We finish our series on Christopher Wren by providing a quick recap…
1. The Old Court House, Hampton Court Palace Green…
9. St James’s Street, Piccadilly…
We’ll start a new series in the New Year!
We finish our series on Christopher Wren by providing a quick recap…
1. The Old Court House, Hampton Court Palace Green…
9. St James’s Street, Piccadilly…
We’ll start a new series in the New Year!
For the final entry in our Wednesday special series, we go to see Sir Christopher Wren’s greatest work – and also his resting place, St Paul’s Cathedral.
Following his death on 25th February, 1723, Wren was buried in the crypt of St Paul’s Cathedral on 5th March.

His burial location was in the south-east corner of the crypt and a simple memorial was placed there near that of his daughter Jane and his sister Susan Holder and her husband William.
The plaque which marks the location was written by his eldest son Christopher. Inscribed in Latin, it reads: “Here in its foundations lies the architect of this church and city, Christopher Wren, who lived beyond ninety years, not for his own profit but for the public good. Reader, if you seek his monument – look around you. Died 25 Feb. 1723, age 91.”
It’s a fitting tribute to one responsible for some of London’s most famous landmarks.
Interestingly, a fragment of Wren’s coffin can be seen at the RIBA Library. It was taken from his tomb in 1851 when it was last opened to allow for his last surviving direct descendent to be placed within.
WHERE: St Paul’s Cathedral (nearest Tube stations are St Paul’s, Mansion House and Blackfriars); WHEN: 8.30am to 4.30pm Monday to Saturday; COST: £23 adults/£20.50 concessions/£10 children/£56 family (these are walk-up rates – online advanced and group rates are discounted); WEBSITE: www.stpauls.co.uk.

As noted at the outset of this series, in his latter years Sir Christopher Wren retired to the property on Hampton Court Palace Green, a property he was granted after he was appointed Surveyor-General to King Charles II in 1669.
But he also still spent time in London and, no longer having access to Scotland Yard, he lodged at his son Christopher’s house in St James’s Street, off Piccadilly. In fact, it was in this property that Wren, having suffered a chill, died while sitting in a chair at the age of 91 on 25th February, 1723.
It’s been suggested that the house in which Wren died was on the west side of the street. There’s an apocryphal story that suggests Wren came to London to check up on his greatest work, St Paul’s Cathedral.

Sir Christopher Wren’s name is one which pops up in association with buildings all over London – some authentically so, others less so.

One of the more talked about locations where it can be physically seen is on a plaque attached to the front of a house overlooking the Thames at 49 Bankside, on the corner with Cardinal Cap Alley.
The plaque, written in a flowery script, claims that “Here lived Sir Christopher Wren during the building of St Pauls Cathedral” before going on to state that the property was also where in 1502, Catherine of Aragon, “took shelter” on first arriving in London before her marriage to King Henry VIII.
But author and historian Gillian Tyndall debunks the claim in her 2006 book The House by the Thames and the People who Lived There.
Tyndall explains that the property apparently dates from 1710 – St Paul’s was officially declared complete in 1711, leaving little cross-over (and certainly ruling out any residence by Queen Catherine who actually landed in Plymouth). She says that while it’s true the present house stands in the footprint of an older one, the house where Wren may have actually lodged during the 1670s is located further west along Bankside.
London Remembers notes that this property was apparently marked with an 18th century plaque commemorating Wren. But when that house was demolished in 1906, the plaque was saved and subsequently attached to a power station’s outer wall. When that was redeveloped in the post-war period, the plaque disappeared.
It was apparently that plaque which inspired the creation of the current plaque which was created by Major Malcolm Munthe, who acquired the property in 1945, and subsequently had the plaque made for the home’s exterior.
So it seems the plaque, despite what it says, does not commemorate a Wren residence (although perhaps it may commemorate the residence of Wren in the area). And, it’s been suggested, that while the plaque may not actually have marked a Wren home, its presence may have been enough to protect the building it adorns from threatened redevelopment in the mid-20th century.

While this series is more focused on Sir Christopher Wren’s life rather than the many works he left behind, we’ve included the remarkable church of St Stephen Walbrook for a couple of reasons.

The first is that it is generally seen as being one of the more important church designs he created, particularly with regard to his later design of St Paul’s Cathedral, of which the St Stephen Walbrook dome is said to be a prototype.
The second is it’s claimed St Stephen Walbrook had a rather personal connection in that Wren lived at number 15 Walbrook during the period the church was being built, making it his parish church.
But the church was built between 1672 and 1679 and we know that from 1669 onwards – when Wren was appointed Surveyor-General of the King’s Works by King Charles II – Wren had a substantial home and office at Scotland Yard which was a perk of the office. Prior to that, he was largely based in Oxford and had rooms within Gresham College.
We’ve been unable to find any detailed reference to Wren living at 15 Walbrook either online or in the biographies we’ve read (we’ll keep searching).
But, his residency in Walbrook aside, it’s clear that St Stephen Walbrook – which has been described as the “pride of English architecture” – was a special church for Wren.
Designed to a rectangular form by Wren (and it’s certain this design was that of Wren himself), the church features a dome located toward the east end supported by eight Corinthian columns with the interior light by sizeable windows at the east end. A tower stands at the west end. The altar, a modern design by Henry Moore, sits under the centre of the dome.
As an interesting final note, it is recorded that Wren attended a dinner hosted by the church wardens – along with collaborator Robert Hooke – at the Swan Tavern in Old Fish Street on 4th March, 1673, as work for the church was underway.
WHERE: St Stephen Walbrook, 39 Walbrook (nearest tube stations are Bank and Cannon Street); WHEN: Opening times vary – check website details; COST: Free; WEBSITE: www.ststephenwalbrook.net.

Think of Sir ChristopherWren and chances are it’s St Paul’s Cathedral – perhaps the most famous building he designed – which comes to mind. Certainly not Westminster Abbey, which he did not.
Yet, aside from his time at the Westminster School as a child, Wren did have a long relationship with the royal church at Westminster. In March, 1698, he was appointed the Surveyor of the Fabric at Westminster Abbey, a post he held until his death (when he was succeeded by Sir Nicholas Hawksmoor).
Wren did some work on the building. Prior to being appointed surveyor he had undertaken some work on schoolmaster Dr Richard Busby’s house (Wren had been one of his students) in the Little Cloister in 1683 (the house was destroyed during the Blitz in World War II).
Following his appointment, Wren did undertake a major restoration of the decayed stonework and roof of the church. He also approved designs by his deputy, William Dickinson, for the north front and an altarpiece which Wren had originally designed for the royal chapel at the Palace of Whitehall was given to the minster by Queen Anne (it was removed in the 19th century).
In 1713, Wren had also created designs for a series of works at the abbey which included the addition of a central tower and spire at the abbey and the completion of the west front which were never realised and which were shelved after his death (the wooden model for the tower and spire is located in Queen’s Diamond Jubilee Galleries, along with a pair of wooden obelisks he designed for the entrance to the Quire).
While there’s no memorial to him in the Abbey, Wren’s image can be seen in the lower right section of a memorial window in the north choir aisle dedicated to 19th century engineer Robert Stephenson while his coat of arms is shown along with numerous others in some post-war glass windows in the Chapter House.
WHERE: Westminster Abbey (nearest Tube stations are Westminster and St James’s Park); WHEN: Times vary – see the website for details; COST: £29 adults/£26 concession/£13 children (family rates available); WEBSITE: www.westminster-abbey.org.
Sir Christopher Wren was apparently a frequent visitor to London’s burgeoning coffee houses in the late 17th and early 18th centuries.

Wren apparently started visiting coffee houses during his time in Oxford (the first in England is said to have opened there in 1652; the first in London – Pasqua Roseé’s premises st Michael’s Alley off Cornhill – opened late that same year) and continued to do so in London.
While it’s hard to pin down those he preferred, he reportedly met Robert Hooke at Man’s Coffee House in Charing Cross. The premises was apparently frequented by stockjobbers.
Wren was in good company attending such premises – other luminaries known to have done so at the time include diarist and naval administrator Samuel Pepys, John Locke, Edmund Halley, John Dryden and Alexander Pope.
Among other prominent coffee houses at the time was Jonathan’s – where in, 1698, the London Stock Exchange was born – and Garraway’s Coffee House, both of them located in Exchange Alley, as well as Button’s in Covent Garden.
Described as “probably the most famous Gresham College professor in history”, Sir Christopher Wren was appointed professor of astronomy at the college in 1657.
Wren is believed to have been educated at the Westminster School before attending Wadham College in Oxford and graduating with a BA in 1651. An MA followed in 1653 and he was subsequently elected a fellow of All Soul’s College in Oxford.
That was followed by the Gresham appointment with Wren giving his inaugural lecture in August of 1657. His tenure was somewhat interrupted when, following the resignation of Richard Cromwell in May, 1659, the college was occupied by the military (and Wren stayed in Oxford). He returned to London following the Restoration which culminated in King Charles II’s entry into London in May, 1660.
Wren left Gresham later that same year and four years later, in 1664, he was appointed Savilian professor of astronomy at Oxford – a position he held until his appointment surveyor of works to King Charles II.
Gresham College was established in 1597 under the terms of the will of Sir Thomas Gresham and was originally located in Sir Thomas’ former mansion on Bishopsgate. It was here that Wren – and other lecturers including Sir Robert Hooke – lectured.
In the mid-18th century, Gresham moved to the corner of Gresham and Basinghall Streets. In 1991, it again relocated – this time to the 14th century Barnard’s Inn Hall near Chancery Lane. The college today continues its founding tradition of providing free lectures (there’s now a considerable archive of these online).
There was a Corporation of the City of London plaque commemorating the original location of Gresham College in Old Broad Street but it’s apparently been removed.
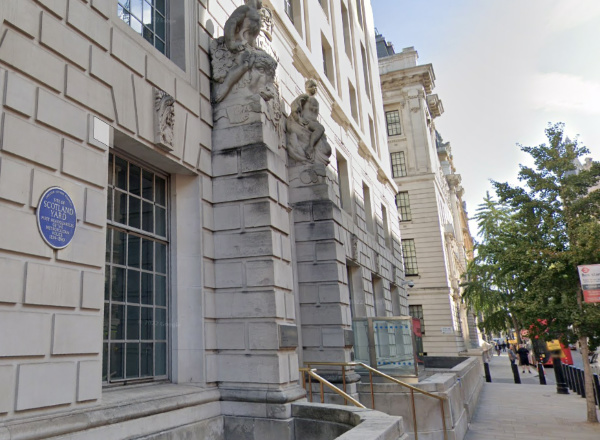

OK, so there’s not much left to see here – at least not from Wren’s time. But it was in Scotland Yard that Wren spent much of his time after being appointed Surveyor-General of the King’s Works.
The yard, which was located just north of the kitchens serving the Palace of Whitehall and to the south of aristocratic mansions built along the Strand, was the location of the Office of Works. It served as a workplace for Wren and was also the location of his main residence between 1669 and 1718 when he lived in a house built by his predecessor in the office, John Denham.
According to a recent lecture by Professor Simon Thurley at Gresham College, newly identified plans of the house show the ground floor contained a hall, with a kitchen and scullery to the rear while on the first floor was a great dining room, a smaller private dining room, bedroom and dressing room. A floor above contains quarters for servants and possibly the nursery for his children. There were cellars below, two yards and a long narrow walled garden (he also had a stable nearby for his horses and carriage). Most importantly, a door connected the house directly with the Office of Works next door.
Said Thurley: “Although slightly further [from] the royal lodgings than some apartments, Wren’s house was amongst the largest and best appointed of all the houses allocated to senior courtiers.”
Wren lived here with his two wives – his first wife Faith Coghill died of smallpox here in 1675 and his second wife Jane Fitzwilliam died of tuberculosis in 1680 as well as their children – Christopher, William and Elizabeth. Both William and Elizabeth never left their father’s care and died before him.
The origins of the name of Scotland Yard – which has since become synonymous with the Metropolitan Police (now based at New Scotland Yard) – apparently come from the fact the site contained lodgings where the Kings of Scotland stayed when visiting London (the last Scottish royal to stay here did so before Wren’s time, apparently in the reign of King Henry VIII).
From the Stuart period onward, the site was used for government offices – as well as Wren, other famous residents included Inigo Jones, one of Wren’s predecessors as Surveyor of Works, and, during the Commonwealth, John Milton, while serving as Latin Secretary to Oliver Cromwell.
The location of Scotland Yard is these days commemorated in the name of Great Scotland Street and Scotland Place, just off Whitehall. There’s also an English Heritage Blue Plaque marking the site in Whitehall Place, although Wren doesn’t get a mention on that (it’s entirely devoted to the former police presence).
Not one of the many churches rebuilt by Wren after the Great Fire of 1666, St Martin-in-the-Fields, located just to the east of what is now Trafalgar Square, is special to the great architect for very personal reasons.
For it was in this church that his first wife Faith (nee Coghill) and his first son Gilbert were both buried, having died within a few years of each other, along with his second wife Jane (nee Fitzwilliam).
Wren married Faith Coghill, a childhood neighbour and daughter of Sir Thomas Coghill of Bletchingdon, at the age of 37 on 7th December, 1669, at the Temple Church (it’s been suggested it was his appointment that year as Surveyor of the King’s Works that may have provided him with the financial security he desired before marrying).
Their first child – Gilbert – was born in October, 1762. But he died at the age of just 18-months-old. A second child, Christopher (Wren the Younger), was born in February, 1675 (he would go on to live a full life and follow in his father’s footsteps as an architect).
Faith died of smallpox on 3rd September that same year. She was buried beneath the chancel of St Martin-in-the-Fields beside Gilbert.
On 24th February, 1677, Wren married again, this time to Jane Fitzwilliam, daughter of William FitzWilliam, 2nd Baron FitzWilliam, and Jane Perry, in a private ceremony believed to have been undertaken in the Chapel Royal at Whitehall. The couple had two children together – Jane in November that year and William in June, 1679.
Tragically, Jane also died after only a few years of marriage of tuberculosis on 4th October, 1680. She was buried alongside Wren’s first wife and child in St Martin-in-the-Fields.
Wren was not to marry again – and for his long 90 years of life, he was only in the end married for nine.
The medieval church of St Martins-in-the-Fields was altered several times during its lifetime – including being enlarged and beautified – but it’s this earlier church that Wren would have known. The current church was rebuilt to the designs of James Gibbs in the early 1720s and was completed in 1726 after Wren’s death in 1723.
Interestingly, the first wife of Wren’s son Christopher – Mary – was also buried in the church in 1712 and a monument to her can still be seen in the crypt.
This year marks the 300th anniversary of the death of Sir Christopher Wren (25th February, 1723), whose designs helped to transform post-Great Fire London.
In a new series we’re looking at 10 locations which help tell Wren’s story but while we’ve previously runs numerous articles focused on the many buildings he designed, in this series the focus is more on his personal life.
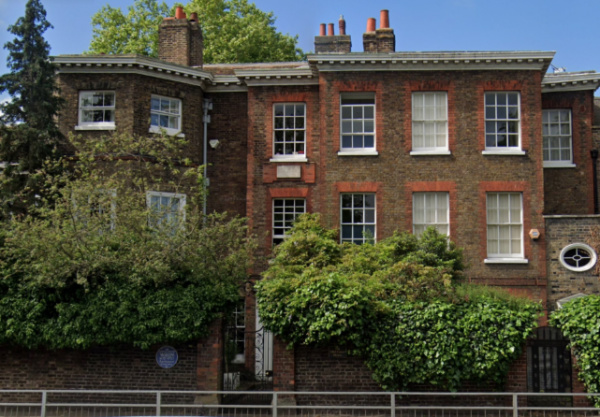

First up, it’s one of the most well-known properties related to Wren’s life – the home in which he spent the latter years after his life just outside Hampton Court Palace.
Known as the Old Court House, Wren first came to live in the house after he was appointed Surveyor-General to King Charles II in 1669. His post brought with it lodgings at the royal palaces and at Hampton Court Palace, it was the Old Court House (the property had been built for in 1536 as a wood and plaster house; Wren’s immediate predecessor in the office, Sir John Denham, had rebuilt it partly in brick).
Then in 1708, Queen Anne granted him a 50-year lease on the property, apparently at least partly in lieu of overdue fees he was owed for the building of St Paul’s Cathedral. It’s also believed that the Queen had granted the lease on condition that Wren repair or rebuilt the property.
Wren, who had hitherto only lived intermittently at the property (presumably while working on Hampton Court Palace on the orders of King William III and Queen Mary II), made some major alterations to the property from 1710 onwards (it’s suggested this was done to the designs of Wren’s assistant William Dickinson).
He came to live here on a more permanent basis after he retired from the Office of Works in 1718 and remained here until his death in 1723 (although he didn’t die here – more on that later).
It’s said Wren, whose time as the Royal Surveyor-General spanned the reigns of six monarchs, spent his time here “free from worldly affairs”, choosing to and pass his days ‘in contemplation and studies”.
It was subsequently the home of Wren’s son Christopher (1645-1747) and his grandson Stephen (b 1772). It remained a grace and favour house associated with Hampton Court Palace until 1958.
The Grade II* brown and red brick property, which was combined with the house next door in the early 19th century and them divided off in 1960, is now in private ownership and there’s an English Heritage Blue Plaque on the outside wall mentioning Wren’s residence.