Now long gone, this central London property was once the residence of the, you guessed it, bishops of Durham.
Queen Elizabeth I
What’s in a name?…Honor Oak
Yes, this small south London district, located to the south of Peckham, was actually named for an oak.
In this case it was an oak which stood atop the 90 metre high One Tree Hill – the last in a line of hills which stretch north from Croydon.
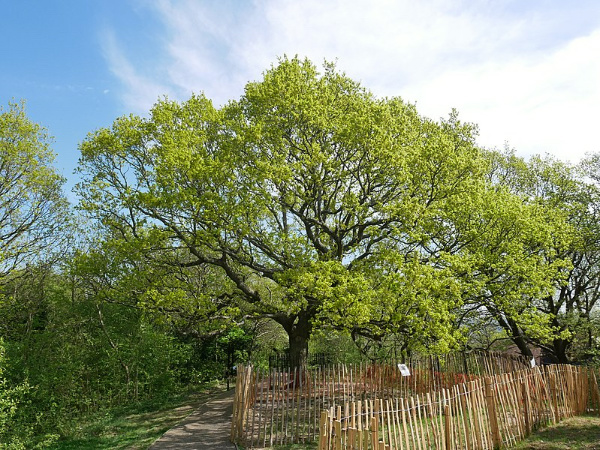

There’s a couple of possible explanations for the name – the first is that the oak in question once marked the southern boundary of the estates or “honour” of the 12th century Earls of Gloucester – hence ‘Honor Oak’.
The second is that Queen Elizabeth I apparently had a picnic with Sir Richard Bulkeley of Beaumaris under its branches on May Day, 1602. Hence again ‘Oak of Honor’ or ‘Honor Oak’.
Sadly, the original tree is gone – it was apparently hit by lightning in the 1880s – and a replacement, which can still be seen today, was subsequently planted nearby.
There’s a few stories surrounding the hill and its oak including that it was here that the Roman general Paulinus overcome Boudicca in 61AD. Another says that the highwayman Dick Turpin used it as a lookout.
Its height did see the hill put to use as a beacon by the Admiralty during the Napoleonic Wars and as a semaphore station by the East India Company. A beacon on top of the hill was erected to commemorate the Silver Jubilee of King George V in 1935 and subsequently used for celebrations including the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II and the Queen’s silver and golden jubilees.
There was also a gun emplacement built upon the hill during World War I.
The area around the hill was largely rural until the late 18th century. In 1809, the Croydon Canal Company constructed a canal which ran from Croydon north to New Cross and which included numerous locks. It was taken over almost 30 years later by the Croydon and London Railway for its new line (the current railway line, the stops on which include Honor Oak Park (opened in 1886), runs along the same course).

There was a bid to incorporate One Tree Hill into a golf course in the late 1800s but following a protest, this was halted and in 1905 the hill was acquired by the Camberwell Borough Council as public open space. It remains so today.
The Church of St Augustine was built to the designs of William Oakley on the hill’s east side in the late 19th century.
Famous residents in the streets around the hill have included Spike Milligan.
The Honor Oak Reservoir lies just to the north of the hill. It was constructed between 1901 and 1909 and was the largest brick built underground reservoir in the world. The roof of the still-in-use reservoir is grassed over and used as a golf course. A rather grand pumping station stands nearby.
10 towers with a history in London – 8. The Bell Tower…
We return to the Tower of London this week to look at the history of another of its storied towers.
Support out work and subscribe for just £3 a month for full access to the site.
10 towers with a history in London – 1. The Bloody Tower…

Carrying rather a gruesome name, this rectangular-shaped tower sits over a gate leading from outer ward into the inner ward in the Tower of London.
The tower, which once controlled the watergate before the outer walls were constructed, was originally known as the Garden Tower due to its location adjoining the Tower Lieutenant’s Garden.
To see the rest of this post (and all of our coverage), subscribe for just £3 a month. This small contribution – less than the cost of a cup of coffee – will help us continue and grow our coverage. We appreciate your support!
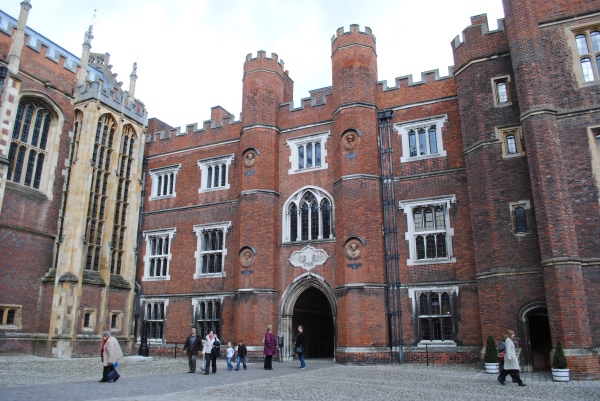
Treasures of London – The Abraham Tapestries, Hampton Court Palace…
Hanging in the Tudor Great Hall at Hampton Court Palace, this series of 10 huge tapestries are believed to have been commissioned by King Henry VIII and were first hung in the hall in 1546.
To see the rest of this post (and all of our coverage), subscribe for just £3 a month. This small contribution – less than the cost of a cup of coffee – will help us continue and grow our coverage. We appreciate your support!
10 significant (and historic) London trees…9. The Fulham Palace Oak…

Said to be the oldest of its species in the UK (and a contender for the oldest tree in London), this holm oak (Quercus ilex), also known as a holly leaved oak, is believed to be more than 500-years-old.
The site was the home of senior clergy for much longer – Waldhere, the Bishop of London, first bought the site in 704 AD. And over the years, Fulham Palace and its gardens have evolved significantly with some of the current structures dating from Tudor times.
The Bishops of London left the palace in 1973 and it’s now managed under a trust which was established in 2011.
It’s possible this immense evergreen oak, which is native to the Mediterranean region, was among a number planted in the mid-16th century during the tenure of Bishop Edmund Grindal (about 1553 to 1559).
Bishop Grindal is known to have had a keen interest in the garden and who is credited with introducing the tamarisk tree to England and growing grapes which were sent to Queen Elizabeth I.
It’s also possible the tree was planted during the later tenure of Bishop John Aylmer (1576 to 1594).
The oak, which was coppiced many years ago extending its life, is among the original 41 trees awarded “Great Tree” status in 1988.
WHERE: Fulham Palace Gardens, Bishop’s Avenue, Fulham (nearest Tube station is Putney Bridge); WHEN: 10.30am – 5pm daily; COST: Free; WEBSITE: https://www.fulhampalace.org
10 significant (and historic) London trees…1. Queen Elizabeth’s Oak, Greenwich…
Spring is upon us, so we thought it an appropriate time to consider some of London’s greatest natural assets – its trees. But, as well as being significant for their environmental impact, each of these trees (or, in some cases, the remains of them), are significant for historic reasons (we’ve previously mentioned a couple including what’s believed to be the oldest tree and the unusual – and sadly now deceased – Hardy Tree).
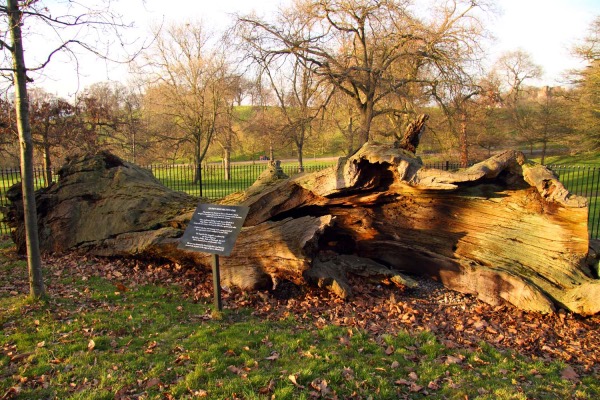

First up, it’s the tree known as Queen Elizabeth’s Oak in Greenwich. Thought to date from possibly as far back as the late 13th century, this tree survived until the 19th century before its carcass finally fell to the ground during a storm in 1991. It has lain in Greenwich Park ever since.
The tree, which is located at the end of what is now Lover’s Walk close to the Maze Hill Gate, was located in the grounds of Greenwich Palace (also known as the Palace of Placentia) and was there when King Henry VIII resided at the palace.
In fact, it’s said that he and Anne Boleyn danced around the oak while courting, and (and here’s where the name comes from) that Elizabeth, their daughter (and later Queen Elizabeth I), picnicked under its canopy (some accounts suggest she actually picnicked in the tree’s hollow – but still then upright – trunk).
Following the creation of what is now Greenwich Park, the hollow tree was apparently used as a prison for those caught illicitly on the grounds. They were secured behind a heavy wooden door fitted to the trunk (a park keeper’s lodge was built nearby in the 17th century; it was demolished in the 1850s).
The tree, one of 3,000 in the park, had died in the 19th century and was reduced to an eight metre high stump, partly supported by ivy, when it was blown over by the storm in June, 1991.
A replacement oak, which was donated by the Greenwich Historical Society was planted nearby by the Duke of Edinburgh on 3rd December, 1992, to mark Queen Elizabeth II’s 40 years on the throne.
A ring analysis carried out on the tree found in 2014 it dated back to at least 1569 but with the core missing a precise date of germination couldn’t be found. Estimates, however, place the date of germination to the last 13th or early 14th century. The analysis placed the tree’s death to between 1827 and 1842.
The tree is marked with a plaque and both it and the new tree are surrounded by an iron railing.
WHERE: Queen Elizabeth Oak, Greenwich Park (nearest DLR station is Greenwich); WHEN: 6am to 8pm daily; COST: Free; WEBSITE: https://www.royalparks.org.uk/visit/parks/greenwich-park.
This is an expanded version of a post first made in 2017.
8 locations for royal burials in London…5. Henry VII’s Lady Chapel, Westminster Abbey…
Located just to the east of St Edward the Confessor’s Chapel in Westminster Abbey is the lavishly ornate Lady Chapel built on the orders of King Henry VII.
Described as the “last masterpiece of English medieval architecture”, the chapel is the resting place of King Henry VII and his wife Queen Elizabeth of York.

The couple were the first to be buried in a vault under the floor rather than a tomb but still features an elaborate monument above the floor.
The monument was designed in the Renaissance style by Italian sculptor Pietro Torrigiano and features gilt bronze effigies of the King and Queen lying side-by-side above a black marble base decorated with six medallions representing the Virgin Mary and Henry’s patron saints (who included St Edward the Confessor). At either end of the base are coats of arms supported by cherubs.
A fine grille, designed by Thomas Ducheman, surrounds the monument – once gilded, it featured 30 statues in niches but only six – depicting saints – now remain. The lengthy Latin inscription written on the grille lauds King Henry as “a wise and watchful monarch, a courteous lover of virtue” among other superlatives. There are further inscriptions on the monument.
They’re not the only kings and queen’s buried in the chapel. King James I is buried in the vault under the King Henry VII’s tomb and his wife Queen Anne of Denmark is buried nearby.

Queen Elizabeth I is buried in the chapel’s north aisle with a monument above depicting her effigy. Her coffin was placed on top of her half-sister Queen Mary I whose body had been placed there after her death in 1558. The monument was installed on the orders of King James I who, while commissioning a depiction of Queen Elizabeth, didn’t order an effigy of Mary to be made. Instead, she is commemorated with an inscription translated as “Partners both in throne and grave, here rest we two sisters, Elizabeth and Mary, in the hope of the Resurrection.”
The religious differences of the two Queens – Elizabeth being a Protestant and Mary a Catholic – are meanwhile commemorated in an inscription on the floor which reads: “Remember before God all those who divided at the Reformation by different convictions laid down their lives for Christ and conscience sake.”
Buried in a vault beneath the south aisle of the chapel – with just simple inscriptions on stones above (no monuments were erected due to the lack of space apparently – are the remains of the Stuart monarchs King Charles II, Queen Anne (and her husband Prince George), Queen Mary II and King William III.
The rather flamboyant tomb of Mary, Queen of Scots, is also in this aisle. King James I had her remains brought to the abbey from Peterborough Cathedral in 1612 and laid to rest in a marble tomb featuring an elaborate canopy and a white marble effigy at the feet of which stands a crowned Scottish lion. The eldest son of King James I, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, was also buried in the Queen’s vault (she was his grandmother), probably due to lack of space.
The young king Edward VI is buried beneath the floor in front of the altar and the last monarch to be buried in the abbey – King George II – lies in a vault under the central aisle along with his wife Queen Caroline and some of their children as well as other family members. On the King’s orders, the sides of the coffins of King George II and that of Queen Caroline were removed so their remains could mingle.
Several other royals – including Princess Mary of Orange, eldest daughter of Charles I and Henrietta Maria, and Prince Rupert of the Rhine – are also buried in the chapel.
HERE: Lady Chapel, Westminster Abbey (nearest Tube stations are Westminster and St James’s Park); WHEN: Times vary – see the website for details; COST: £27 adults/£24 concession/£12 children (discounts for buying online; family rates available); WEBSITE: www.westminster-abbey.org
Famous Londoners – Will Somers…
The most famous of court jesters during the reign of King Henry VIII, little is known of Will Somers’ early life although it is suggested he was born in Shropshire.
It’s said Somers (also spelt Somer or Sommers) entered the service of a wealthy Northamptonshire merchant Sir Richard Fermor who presented him to King Henry VIII at Greenwich in 1525 (he is known to have been in service by 1535).
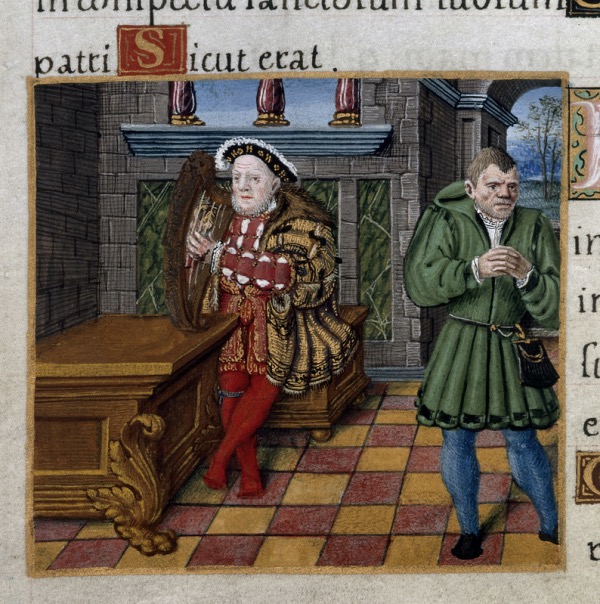

Somers’ role as jester involved using his wit to comment on court life and those in it – including the likes of Cardinal Wolsey – and while he was permitted a wide latitude he would over-step including when he insulted Queen Anne Boleyn and her daughter Princess Elizabeth, leading to the King to threaten to kill Somers himself.
Somers was provided with royal livery to wear at court (he also sometimes apparently wore elaborate costumes) and was provided with a “keeper” to look after him.
Such was the esteem Somers’ was held in, he is believed to be the fool depicted in a family portrait of the King, his wife Jane Seymour and children Prince Edward and Princesses Mary and Elizabeth (Somers has a monkey on his shoulder in the painting; Jane Foole also appears in the portrait). He’s also believed to be depicted in an image with King Henry VIII which appeared in a psalter (pictured)
Towards the end of King Henry’s life it’s said Somers was the only one who could make him laugh. He remained at court following the King’s death through the reigns of King Edward VI and Queen Mary I and present at the coronation of Queen Elizabeth I, eventually retired during her reign.
Somers is believed to have died on 15th June, 1560, and be buried in St Leonards, Shoreditch. There’s now a plaque to Somers there commemorating his burial.
Sommers subsequently appeared in various works of literature in following centuries including in more recent years when he has also appeared in TV shows – including the series The Tudors – as well as various novels including Paul Doherty’s The Last of Days.
This article contains an affiliate link.
10 (lesser known) statues of English monarchs in London…10. Four Queens…
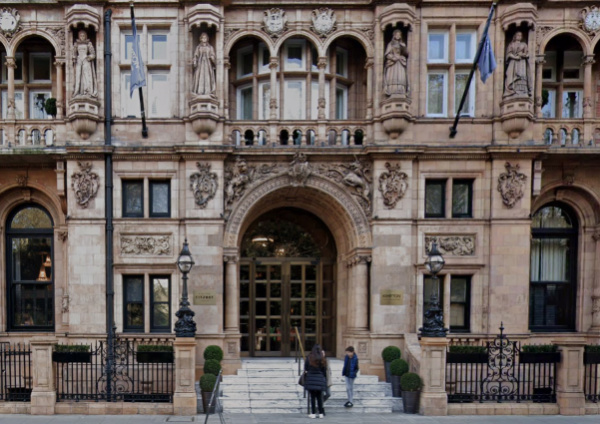

We finish our series of lesser known statues of English monarchs with a Bloomsbury building featuring four English queens.
Tucked away in niches over the main entrance of the Hotel Russell – which opened in 1898, the four queens – Elizabeth I, Mary II, Anne, and Victoria – were the work of Henry Charles Fehr.
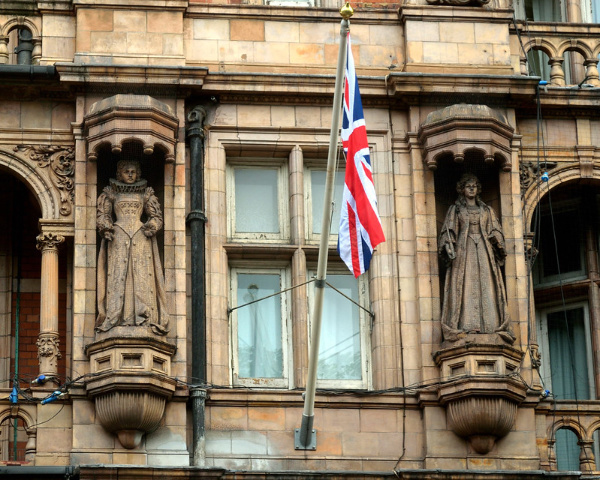

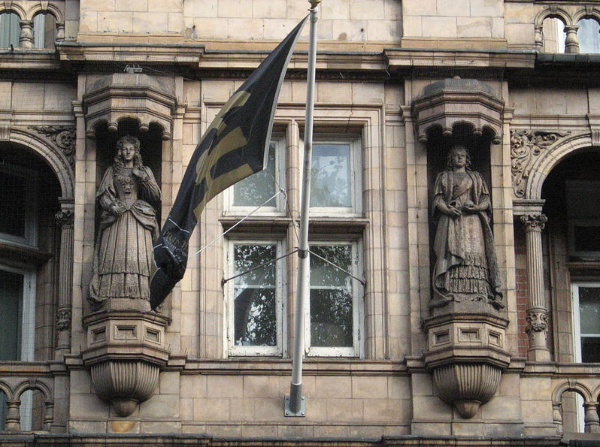
The larger than lifesize terracotta statues – which face out to Russell Square – don’t include Queen Mary I and are rather unusual and represent idealised versions of the queens. Elizabeth is readily identifiable due to the ruff she wears but there is some confusion over who’s who when it comes to Mary II and Anne. Victoria, meanwhile, is depicted as a very young woman.

Among other ornamentation, the building – which was designed by C Fitzroy Doll, also features the busts of four Prime Ministers – Lord Derby, Lord Salisbury, William Gladstone and Benjamin Disraeli – on the Guilford Street facade.
The hotel is now the Kimpton Fitzroy London.
10 (lesser known) statues of English monarchs in London…5. Queen Elizabeth I at Westminster School…

This rather unusual statue of Queen Elizabeth I is a relatively new addition – it was dedicated 12 years ago on what was the 450th anniversary of the refounding of Westminster School – more properly The Royal College of St Peter in Westminster – by the aforementioned Queen.
The larger-than-life statue, which can be found in Little Dean’s Yard, is the work of a former pupil, sculptor Matthew Spender.
It depicts the Queen in white Travertino Noce stone while her head, surrounded by a giant white ruff is gilded bronze with what was auburn hair. The unusual depiction has certainly attracted its share of detractors.
The statue, which was commissioned by the Westminster School Society, was unveiled by the Queen’s namesake, Queen Elizabeth II, on 21st May, 2010.
There’s a more famous – and more typical – statue of Queen Elizabeth I on the exterior of St Dunstan-in-the-West in Fleet Street and another on the exterior of Guildhall.
Guided tours of the school can be arranged during the school’s holidays. For more information, see www.westminster.org.uk/about/our-history/guided-tours/.
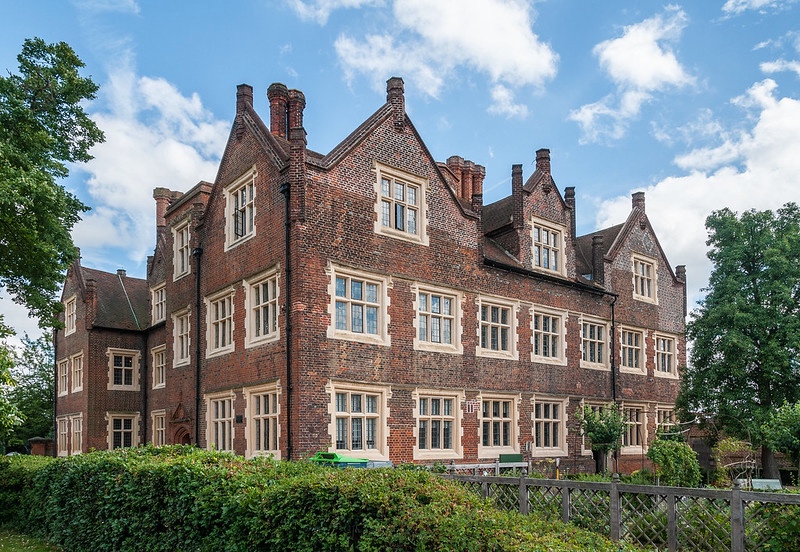
Lost London – Arundel House…

One of a string of massive residences built along the Strand during the Middle Ages, Arundel House was previously the London townhouse of the Bishops of Bath and Wells (it was then known as ‘Bath Inn’ and Cardinal Thomas Wolsey was among those who resided here during this period).
Following the Dissolution, in 1539 King Henry VIII granted the property to William Fitzwilliam, Earl of Southampton (it was then known as Hampton Place). After reverting to the Crown on his death on 1542, it was subsequently given to Thomas Seymour, 1st Baron Seymour of Sudeley, a younger brother of Queen Jane Seymour, Henry VIII’s third wife, and known as ‘Seymour Place’. Then Princess Elizabeth (late Queen Elizabeth I) stayed at the property during this period (in fact, it’s said her alleged affair with Thomas Seymour took place here).

Seymour significantly remodelled the property, before in 1549, he was executed for treason. The house was subsequently sold to Henry Fitz Alan, 12th Earl of Arundel, for slightly more than £40. He was succeeded by his grandson, Philip Howard, but he was tried for treason and died in the Tower of London in 1595. In 1603, the house was granted to Charles, Earl of Nottingham, but his possession was short-lived.
Just four years later it was repurchased by the Howard family – in particular Philip’s son, Thomas Howard, 14th Earl of Arundel – who had been restored to the earldom.
Howard, who was also the 4th Earl of Surrey, housed his famous collection of sculptures, known as the ‘Arundel Marbles’, here (much of his collection, described as England’s first great art collection, is now in Oxford’s Ashmolean Museum).
During this period, guests included Inigo Jones (who designed a number of updates to the property) and artist Wenceslas Hollar who resided in an apartment (in fact, it’s believed he drew his famous view of London, published in 1647, while on the roof).
Howard, known as the “Collector Earl”, died in Italy in 1646. Following his death, the property was used as a garrison and later, during the Commonwealth, used as a place to receive important guests
It was restored to Thomas’ grandson, Henry Howard, 6th Duke of Norfolk, following the Restoration. Following the Great Fire of London in 1666, for several years the property was used as the location for Royal Society meetings.
The house was demolished in the 1678. It’s commemorated today by the streets named Surrey, Howard, Norfolk and Arundel (and a late 19th century property on the corner of Arundel Street and Temple Place now bears its name).
Treasures of London – Great Seal of Queen Elizabeth I…
Held in the National Archives at Kew, this great seal was used during the second half of Queen Elizabeth I’s reign – from 1586 to 1603.
The seal, which replaced an earlier one used by Queen Elizabeth I, was used by the Chancery to prove the document it was attached to was issued in the Queen’s name. The seal also acted as a security device, ensuring the document couldn’t be read before reaching the intended recipient. Made of wax, it was created using a metal pattern or matrix.
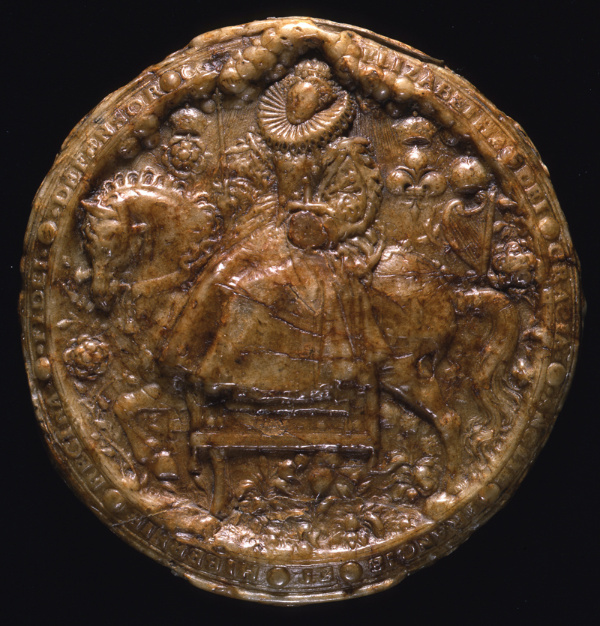

The metal pattern for this seal was created by court miniaturist Nicholas Hilliard.
The obverse or front side of the seal, which is made of resin and beeswax which turns brown with age, shows Queen Elizabeth I on her throne, her hands holding a sceptre and an orb – royal insignia – and accompanied by the Royal Coat of Arms. The reverse (pictured) shows Queen Elizabeth I mounted on a horse and surrounded by symbols including the Tudor Rose, a harp representing Ireland and fleur de lys representing France. The inscription around the seal reads: Elizabetha dei gracia Anglie Francie et Hibernie Regina Fidei Defensor (‘Elizabeth, by grace of God, Queen of England, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith’).
The seal was traditionally carried before the Lord Chancellor and Keeper of the Great Seal in a purse or burse. One used to carry Queen Elizabeth I’s matrix is in the collection of the British Museum.
The matrix used to create the second seal was surrendered to King James I on his accession to the throne on 3rd May, 1603. James then used it for the next 11 weeks until his own was ready (at which time Queen Elizabeth I’s matrix was defaced).
This Week in London – Elizabeth I and Mary, Queen of Scots; Ellen and William Craft honoured; and, Kehinde Wiley’s ‘Portrait of Melissa Thompson’…

• The complex relationship between Queen Elizabeth I and Mary, Queen of Scots, is the subject of a new exhibition opening at the British Library in King’s Cross tomorrow. Highlights of Elizabeth and Mary: Royal Cousins, Rival Queens, the first major exhibition to consider both women together, include Queen Elizabeth I’s 1545 handwritten translation of her stepmother Katherine Parr’s Prayers and Meditations – a gift for her father King Henry VIII, a sonnet by Mary, Queen of Scots, which was handwritten the night before she was executed in 1587 (possibly the last thing she ever wrote), the ‘Penicuik Jewels’ which she is thought to have given away on the day of her death and Robert Beale’s eye-witness drawing depicting her entering the hall, disrobing, and placing her head on the block (pictured right). Other items on show include King Henry VIII’s Great Bible (dating from 1540, it was later inherited by Elizabeth I), Elizabeth I’s mother-of-pearl locket ring (c1575) containing miniature portraits of herself and her mother Anne Boleyn, and the warrant confining Mary, Queen of Scots, in Lochleven Castle in 1567. The exhibition is accompanied by a programme of events. Runs until 20th February. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.bl.uk/events/elizabeth-and-mary.
• Nineteenth century African-American abolitionists Ellen and William Craft have been honoured with an English Heritage Blue Plaque at their former Hammersmith home. The Crafts escaped from enslavement in Georgia in the US in December, 1848, and fled to Britain, settling in a mid-Victorian house at 26 Cambridge Grove where they raised a family and campaigned for an end to slavery. The Crafts returned to the US following the end of the American Civil War and the emancipation of enslaved people and settled in Boston with three of their children. In 1873, they established the Woodville Cooperative Farm School in Bryan County, Georgia, for the children of those who had been emancipated. Ellen died in Georgia in 1891 and William in Charleston in 1900.

• American artist Kehinde Wiley’s monumental Portrait of Melissa Thompson has gone on display in the V&A’s British Galleries, alongside William Morris’s Wild Tulip designs that inspired it. The massive oil painting, which was created as part of Wiley’s series The Yellow Wallpaper and was first exhibited at the William Morris Gallery in Walthamstow in 2020, was acquired earlier this year and is being displayed as part of a series of initiatives marking the 125th anniversary of William Morris’s death this October. The painting will be displayed in the William Morris Room (room 125) until 2024, after which it will move to its permanent home at V&A East Museum in 2025. Admission is free. For more, head to vam.ac.uk.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
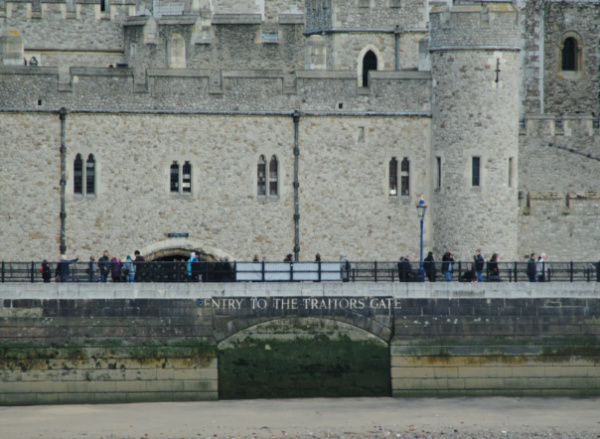
Treasures of London – Traitor’s Gate…
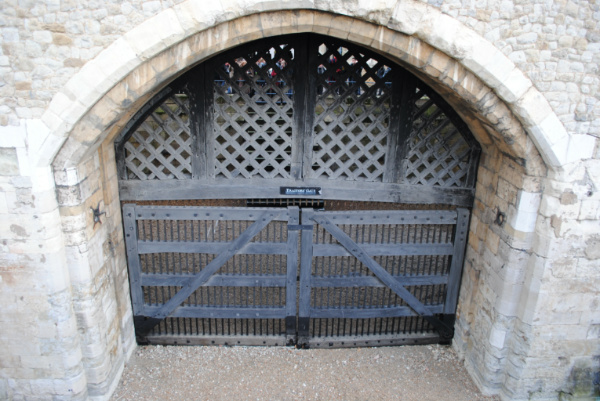

Built by King Edward I in the 13th century as a water gate to provide access from the Tower of London to the River Thames, the name ‘Traitor’s Gate’ came to be applied to this portal in Tudor times in relation to those accused of treason who were brought into the tower under its arch.
The double gateway is part of St Thomas’s Tower, which was designed by a Master James of St George, and behind it is a pool which was used to feed water to a cistern on the roof of the White Tower. While the gate was originally built to give access directly to the river, Traitor’s Gate now sits behind a wharf which runs along the river bank (and where can be seen the bricked up entrance says ‘Entry to the Traitor’s Gate’ – this was bricked up in the 19th century when embankment works were carried out)
Sir Thomas More, Sir Walter Raleigh and even the future Queen Elizabeth I (when a princess) were among those who were brought in by barge through the Traitor’s Gate (their journey would have led them under London Bridge where the heads of executed prisoners were on display). Whether Henry VIII’s disgraced Queen Anne Boleyn entered the tower through the gate remains a matter of some dispute.

A Moment in London’s History – The opening of the Royal Exchange…
This month marks the 450th anniversary of the opening of London’s Royal Exchange, a complex created to act as a commercial centre in the City of London.

The exchange was built on the orders – and with the funds – of the merchant Sir Thomas Gresham at a site on the junction of Cornhill and Threadneedle streets which was – and still is – jointly owned by the City of London Corporation and the Worshipful Company of Mercers.
Drawing inspiration from the Antwerp Bourse, credited as the oldest financial exchange in the world (and where Sir Thomas had served as an agent of the crown), the Royal Exchange was built in ranges around a central courtyard and designed by an architect from Antwerp.
It was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth I on 23rd January, 1571. The Queen, who was lodging in Somerset House at the time, reportedly took a detailed look at the premises – which had apparently been completed a few years earlier.
At the close of her visit, she awarded the exchange the use of the word ‘Royal’ in its title (an honour announced by a herald and with the sound of a trumpet). She also granted it a license to sell alcohol and other luxury goods.
Earlier in the day, the Queen had dined at Sir Thomas’ own house in Bishopsgate. She was later to return to Somerset House.
Gresham’s original building – to which two floors of retail had been added in 1660, creating what is said to have been England’s first shopping mall – was sadly destroyed in the Great Fire of London in 1666.
It was replaced by a second complex, this time designed by Edward Jarman, in 1669, but this too succumbed to fire, this time on 10th January, 1838. The building which now stands on the site – and is now an upmarket retail centre – was designed by Sir William Tite and was opened by another Queen, Victoria, in 1844.
Gresham’s contribution is remembered by the building’s weathervane which features a golden grasshopper – an insect featured on Sir Thomas’ crest.
A Moment in London’s History – The National Trust acquires Eastbury Manor House…
This month (12th January to be exact) marks 125 years since the National Trust was founded by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Canon Hardwicke Rawnsley. So we’re taking a quick look at another, somewhat related, milestone – the acquisition of the Trust’s first London property.
Located in Barking, Eastbury Manor House, initially known as Eastbury Hall, was built between 1560 and 1573 (during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I) for Clement Sisley on land which once belonged to Barking Abbey.
The H-shaped house and surrounding estate remained in the family until 1629 after which it passed through the hands of a number of well-to-do families, gradually falling into disrepair.
By the early 19th century, decay had led to one of the property’s unique octagonal stair turrets being pulled down and wooden flooring and fireplaces removed. The ground floor was being used as a stable and dairy.
The property struggled on into the early 20th century when it was threatened with demolition. The Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings, recognising its significance as a rare example of mid-16th century brick built gentry house, lobbied for it to be saved and, working alongside the National Trust, ran a campaign to raise funds for its acquisition.
The house – and surrounding gardens – were acquired by the Trust for the nation in 1918 and then, in 1934, leased to Barking Borough Council. The following year the property became the home of Barking Museum.
It was awarded Grade I-listed status in 1954 and is now managed by the Borough of Barking and Dagenham. A restoration program in recent years has seen the addition of a permanent exhibition on the property’s history.
WHERE: Eastbury Manor House, Eastbury Square, Barking (nearest Tube station is Upney); WHEN: From 13th February, 10am to 4pm Thursdays and Fridays and, from 22nd March, 11am to 4pm Sundays; COST: £5.20 adults/£2.60 children and concessions/£9.30 family (LBBD residents, SPAB and National Trust members free); WEBSITE: www.eastburymanorhouse.org.uk.
PICTURE: David Nicholls (licensed under CC BY-NC 2.0)
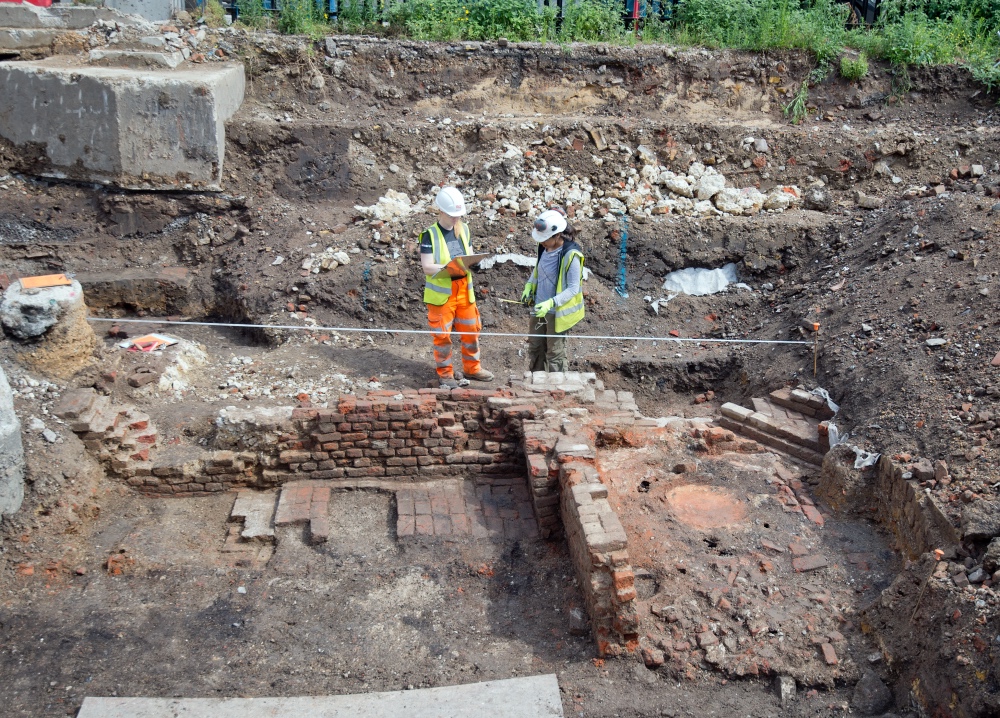
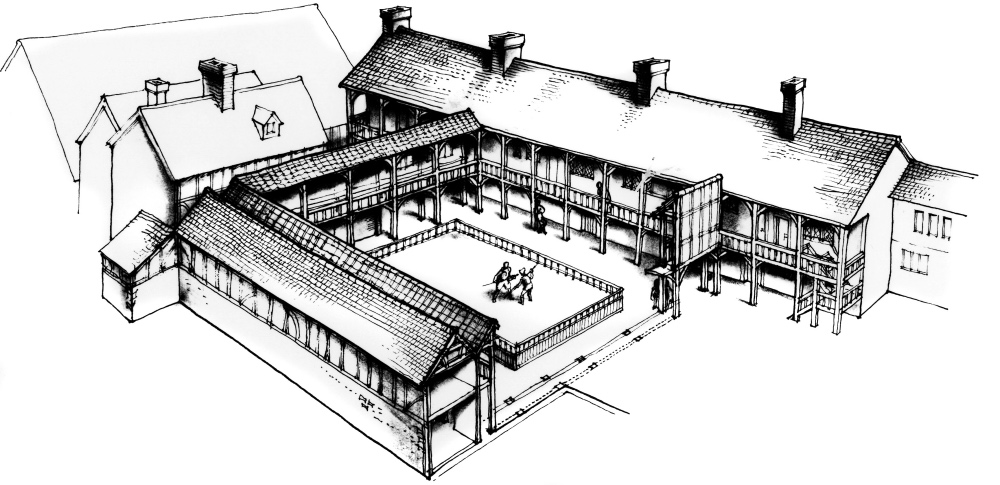
LondonLife – The Boar’s Head Playhouse excavations…
MOLA archaeologists have started excavating the site of The Boar’s Head Playhouse in Middlesex Street, Whitechapel, before construction of a new student housing complex. The playhouse, the location of which is known from historical accounts, was created in 1598 when inn owner Oliver Woodliffe converted his establishment by adding tiered galleries, a stage and central open air yard (extra galleries and a roof over the stage were added a year later). The playhouse hosted popular acting troupes including Lord Derby’s Men and the Lord Worcester’s Men, later the Queen’s Men, led by the famous actor and playwright Thomas Greene, and among the plays performed was the comedy No-body and Some-body as well as a chronicle of the life and reign of Elizabeth I, If You Know Not Me, You Know No Bodie. It is hoped the excavations will provide new insights into the theatre. The accommodation, being developed by Unite Students, will provide housing for 915 students and is expected to open in 2021. PICTURES: Top – Archaeologists record an 18th century clay tobacco pipe kiln built against 16th century walls associated with the Boar’s Head playhouse © MOLA; Below – Reconstruction of the Boar’s Head Playhouse from 1598, by C Walter Hodges.
This Week in London – A rare surviving piece of Queen Elizabeth’s dress on show?; Inside Ronnie Scott’s Jazz Club, and, Islamic influences on art…
• An altar cloth which may have once been part of a dress worn by Queen Elizabeth I goes on show at Hampton Court Palace (pictured) this Saturday. The Bacton Altar Cloth, which was discovered in a church in Bacton in rural Hertfordshire, has undergone two years of conservation work and will be displayed alongside a portrait of the “Virgin Queen” featuring a dress of similar design. The altar cloth has long been associated with Bacton-born Blanche Parry, one of Queen Elizabeth’s servants who became her Chief Gentlewoman of the Bedchamber. Records show the Queen regularly gave her discarded clothing to Parry and for years there has been speculation that the altar cloth was part of one such discarded item. Historic Royal Palaces curator Eleri Lynn, an expert in Tudor court dress, was able to identify previously unseen features and studied the seams of the fabric to show it had once been part of a skirt. Further research – including an examination of the dyes used in the item – have added weight to the theory it was once part of a dress. The altar cloth, on loan from St Faith’s Church in Bacton, can be seen until 23rd February. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.hrp.org.uk. PICTURE: David Adams.
• A photographic exhibition of the first ‘golden’ decade of Ronnie Scott’s Jazz Club – featuring images of legendary British and American jazz singers – opens at the Barbican Music Library on Saturday. Ronnie Scott’s 1959-1969: Photographs by Freddy Warren, which marks the club’s 60th anniversary, features Warren’s photographs of the likes of Miles Davis, Duke Ellington, Dizzy Gillespie, Count Basie, Ella Fitzgerald, Zoot Sims, Cleo Laine and Tony Bennett. Warren was the in-house photographer at the Soho club from the opening night in 1959, when it was based in Gerrard Street, and documented the construction of the new site in Frith Street in the mid-1960s along with the arrival in London of big American stars. The exhibition includes rare vintage prints – some which were salvaged from the walls when the club was renovated in 2006, Freddy Warren’s original contact sheets, and previously unseen prints specially produced from the original negatives. The exhibition is free. Runs until 4th January. For more, see www.barbican.org.uk/your-visit/during-your-visit/library.
• An exhibition exploring how western artists have been inspired by the Islamic world opens at the British Museum today. Inspired by the east: how the Islamic world influenced western art features paintings by leading ‘Orientalists’ including Eugène Delacroix, John Frederick Lewis and Frederick Arthur Bridgman as well as less well-known pieces like British artist Edmund Dulac’s original illustrations for a 1907 edition of the Arabian Nights, and ceramics by Frenchman Théodore Deck, who in the late 19th century created a range of pieces directly inspired by Islamic originals. The display also includes contemporary reactions to the imagery of Orientalism by Middle Eastern and North African female artists such as Lalla Essaydi’s Women of Morocco triptych and Inci Eviner’s 2009 video work Harem. The display can be seen in The Sir Joseph Hotung Exhibition Gallery until 26th January. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.britishmuseum.org.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
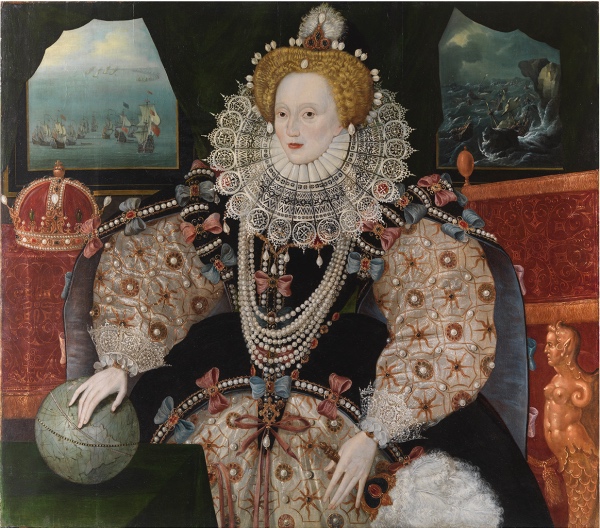
Treasures of London – The Armada Portrait of Elizabeth I…
Saved for the nation following a public appeal by the Art Fund and Royal Museums Greenwich in 2016 and subsequently having undergone an extensive conservation and restoration process, the ‘Armada Portrait of Elizabeth I’ now hangs in the 400-year-old Inigo Jones-designed Queen’s House in Greenwich.
The life-sized portrait, which is unusually presented in a landscape format, commemorates the failed invasion of England by the Spanish Armada in the summer of 1588. It was painted in about 1590 by an unknown artist when the queen was aged in her mid-50s and may have been commissioned by Sir Francis Drake, second-in-command of the English fleet assembled to defend England from the Spanish.
Up until its £10.3 million acquisition (which was funded by various donations including a £1 million donation from the Art Fund, £400,000 from the Royal Museums of Greenwich, some 8,000 individual donations from members of the public totalling £1.5 million, and a Heritage Lottery Find grant of £7.4 million), it had been owned by Drake’s descendants – now known as the Tyrwhitt-Drakes – who have had possession since at least 1775. It spent much of its life hanging at Shardeloes, a Buckinghamshire country house built for William Drake in the late 18th century.
Designed to inspire a sense of awe in its viewers, the portrait contains numerous references which would have conveyed specific meanings to the Tudor mind. The Queen’s upright posture, open arms and clear gaze, for example, convey vitality and strength while her pearls are symbols or chastity and the Moon. The gold suns embroidered on her skirt and sleeves are said to symbolise power and enlightenment and the queen rests her hands on a globe with her fingers seeming tapping on the new world with the imperial crown sitting overhead in fairly obvious statement of her ambitions overseas.
Two maritime scenes in the background, both of which are actually early 18th century reworking over late 16th century originals, depict firstly the English fleet preparing to engage the Spanish Armada in the English Channel and, secondly, Spanish ships being wrecked on the Irish coast during their passage home.
One of the best known images from English history, the portrait has inspired countless portrayals of Elizabeth on stage and screen, including Cate Blanchett’s in two ‘Elizabeth’ films.
The Queen’s House, where the painting is being displayed, is built on the site of what was once Greenwich Palace, birthplace of Queen Elizabeth I.
WHERE: Queen’s House, Romney Road, Greenwich (nearest overground station is Greenwich/DLR is Cutty Sark for Maritime Greenwich); WHEN: 10am to 5pm daily; COST: free; WEBSITE: www.rmg.co.uk/queens-house.
PICTURE: © National Maritime Museum, London