the home of senior clergy for much longer – Waldhere, the Bishop of London, first bought the site in 704 AD. And over the years, Fulham Palace and its gardens have evolved significantly with some of the current structures dating from Tudor times.
The Bishops of London left the palace in 1973 and it’s now managed under a trust which was established in 2011.
It’s possible this immense evergreen oak, which is native to the Mediterranean region, was among a number planted in the mid-16th century during the tenure of Bishop Edmund Grindal (about 1553 to 1559).
Bishop Grindal is known to have had a keen interest in the garden and who is credited with introducing the tamarisk tree to England and growing grapes which were sent to Queen Elizabeth I.
It’s also possible the tree was planted during the later tenure of Bishop John Aylmer (1576 to 1594).
The oak, which was coppiced many years ago extending its life, is among the original 41 trees awarded “Great Tree” status in 1988.
WHERE: Fulham Palace Gardens, Bishop’s Avenue, Fulham (nearest Tube station is Putney Bridge); WHEN: 10.30am – 5pm daily; COST: Free; WEBSITE: https://www.fulhampalace.org
10 significant (and historic) London trees…1. Queen Elizabeth’s Oak, Greenwich…
Spring is upon us, so we thought it an appropriate time to consider some of London’s greatest natural assets – its trees. But, as well as being significant for their environmental impact, each of these trees (or, in some cases, the remains of them), are significant for historic reasons (we’ve previously mentioned a couple including what’s believed to be the oldest tree and the unusual – and sadly now deceased – Hardy Tree).
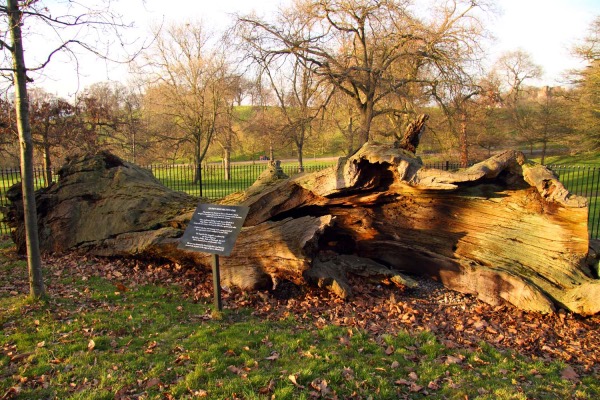

First up, it’s the tree known as Queen Elizabeth’s Oak in Greenwich. Thought to date from possibly as far back as the late 13th century, this tree survived until the 19th century before its carcass finally fell to the ground during a storm in 1991. It has lain in Greenwich Park ever since.
The tree, which is located at the end of what is now Lover’s Walk close to the Maze Hill Gate, was located in the grounds of Greenwich Palace (also known as the Palace of Placentia) and was there when King Henry VIII resided at the palace.
In fact, it’s said that he and Anne Boleyn danced around the oak while courting, and (and here’s where the name comes from) that Elizabeth, their daughter (and later Queen Elizabeth I), picnicked under its canopy (some accounts suggest she actually picnicked in the tree’s hollow – but still then upright – trunk).
Following the creation of what is now Greenwich Park, the hollow tree was apparently used as a prison for those caught illicitly on the grounds. They were secured behind a heavy wooden door fitted to the trunk (a park keeper’s lodge was built nearby in the 17th century; it was demolished in the 1850s).
The tree, one of 3,000 in the park, had died in the 19th century and was reduced to an eight metre high stump, partly supported by ivy, when it was blown over by the storm in June, 1991.
A replacement oak, which was donated by the Greenwich Historical Society was planted nearby by the Duke of Edinburgh on 3rd December, 1992, to mark Queen Elizabeth II’s 40 years on the throne.
A ring analysis carried out on the tree found in 2014 it dated back to at least 1569 but with the core missing a precise date of germination couldn’t be found. Estimates, however, place the date of germination to the last 13th or early 14th century. The analysis placed the tree’s death to between 1827 and 1842.
The tree is marked with a plaque and both it and the new tree are surrounded by an iron railing.
WHERE: Queen Elizabeth Oak, Greenwich Park (nearest DLR station is Greenwich); WHEN: 6am to 8pm daily; COST: Free; WEBSITE: https://www.royalparks.org.uk/visit/parks/greenwich-park.
This is an expanded version of a post first made in 2017.
Lost London – Nonsuch House, London Bridge…
Once located at the southern end of London Bridge, Nonsuch House is the earliest documented prefabricated building.
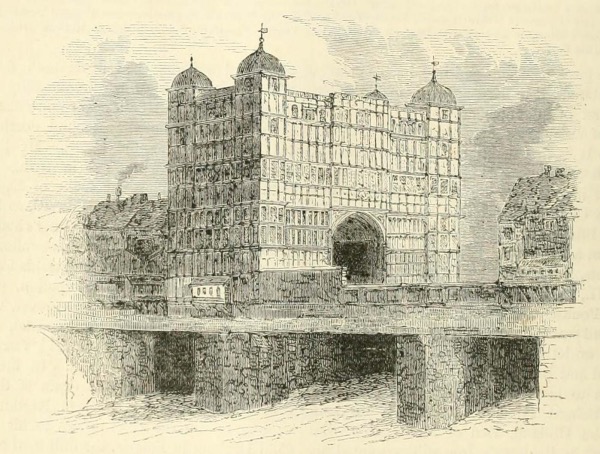
Originally constructed in what is now The Netherlands, it was shipped to London in pieces – each individually marked – in 1578 with the reassembly completed the following year.
The four storey building, which was said to have been constructed using wooden pegs and no nails, featured an arched tunnel through the middle through which bridge traffic would pass.
The main facade faced toward Southwark and there were towers at each of the four corners, topped with onion domes. The east and west sides of the building, which protruded beyond the bridge out over the Thames were elaborately carved.
The northern facade of the building abutted other properties while the southern side had a clear space in front over which a drawbridge is believed to have been located (it could be raised to allow larger ships through).
The name may have referenced King Henry VIII’s Nonsuch Palace, located near Ewell in Surrey, and was said to refer to the fact there was no such building as splendid.
The property was demolished along with the other buildings on the bridge in about 1757.
10 atmospheric ruins in London – 6. Tudor and medieval remains at Eltham Palace…
Once a medieval royal palace, Eltham Palace in London’s east was transformed into a 1930s house which incorporates the medieval great hall.
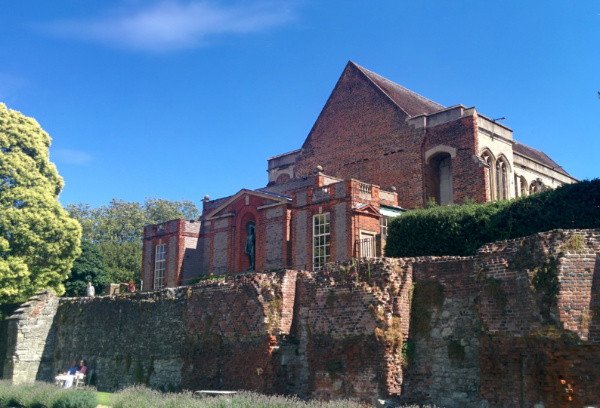

But there are also some other remains of the former medieval palace on the site – including the footings of the palace’s west range incorporating royal apartments used in the Tudor era.
These included separate apartments for the king and queen as well as a gallery where the king could walk in inclement weather.
The ruins feature diamond-patterned brickwork (pictured), part of the west range which was built during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I in the 1580s.
There are also the remains of a tower of yellow brick, which possibly dates from the 14th century when, prior to the site being a royal palace, it was rebuilt as a manor house by Anthony Bek, Bishop of Durham (it was Bek who gave the manor to the future Edward II in 1305).
These days the ruins lie within the home’s magnificent gardens, recreated to show how they might hav. Alongside the remains of the west range (and the medieval great hall which dates from the reign of King Edward IV and is largely intact), are the remains of a late 15th century bridge over a medieval moat, at the south end of which are the remains of a gatehouse.
There’s also an oak pedestrian bridge, supported by medieval brick and foundations which once formed part of the main southern entrance to the palace.
WHERE: Eltham Palace, Court Yard, Eltham, Greenwich (nearest train station is Mottingham); WHEN: 10am to 4pm Wednesday to Sunday; COST (advance online tickets): £14.50 adults/£8.60 children/£12.70 concessions/£37.60 family (can include a donation/English Heritage members free); WEBSITE: www.english-heritage.org.uk/visit/places/eltham-palace-and-gardens/.
10 London locations related to Sir Christopher Wren…1. The Old Court House, Hampton Court Palace Green…
This year marks the 300th anniversary of the death of Sir Christopher Wren (25th February, 1723), whose designs helped to transform post-Great Fire London.
In a new series we’re looking at 10 locations which help tell Wren’s story but while we’ve previously runs numerous articles focused on the many buildings he designed, in this series the focus is more on his personal life.
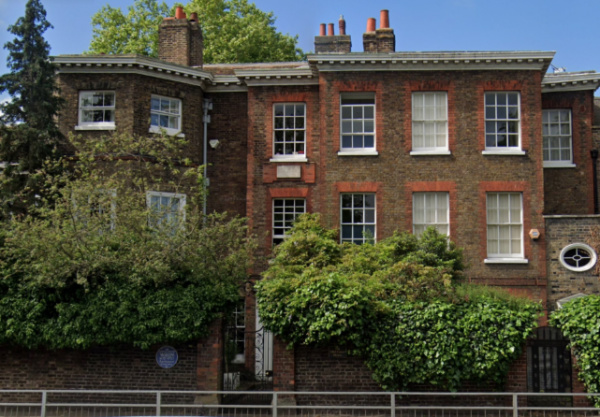

First up, it’s one of the most well-known properties related to Wren’s life – the home in which he spent the latter years after his life just outside Hampton Court Palace.
Known as the Old Court House, Wren first came to live in the house after he was appointed Surveyor-General to King Charles II in 1669. His post brought with it lodgings at the royal palaces and at Hampton Court Palace, it was the Old Court House (the property had been built for in 1536 as a wood and plaster house; Wren’s immediate predecessor in the office, Sir John Denham, had rebuilt it partly in brick).
Then in 1708, Queen Anne granted him a 50-year lease on the property, apparently at least partly in lieu of overdue fees he was owed for the building of St Paul’s Cathedral. It’s also believed that the Queen had granted the lease on condition that Wren repair or rebuilt the property.
Wren, who had hitherto only lived intermittently at the property (presumably while working on Hampton Court Palace on the orders of King William III and Queen Mary II), made some major alterations to the property from 1710 onwards (it’s suggested this was done to the designs of Wren’s assistant William Dickinson).
He came to live here on a more permanent basis after he retired from the Office of Works in 1718 and remained here until his death in 1723 (although he didn’t die here – more on that later).
It’s said Wren, whose time as the Royal Surveyor-General spanned the reigns of six monarchs, spent his time here “free from worldly affairs”, choosing to and pass his days ‘in contemplation and studies”.
It was subsequently the home of Wren’s son Christopher (1645-1747) and his grandson Stephen (b 1772). It remained a grace and favour house associated with Hampton Court Palace until 1958.
The Grade II* brown and red brick property, which was combined with the house next door in the early 19th century and them divided off in 1960, is now in private ownership and there’s an English Heritage Blue Plaque on the outside wall mentioning Wren’s residence.
Moments in London’s history – Five (more) unusual facts about royal coronations past…
Following last week’s unusual facts, here’s five more…

• The coronation of King William I (aka William the Conqueror) was marred by riots. The new King had chosen to be crowned in Westminster Abbey on Christmas Day, 1066, in a display of power (kings had in the past been crowned in Winchester). But when shouts of support for the new king were mistakenly thought to be an assassination attempt, Norman soldiers outside the abbey began setting fire to nearby houses, causing the abbey to fill with smoke and the congregation to flee while outside people rioted. William nonetheless ensured the service was completed.
• Henry, the eldest son of King Henry II, had a coronation service at Westminster Abbey while his father was still monarch – the only instance of this occurring. While crowning the heir during the lifetime of the monarch was a more common practice in France, it was not so in England. But in an effort to settle the succession, King Henry II had Henry crowned on 14th June, 1170. Sadly Henry, known as Henry the Young King, did not live to succeed his father but died at just the age of 28 in 1183 after contracting dysentery while campaigning with his younger brother Richard (later King Richard I) against their father. King Henry II died on 6th July, 1189, and was succeeded by Richard.
• There has only been one coronation in the abbey in which two monarchs were crowned at the same time. After King James II was deposed, William of Orange and his wife Mary were jointly invited to rule in what was known as the Glorious Revolution. They were crowned together at Westminster Abbey on 11th April, 1689. King William III sat in the Coronation Chair while another chair was specifically made for Queen Mary II, and, while the king was crowned using the traditional regalia, a special set of regalia was made for Mary.
• Only two of King Henry VIII’s six wives had coronations. Catherine of Aragon was crowned alongside the King on 24th June, 1509 (she sat on a lower chair). Anne Boleyn, meanwhile, was crowned on 1st June, 1533. Interestingly, she was crowned with St Edward’s Crown which had up until then only been used to crown the monarch. Jane Seymour died before she could be crowned (there had been plague in London at the time she married Henry), while his marriage with Anne of Cleves was annulled before she could be crowned and Catherine Howard was executed before any coronation took place. By the time the king married Catherine Parr, he was ageing and ill and a coronation was unlikely to be high on his agenda.
• King Henry VI is the youngest monarch to have been crowned at Westminster Abbey. He was aged just eight-years-old when he was crowned on 6th November, 1429, having become king at the age of just eight-months-old when his father, King Henry V, died on 31st August, 1422 (other children to have been crowned in the abbey include King Edward VI, who was just nine at his coronation). King Charles III – whose coronation will take place on 6th May – will be the oldest monarch to have been crowned at the abbey.
Correction: We’ve corrected the position of the two Catherines after the names were accidentally transposed.
8 locations for royal burials in London…6. St Peter ad Vincula…
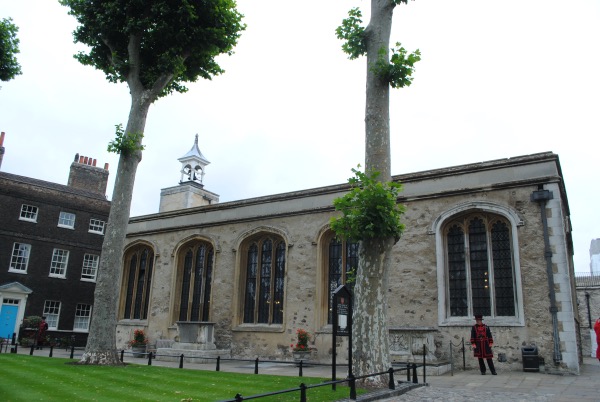

Officially the The Chapel Royal of St Peter ad Vincula, this small church is located in the Inner Ward of the Tower of London.
Under the direct jurisdiction of the monarch as a “royal peculiar”, the current building – and the name means “Peter in Chains”, a reference to St Peter’s imprisonment at the hands of King Herod – dates from 1520 and was constructed on the orders of King Henry VIII.
As well as being the burial place of officers who served at the Tower, the chapel – which is located only a few steps away from the execution site on Tower Green – is also the final resting place of many who were executed within the Tower’s precincts including the likes of Thomas Cromwell and Bishop John Fisher.
Those buried here include two of King Henry VIII’s wives who both suffered the ignominy of being beheaded. Queen Anne Boleyn and Queen Catherine Howard – respectively the second and fifth wives of the king – were both interred here after their executions.

Anne Boleyn, who was executed on 17th May, 1536, was buried under the floor in front of the high altar (along with her brother George who was executed two days before the Queen). Catherine Howard was executed several years later on 13th February, 1542, and was also buried beneath the floor.
The other royal figure buried in the Chapel was Lady Jane Grey, the “Nine Day Queen” who was executed on Tower Green on 12th February, 1554, at just the age of 17 on the orders of Queen Mary I. She was buried beneath the chapel’s altar (along with her husband, Lord Guilford Dudley, who was also executed on Tower Green).
The chapel fell into some neglect by the mid-19th century and in 1876 works were carried out under the direction of architect Anthony Salvin to restore the building. This included replacing the floor which had collapsed owing, it’s said, to the large number of burials that had taken place under it since the 16th century.
Many of the bodies were exhumed and identified, including that of Queen Anne Boleyn and Lady Jane Grey, and moved into a newly created crypt underneath.
The marble floor which was installed over the top features memorials commemorating those interred underneath. These include individual memorial stones for Henry VIII’s two Queens and a stone commemorating several of other prominent figures buried beneath including Lady Jane Grey.
WHERE: St Peter ad Vincula, Inner Ward, Tower of London (nearest Tube station Tower Hill); WHEN: 10am to 4.30pm (last admission 3.30pm), Tuesday to Saturday, 9am to 4.30pm (last admission 3.30pm) Sunday to Monday; COST: £29.90 adults; £14.90 children 5 to 15; £24 concessions (family tickets available; discounts for online purchases/memberships); WEBSITE: www.hrp.org.uk/toweroflondon/.
10 (lesser known) statues of English monarchs in London…1. King Edward VI at St Thomas’…
In honour of Queen Elizabeth II’s Platinum Jubilee, we have a new series looking at 10 lesser known statues of previous monarchs in London.
We kick off with not one, but actually two, statues of King Edward VI, the son of King Henry VIII and his third queen, Jane Seymour, can be found at St Thomas Hospital in Southwark.
Both of the statues were commissioned to commemorate the king’s re-founding of the hospital – which had been first founded in the 12th century and had been closed in 1540 as part of the Dissolution – in 1551 and which saw the complete rebuilding of the hospital under the stewardship of the hospital’s President, Sir Robert Clayton.

The oldest of the statues, now located outside the north entrance to the hospital’s North Wing on Lambeth Palace Road, was designed by Nathaniel Hanwell and carved from Purbeck limestone by Thomas Cartwright in 1682.

It originally was part of a group – the King standing at the centre holding his raised sceptre surrounded by four figures which were innovative in that they depicted patients of the time – which adorned the gateway to the hospital on Borough High Street.
It was moved when the gate was widened in around 1720 and subsequently occupied several different positions – including spending some time in storage – before eventually, without the surrounding figures, being moved to its current position in 1976. It was designated a Grade II* monument in 1979.
The second of the two statues is a bronze figure in period dress which was created by sculptor Peter Scheemakers in 1737.
It can now be found inside the hospital’s North Wing, having been moved there last century, and like its counterpart, was designated a Grade II* monument in 1979.
The inscription on the front of the plinth describes the King as “a most excellent prince of exemplary piety and wisdom above his years, the glory and ornament of his age and most munificent founder of this hospital” and adds that the statue was erected at the expense of Charles Joye, Treasurer of the hospital.
This Week in London – Anne Boleyn’s heraldic badge at Hampton Court; and, St Patrick’s Day parade returns…
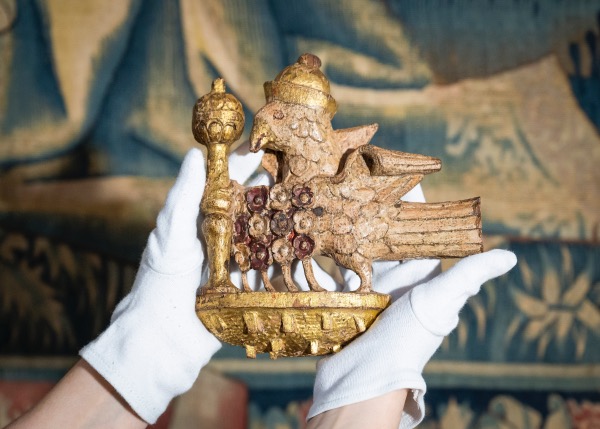

• Five hundred years after Queen Anne Boleyn is recorded as first appearing before her future husband, King Henry VIII, her carved heraldic badge has gone on show at Hampton Court Palace. The blackened oak carving, which features a crowned falcon atop a tree stump flowering with Tudor roses, was discovered by antiques expert Paul Fitzsimmons. While it had been covered in centuries of soot, grime and wax, conservation saw the removal of a layer of black paint to reveal the original colouring of white, gold and red. Subsequent research revealed the carving’s similarity to the 43 surviving falcon badges with the ‘frieze’ above the windows and hammer beams in the palace’s Great Hall, leading researchers to believe that the carving is an element of the room’s original Tudor scheme. Records show one Michael Joyner was paid to create carvings of the King’s and Queen’s badges. Following Boleyn’s downfall and Henry VIII’s subsequent marriage to Jane Seymour, craftsmen were paid to overpaint the former Queen’s white falcons in black, severing their association with her. Boleyn, who first appeared before Henry playing the role of Perseverance in a court masque, first started using the white falcon as her device around the time she was created Marquess of Pembroke, shortly before her public marriage to Henry in 1533. After her marriage and coronation, new imperial falcon badge was created, featuring the crown and sceptre. The badge can be seen in the Great Hall (included in general admission). For more, see www.hrp.org.uk/hampton-court-palace/.
• St Patricks’ Day will be marked in London this weekend for the first time in three years with a parade through central London and festivities in Trafalgar Square. The annual parade of Irish marching bands and dancers will start at Green Park at noon on Sunday and wind its way through the streets to Whitehall. Trafalgar Square, meanwhile, will play host to a line-up of Irish talent from noon to 6pm on Sunday with family-friendly concerts, storytelling, children’s films and youth performances, as well community choirs, schools, dance troupes and children’s workshops featuring camogie games, medal-making and face painting as well as a food and drinks stalls. For the full programme, head to www.london.gov.uk/st-patricks.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com
A Moment in London’s History – The execution of Catherine Howard…
It’s 480 years this month since Catherine Howard, fifth wife of Henry VIII of England, was executed for treason inside the Tower of London.

Catherine, who it has been suggested may have been just 17-years-old when she died, was beheaded on the morning of 13th February, 1542, less than two years after her hastily arranged marriage to the King, just three weeks after his prior marriage to Anne of Cleves was annulled.
Catherine, also spelt as Katherine, was condemned to death after a young noble named Francis Dereham admitted, under torture, to having a sexual relationship with her prior to her marrying the king, and, more importantly, Thomas Culpeper, a Gentleman of the King’s Privy Chamber, who admitted to having an affair with her after her marriage.
Both men were executed at Tyburn following their admissions and their heads were displayed on London Bridge. Catherine sailed under it aboard a barge as she was taken to the Tower on 10th February, 1542.
She is said to have spent the night before her execution practising placing her head on the block – which was brought to her at her request.
Catherine was beheaded with the single stroke of a headsman’s axe on Tower Green – King Henry did not attend but some of her cousins, including the Earl of Surrey, were among the witnesses.
She was said to have been composed, although she needed help mounting the scaffold. It’s often said that her last words were “I die a Queen, but I would rather have died the wife of Culpeper” but there’s no eyewitness report which suggests this and instead she is believed to have stuck to a more traditional script, saying her punishment was just for her crimes and asking forgiveness.
Her maid – Jane Boleyn, Lady Rochford – followed her to the block for her role in facilitating the affair while Henry was away from court. Catherine had apparently spent the night before practising how to lay her head upon the block.
Catherine was buried in an unmarked grave at in the Chapel of St Peter ad Vincula next to Tower Green – there’s a memorial to her in the church. The Queen’s ghost is famously said to be present in what’s known as the ‘Haunted Gallery’ at Hampton Court Palace – it is here that, when she was arrested, she apparently broke free from her guards and ran to the doors of the Chapel Royal where she believed the king was at prayer. Needless to say, her cries for mercy went unanswered.

