This parish church once stood on the west side of Broad Street in the City of London and dated back to the Norman era.

The church, which originally dated from before 1181 (when it was first mentioned) and was also referred to as St Peter le Poor, may have been so-named because of the poor parish in which it was located or for its connections to the monastery of St Augustine at Austin Friars, whose monks took vows of poverty.
Whatever the reason for its name (and it has been suggested the ‘le Poer’ wasn’t added to it until the 16th century), the church was rebuilt in 1540 and then enlarged in 1615 with a new steeple and west gallery added in the following decade or so.
The church survived the Great Fire of London in 1666 but just over a 100 years later has fallen into such a state of disrepair that parishioners obtained an Act of Parliament to demolish and rebuild it.
The new church, which was designed by Jesse Gibson and moved back off Broad Street further into the churchyard, was consecrated on 19th November, 1792. Its design featured a circular nave topped by a lantern (the curved design was not visible from the street) and placed the altar directly opposite the doorway on the north-west side of the church.
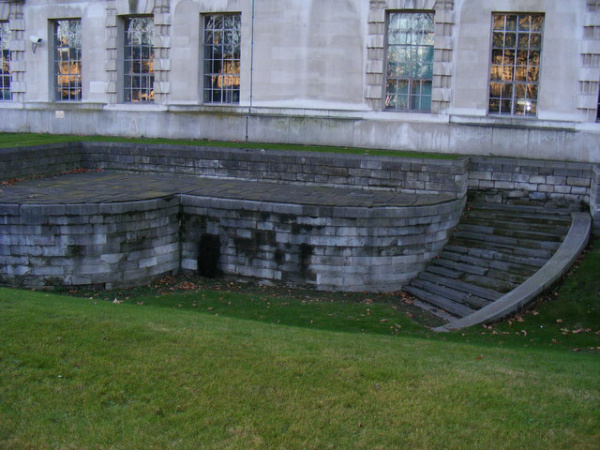
The church had acquired a new organ in 1884 but the declining population in the surrounding area led to its been deemed surplus to requirements. It was demolished in 1907 and the parish united with that of St Michael Cornhill.
Proceeds of the sale were used to build a new church, St Peter Le Poer in Friern Barnet. The new church, which was consecrated on 28th June, 1910, by the Bishop of London, the Rt Rev Arthur Foley Winnington-Ingram, also received the demolished church’s font, pulpit and panelling.