Now found in the Churchill War Rooms, the original black door from the Prime Minister’s residence at 10 Downing Street dates from the 1770s.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to gain access to all Exploring London’s content.
Now found in the Churchill War Rooms, the original black door from the Prime Minister’s residence at 10 Downing Street dates from the 1770s.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to gain access to all Exploring London’s content.
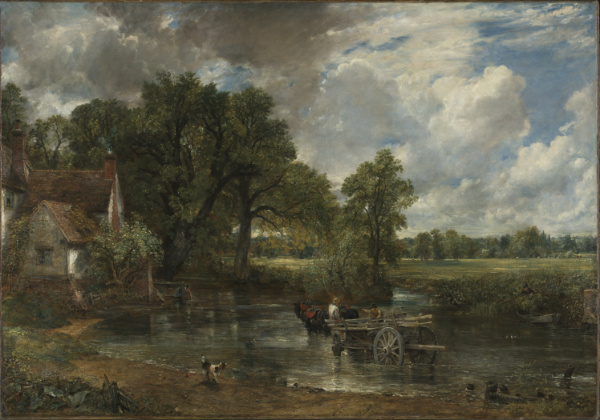
• John Constable’s iconic work The Hay Wain is the focus of a new free exhibition opening at The National Gallery. Discover Constable and The Hay Wain, which is being held as part of the gallery’s 200th anniversary celebrations, will look at the innovative nature of the painting when it was first exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1821 and show how Constable came to be established as a master in the history of British art. It will also examine the subsequent ownership of the painting, its acquisition by the National Gallery in 1886, and the rise in popularity of both Constable and The Hay Wain in the years since. The free exhibition in the Sunley Room opens today. Runs until 2nd February. For more, see www.nationalgallery.org.uk/exhibitions/discover-constable-and-the-hay-wain.
• A new exhibition examining how the British Museum’s collection reflects the legacies of British imperial power opens today. A collaboration with renowned Guyanese-British artist Hew Locke, Hew Locke: what have we here? is Locke’s “personal and emotive exploration” of the collection and features well-known objects from across the museum’s collection alongside specially commissioned new works by Locke. Can be seen until 9th February in the The Joseph Hotung Great Court Gallery (Room 35). For more, see www.britishmuseum.org.
• The first tickets for London’s New Year’s Eve fireworks celebration go on sale at noon tomorrow (Friday 18th October). The tickets, which cost between £20 and £50 depending on the viewing area (London residents pay £15 less on each ticket), represent the first of two batches of tickets to go on sale. Tickets must be purchased to watch the fireworks in person and only tickets bought from the authorised outlet Ticketmaster will be accepted. For those who can’t get tickets, the fireworks show is being broadcast live on the BBC. www.london.gov.uk/nye.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
This free-standing, 287 foot-high tower is a survivor – it’s all that remains of the Imperial Institute.
Subscribe for just £3 a month to get access to all Exploring London’s stories – that’s less than the cost of a cup of coffee!
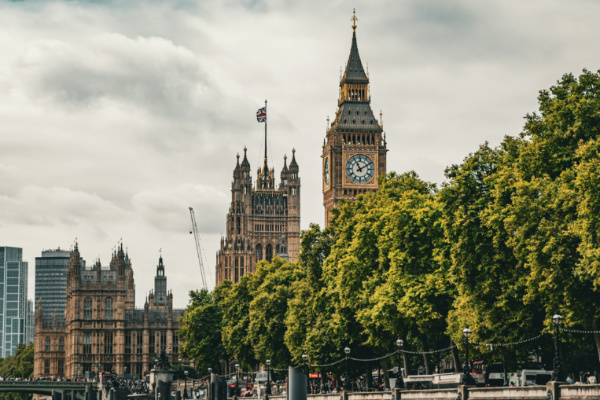

Looking south towards the Houses of Parliament from the River Thames.
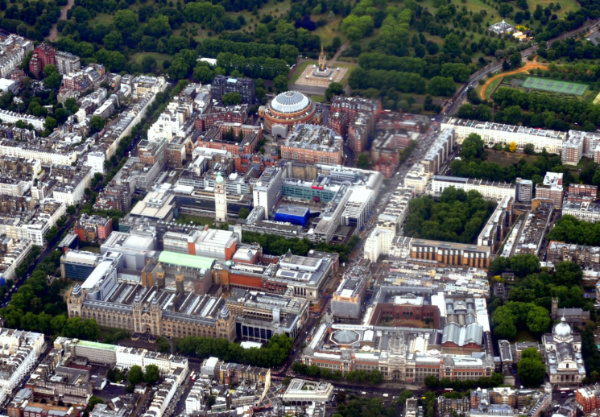

A nickname, connected to Prince Albert (beloved husband of Queen Victoria), which was given to an area of South Kensington centred on Exhibition Road which is packed with various cultural and educational institutions.
The land, which had been the Kensington Gore Estate, was purchased by the Royal Commission for the Exhibition of 1851 on the suggestion of Prince Albert using the profits made from the Great Exhibition which had been held just to the north in Hyde Park. His vision was for arts and science quarter which included schools, colleges and libraries as well as museums, exhibition rooms and spaces for events.
Among the buildings subsequently constructed upon it were those bearing Prince Albert’s name including Royal Albert Hall and the Victoria and Albert Museum along with the huge Albert Memorial.
Other institutions on the land include the Natural History Museum, Imperial College London, the Royal College of Music, the Royal College of Art, the Science Museum, the Royal Geographical Society and the since removed Royal Horticultural Society Gardens.
The area gained its nickname in the 1850s due to the Prince’s role in the Great Exhibition and its subsequent purchase and was seen to both celebrate, but also by some, to satirise him. It fell out of use after the Prince’s death in 1861 but was subsequently revived in the 1960s and since to bring attention to buildings in the area threatened with demolition.
A pedestrian subway under Exhibition Road runs north from South Kensington Station and gives access to the museums (when it was built in 1885, a toll of one penny was charged to use it).
• A new exhibition exploring the life of one of the City of London’s most famous Lord Mayors has opened at the City of London’s Guildhall Library. Marking the library’s 600th anniversary, Whittington, the Man, the Myth and the Cat uses chapbooks (small printed booklets used for street literature in early modern Europe), children’s books, and works relating to pantomimes, to investigate Whittington’s story (including the question of whether or not he owned a cat). The exhibition details Whittington’s “rags to riches” tale and the many myths that later grew up around him, revealing information about his many loans to to kings (Richard II, Henry IV and Henry V), how he was three times Lord Mayor of London (1397, 1406 and 1419) and how he paid for the building of public lavatories at St Martin Vintry and a refuge for unmarried mothers at St Thomas’ Hospital as well as the rebuilding of Newgate Prison, and the establishment of the first library at Guildhall. Addressing the myth of the Whittington’s cat, it explains how it may have come about as a result of a play on words – ‘cat’ (or cattes) being a word used to describe a fleet of boats used for importing and exporting which was a mistranslation of the French word, ‘achat’, for trade. The exhibition, which runs until April next year, is free to visit. For more, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/services/libraries/guildhall-library.
• The first exhibition in almost 20 years to focus on Francis Bacon’s portraits opened at the National Portrait Gallery, off Trafalgar Square, this week. Francis Bacon: Human Presence charts the artist’s career through 50 of his works arranged in five sections – ‘Portraits Emerge’, ‘Beyond Appearance’, ‘Painting from the Masters’, ‘Self Portraits’, and ‘Friends and Lovers’. Works on show include self-portraits as well as Head VI (1949), Study for a Pope I (1961), Three Studies for a Portrait of Isabel Rawsthorne (1965) and Portrait of a Man Walking Down Steps (1972). The exhibition also includes photographic portraits and film of Bacon by some of the century’s leading photographers, including Cecil Beaton, Arnold Newman, and Bill Brandt. Can be seen until 19th January. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.npg.org.uk.

• A Canadian marine conservation photojournalist, Shane Gross, has won this year’s Wildlife Photographer of the Year competition for an image capturing the magical underwater world of western toad tadpoles. The Swarm of Life is among 100 prize-winning images which are going on show at the Natural History Museum in South Kensington from tomorrow as it celebrates the 60th year of its Photographer of the Year competition. This year’s contest attracted a record-breaking 59,228 entries from 117 countries and territories. Among the other images on display are German Alexis Tinker-Tsavalas’ Life Under Dead Wood depicting the fruiting bodies of slime mould with a tiny springtail (Tinker-Tsavalas won Young Wildlife Photographer of the Year). Wildlife Photographer of the Year is developed and produced by the Natural History Museum, London. The exhibition runs until 29th June. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.nhm.ac.uk/wpy.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com
We return to the Tower of London this week to look at the history of another of its storied towers.
Support out work and subscribe for just £3 a month for full access to the site.
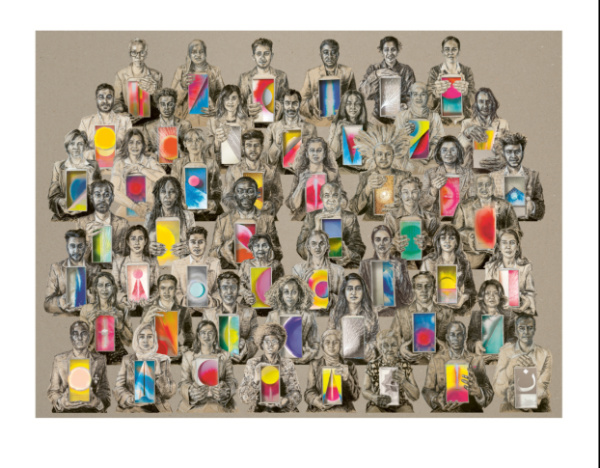

CONGREGATION, a new large-scale installation by Es Devlin, can be seen at the church of St Mary Le Strand – but you’ll have to be quick, it’s only there for two more days (until 9th October). The work, curated by Ekow Eshun, was created in partnership with UK for UNHCR, the United Nations Refugee Agency, and was developed in collaboration with King’s College London and The Courtauld. Created over four months, it features chalk and charcoal portraits of 50 Londoners who have experienced forced displacement from their homelands. Ranging in age from 18 to 90, these “co-authors” have roots in countries ranging from Syria to Sri Lanka; from Rwanda to Albania. An accompanying soundscape has been composed by Polyphonia and features the voices of the sitters while film sequences have been created in collaboration with filmmaker Ruth Hogben and choreographer Botis Seva. CONGREGATION is free to visit and is open to the public daily from 11am till 9pm with free public choral performances outside the church at 7pm each evening to coincide with Frieze London. To book tickets, head to https://www.unrefugees.org.uk/esdevlin-congregation/.

London is filled with bollards designed to prevent vehicles, old and new, from travelling where they shouldn’t. And, of course, there’s much debate over which is the oldest.
The oldest may well be a rather rusty looking one in the courtyard outside the Church of St Helen’s Bishopsgate.
In what was a practice replicated elsewhere in the City around the time, it’s apparently made out of the French naval cannon dating from the 18th century.
The cannon’s muzzle end has been embedded into the pavement with the non-loading end sticking up.
Legend says that another cannon bollard, located just outside the Globe Theatre on South Bank, comes from French ships captured at the Battle of Trafalgar. While it is indeed said to be a cannon, many have cast doubt on its origins as coming from Trafalgar.
Correction: We’ve correct the story to say it was the non-loading end sticking up.
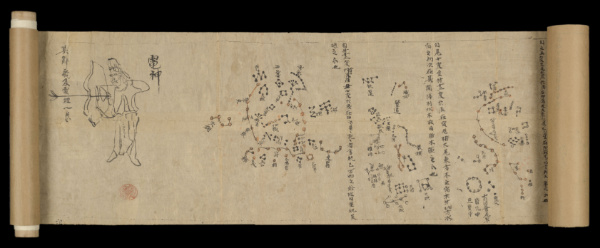
• The world’s earliest complete printed book with a date, the earliest known manuscript atlas of the night sky and the earliest surviving historical document in Tibetan are among treasures on show in a new exhibition at the British Library. A Silk Road Oasis: Life in Ancient Dunhuang features more than 50 manuscripts, printed documents and pictorial works including many which were sealed in the so-called ‘Library Cave’ in the Buddhist Mogao cave complex near the oasis town of Dunhuang in Gansu province, China, for almost 900 years before they were rediscovered in 1900. Highlights in the display include the Diamond Sutra (868 AD) – the world’s earliest complete printed book with a date, the Dunhuang star chart (649-700) – the earliest known manuscript atlas of the night sky (pictured), and the Old Tibetan Annals (641-761) – the earliest surviving historical document in Tibetan. On public display for the first time is a rubbing of the Stele of Sulaiman – a carved stone slab that was erected in the caves in 1348, a copy of the Diamond Sutra written in the scribe’s own blood (considered by Buddhists to be an act of powerful sincerity), and one of the most important and complete manuscripts among the Old Uyghur Manichaean texts, the Xuastuanift. There is also a 9th century manuscript fragment about the prophet Zoroaster or Zarathustra (believed to be nearly 400 years older than any other surviving Zoroastrian scripture) and the longest surviving manuscript text in the Old Turkic script, a Turkic omen text known as the Irk Bitig or Book of Omens (930 or 942). The exhibition, which explores Silk Road interactions through a case of characters including a scribe, merchant and Buddhist nun, runs until 23rd February and is accompanied by a programme of events. Admission charge applies. For more, see https://silkroad.seetickets.com/timeslots/filter/a-silk-road-oasis-life-in-ancient-dunhuang
• Alderman Alastair King has been elected the 696th Lord Mayor of London. King, who succeeds Lord Mayor Professor Michael Mainelli, takes office on 8th November for a one year term with the annual Lord Mayor’s Show, which takes place the following day, his first public event. “It is a tremendous honour to be elected as the 696th Lord Mayor of the City of London,” the Lord Mayor-elect, whose role will see him serving as a global ambassador for the UK financial and professional services industry, said. “London remains the world’s leading financial centre, but global competition is fierce. We have the expertise and talent to thrive, yet we must do more to unlock growth, equip people to innovate, and harness the remarkable dynamic diversity that makes the City exceptional.”
• An “unfiltered” look at the early Emo scene in the UK is the subject of a new exhibition at the Barbican Music Library. I’m Not Okay (An Emo Retrospective), a collaboration between the library and the Museum of Youth Culture (MOYC), features personal photos taken on early digital and phone cameras and focuses on the first-generation Emo scene (2004-2009), a time when bands such as My Chemical Romance, Fall Out Boy, and Finch were “hugely influential”. Jamie Brett, creative director at the MOYC said the Emo scene “resonated deeply with teens who wanted to express their angst, doubts, insecurity, and sense of feeling and being different, and channelled their collective melancholy into a transatlantic subculture”. The exhibition, which is free to enter, can be seen until 15th January. For more, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/services/libraries/barbican-music-library.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
Part of the deconsecrated Church of St Mary-at-Lambeth – now the home of the Garden Museum, is a tower which was first built in the 14th century.
Support our work and subscribe for just £3 a month to see all of Exploring London’s content

The ‘Little Cloud World’ installation by Samuel Borkson and Arturo Sandoval III – aka FriendsWithYou, which has been in Covent Garden’s Market Building since the start of August, ends today. Launched in partnership with charity CALM (Campaign Against Living Miserably), the 40 inflatable clouds were about spreading a message of “spreading kindness, positivity and helping others”. For more, see www.coventgarden.london/experience/things-to-do/little-cloud-world/.
This almost 180-year-old pub, located in the heart of Little Venice, sits in a row of Grade II-listed terraced houses.
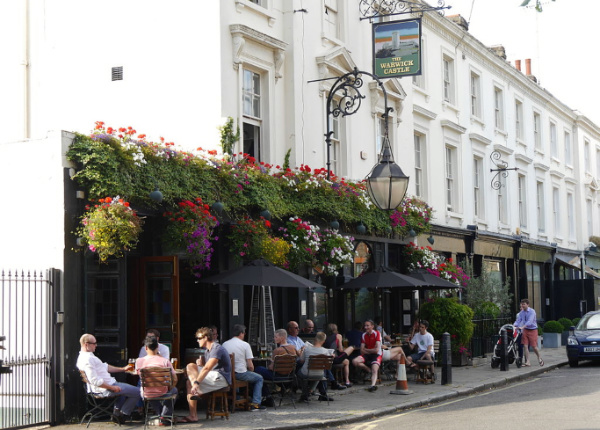

Built in 1847, both it and the name of Warwick Place where it is located as well as nearby Warwick Avenue apparently take their name from Jane Warwick, of Warwick Hall near Carlisle.
It’s all a bit convoluted, but in 1778 she had married into the family that had originally leased the land on which they stand from the Bishop of London.
The pub, which still has original features including its exterior lamp and sign brackets, appeared in journalist Maurice Gorham’s books The Local (1939), and Back to the Local (1949), both of which feature illustrations of the pub by the local artist Edward Ardizzone (the pub featured on the cover of the second book).
Regulars have reportedly included Welsh drug smuggler and Mr Nice author Howard Marks, billionaire Richard Branson and musician Rick Wakeman.
For more on the pub at 6 Warwick Place, see https://www.warwickcastlemaidavale.com.
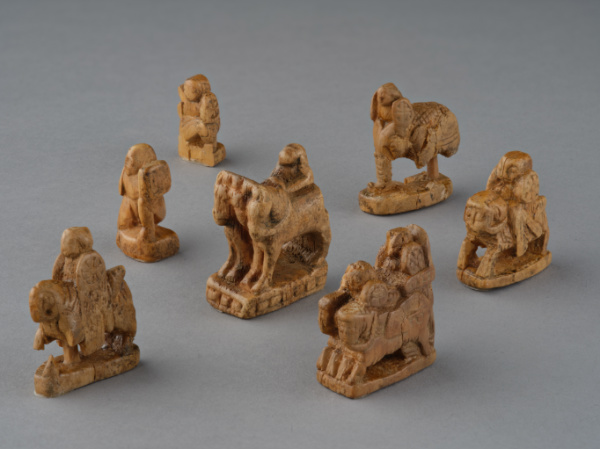

• The popular concept of the ‘Silk Road’ as a simple history of trade between East and West is challenged in a new exhibition which opens at the British Museum today. Silk Roads, which spans the period from about 500 AD to 1,000 AD, explores the overlapping networks which linked communities ranging from the UK to Japan and Scandinavia to Madagascar through a display organised into five geographic zones. The exhibition features more than 300 objects which include the oldest group of chess pieces ever found (pictured), a six metre long wall painting from the ‘Hall of the Ambassadors’ in what is now Samarkand in Uzbekistan, a glass drinking horn from Italy dating from between 550 and 600 AD, and, a map of the world from al-Idrisi’s Nuzhat al-mushtaq fi ikh0raq al-afaq (Pleasure of He who Longs to Cross the Horizons) from a 1533 manuscript which drew on a 1154 original. Visitors will also encounter the stories of people whose stories intertwined with the Silk Roads including Willibald, a balsam smuggler from England, and a legendary Chinese princess her shared the secrets of silk farming with her new kingdom. The display in the Sainsbury Exhibitions Gallery can be seen until 23rd February. Admission charge applies. For more, see britishmuseum.org/silkroads.
• The psychological dimensions of war are explored in a major new temporary exhibition at the Imperial War Museum in Lambeth. War and the Mind features more 150 objects spanning the period from World War I through to the War in Afghanistan. Among them are a letter from Winnie the Pooh author AA Milne which speaks of how dedicated pacifists have changed their mind in the face of direct threat, amphetamine tablets issued to Allied soldiers to help them overcome the psychological effects of fatigue, a newly-acquired mitten belonging to the baby son of an Avro Lancaster bomber rear gunner who carried it for comfort while carrying out operations during the World War II, and a Protect and Survive booklet issued in the UK in 1980 as part of the government’s response to the fear of nuclear weapons during the Cold War. The exhibition, which opens on Friday, is free to visit. For more, see iwm.org.uk/events/war-and-the-mind.
• The artwork of painter, illustrator and caricaturist Sidney Sime is the subject of a new exhibition at the Heath Robinson Museum in Pinner. Sime, who was born in Manchester in 1865, trained at the Liverpool school of art before heading to London where he worked for magazines including Pick-Me-Up, drawing theatrical caricatures and other humorous drawings. He later struck up a friendship with Lord Dunsany and illustrated his first book, The Gods of Pegana, in a collaboration which continued until the 1930s. He also formed friendships with Lord Howard de Walden and composer Joseph Holbrooke, making set and costume designs for their theatrical and operatic productions. After World War I, Sime made a number of large oil paintings, many of which are shown in the display. The Art of Sidney H Sime, Master of Fantasy, which opens on Saturday, can be seen until 5th January. For more, see www.heathrobinsonmuseum.org/whats-on/sidney-sime-artist-and-philosopher/.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
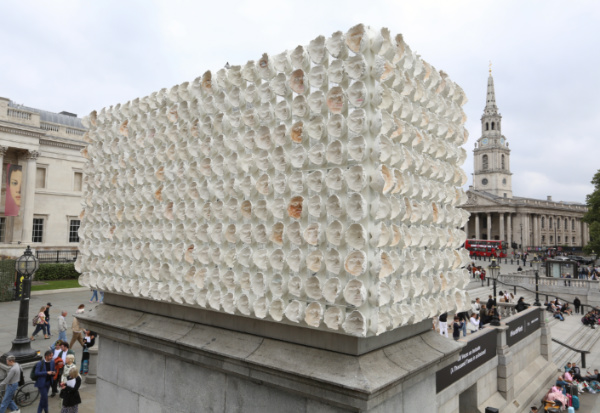

The 15th commission in Mayor of London’s Fourth Plinth programme has been unveiled in Trafalgar Square.
Artist Teresa Margolles’ Mil Veces un Instante (A thousand times an Instant) is made up of plaster casts of the faces of 726 trans, non-binary, and gender non-conforming people which were made in Mexico City and Juárez, Mexico; and London.
The casts – which Margolles spent more than 1,000 hours making – were created by applying plaster directly onto the faces of participants, meaning the plaster is infused with their hair and skin cells.
The next artworks to grace the Fourth Plinth will be Tschabalala Self’s Lady in Blue – a bronze work patinated with Lapis Lazuli blue which will be installed in 2026 – and Andra Ursuţa’s Untitled – a shrouded equestrian statue which will be installed from 2028.
Mil Veces un Instante replaced Samson Kambalu’s Antelope which had been on the Fourth Plinth since 2022.
For more on the Fourth Plinth programme, head to https://www.london.gov.uk/programmes-strategies/arts-and-culture/current-culture-projects/fourth-plinth-trafalgar-square. You can also download the free arts and culture app Bloomberg Connects.
It was on 18th September, 1954 – 70 years ago this month – that archaeologists working on a site in central London discovered one of the greatest archaeological finds in London of the 20th century – a head of Mithras in the remains of a mid-3rd century Roman temple.
Support our work and subscribe for just £3 a month to get full access to our stories.

• The V&A in South Kensington is celebrating the 100th anniversary of its Theatre and Performance collections with Enthoven Unboxed: 100 Years of Collecting Performance, which opened last weekend. The exhibition commemorates the 1924 donation of more than 80,000 playbills, programmes, and ephemera from collector, humanitarian, and campaigner Gabrielle Enthoven. Highlights among the objects on display include John Pasch’s artwork featuring the original Rolling Stones tongue and lips, a pair of semi-quaver spectacles worn by Elton John during his 1981-2 British and world tours, a self-portrait bust by 18th century actress Sarah Siddons, a set model designed by Misty Buckley for Stormzy’s headline set at Glastonbury Festival in 2019, and, a prompt script used by Phoebe Waller-Bridge for Fleabag in the West End. The free display can be seen in the Theatre and Performance Galleries (Rooms 103-106) until 4th January. For more., see www.vam.ac.uk,
• Diana Beck, the first female neurosurgeon in Britain, has been honoured with an English Heritage Blue Plaque. Unveiled earlier this month, the plaque marks the site of her former home and consulting rooms at 53 Wimpole Street in Marylebone. Beck lived at the property from 1948 to 1954, a period during which she created and ran a neurosurgical department at Middlesex Hospital. It was also during this period that Beck operated on her most famous patient – Winnie the Pooh author AA Milne, who had suffered a stroke in 1952. For more, see www.english-heritage.org.uk/visit/blue-plaques/
• The largest retrospective of the work of artist (and Royal Academician) Michael Craig-Martin has opens at the Royal Academy on Saturday. The exhibition in Royal Academy’s Main Galleries features more than 120 works spanning the period from the 1960s through to today and includes sculpture, installation, painting and drawing, as well as works newly created for the display. Among the highlights are the installations On the Table (1970) and An Oak Tree (1973), the large scale wall drawing in tape, Interlocked (MoMA project 1990) and the large scale painting Eye of the Storm (2003) as well as his depictions of single objects and word paintings. The exhibition runs until 10tH December. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.royalacademy.org.uk.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
A well-known landmark in Westminster, the distinctive striped brick and stone campanile of Westminster Cathedral stands 284 feet or 64 metres high.

Building of a Roman Catholic cathedral in Westminster – what would be the largest in England and Wales – was the vision of Cardinal Herbert Vaughan. Construction started in 1895 and was complete eight years later. The campanile was the final part of the building’s structure to be completed.
Conscious that the Gothic Westminster Abbey only a short distance away, architect John Francis Bentley instead designed the cathedral in a neo-Byzantine style and the plans originally included two campanili or bell towers which may have been influenced by those in Venice (it was Cardinal Vaughn who famously said one campanile would be enough for him resulting in just one being built).
The 30 foot square dome-topped tower, like the rest of the building, was constructed of stripes of red brick and Portland stone which reflected existing residential buildings nearby.
Formally known as St Edward’s Tower, it contains the 55cwt St Edward’s Bell (named after St Edward the Confessor) which was a gift of Gwendoline, the Duchess of Norfolk, in 1910. It was cast at the Whitechapel Foundry and bears the inscription, “While the sound of this bell travels through the clouds, may the bands of angels pray for those assembled in thy church. St Edward, pray for England.”
Carved stone eagles surround the apex of the tower – a reference to St John the Evangelist (apparently patron saint of the architect) and the cross on top of the cupola is said to contain a fragment of the True Cross discovered by the Empress Helena in 326 AD.
The campanile famously appears at the end of Alfred Hitchcock’s 1940 thriller, Foreign Correspondent, in a scene in which the bad guy is thrown from the top.
The campanile, which has a lift to the top, is open to the public. Viewing balconies on all four sides of the tower provide 360 degree views of the surrounding city including over the stunning domes of the cathedral itself.
WHERE: The Campanile, Westminster Cathedral (nearest Tube stations are Victoria and St James’s Park); WHEN: 11am to 3:30pm Fridays, Saturdays and Sundays; COST; £6 adults; £12 families (two adults and up to four children); £3 concessions (aged 60+); WEBSITE: https://westminstercathedral.org.uk/tower-viewing-gallery-reopens/
This tower – said to be the oldest building in Hackney – is all that remains of a 16th century church and, as a local symbol, appears on the London Borough of Hackney’s coat-of-arms.
Support our work and subscribe for just £3 a month – less than the price of a cup of coffee – to see all of Exploring London’s content.
