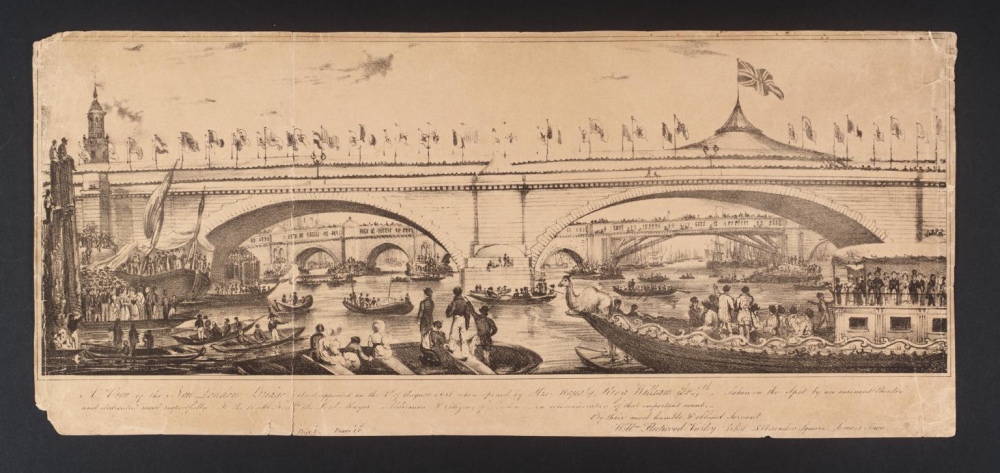
This month marks the 187 years since the opening of “new” London Bridge – the first bridge built over the Thames in London for more than 600 years.
Designed by John Rennie (who had won a competition, beating the likes of Thomas Telford for the honour), work on the new granite bridge had began in 1825 and was completed in 1831.
It was constructed alongside the medieval bridge which had been first completed in the 13th century and added to over the years since (and was eventually completely demolished after the opening of the ‘new’ bridge).
The ‘new’ bridge, said to have cost £506,000 to construct, was formally opened by King William IV on 1st August, 1831, in an event described by The Times as “the most splendid spectacle that has been witnessed on the Thames for many years”.
The royal party – which included Queen Adelaide – had approached the bridge, lined with flags for the occasion, after setting off from Somerset House amid cheering described as “almost deafening” (to add to cacophony of sound, church bells were rung and cannon fired throughout the day).
Watched by thousands of onlookers (who were entertained by bands at various locations), the royal party had processed their way downstream on the river to the bridge with the royal bargemen wearing new livery specially designed for the occasion. Two parallel lines of rivercraft – including barges and steamers – had gathered along the river to provide a sort of honour guard and ensure they had clear passage.
The royals arrived at the bridge at 4pm and the royal party made their way up red carpeted stairs to the bridge’s City end. Following a short ceremony in which the King was presented by the Lord Mayor of London with the sword and keys to the City of London as well as a specially made gold medal to mark the occasion, their Majesties then walked across from the across the bridge to the Southwark end where entertainments had included the ascension of a hot air balloon.
The King and the royal party then returned to the City end of the bridge to attend a banquet – guests were said to number 1,500 people – held under a pavilion erected atop the new structure.
The Gentleman’s Magazine reported that food was provided by a coffee house proprietor, a Mr Leech, and was said to include 150 hams and tongues, 370 “dishes of chickens”, and 300 turtles as well as 200 fruit tarts and 300 “ice-creams”.
The King and royal party then returned up the river.
 Rennie’s bridge was replaced in the mid-20th century with another bridge which was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II in 1973 and rather than being demolished, was sold to US oil magnate Robert P McCulloch who had it dismantled and shipped to Arizona where it was reconstructed at Lake Havasu City where it can now be seen.
Rennie’s bridge was replaced in the mid-20th century with another bridge which was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II in 1973 and rather than being demolished, was sold to US oil magnate Robert P McCulloch who had it dismantled and shipped to Arizona where it was reconstructed at Lake Havasu City where it can now be seen.
A couple of sections of the bridge survive in London – two of its pedestrian alcoves, one of which can be found in Victoria Park in London’s east and the other at King’s College London.
There is a famous painting – Clarkson Stanfield’s, The Opening of New London Bridge, 1 August 1831 – which captures the moment of the bridge’s opening and is part of the Royal Collection.
PICTURES: Top – ‘A View of the New London Bridge as It Appeared on the 1st August 1831, When Opened by His Majesty, King William the 4th’, Unknown artist, Lithograph on paper, Photo © Tate (licensed under CC-BY-NC-ND 3.0 (Unported)); Right – The alcove in Victoria Park (Public Domain).