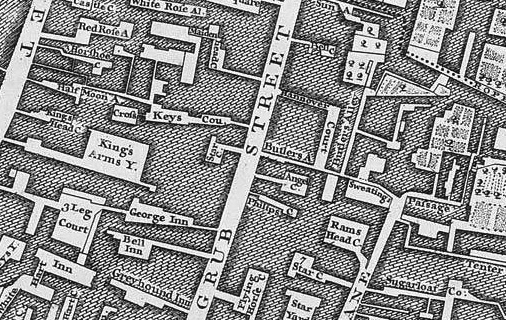
• Carved stone inscriptions, medieval manuscripts and early printed works are among items on display in a new exhibition looking at the act of writing and its impact on human civilisation at the British Library. Writing: Making Your Mark spans five millennia and five continents and includes writing examples from more than 30 writing systems including Greek, Chinese and Arabic. Highlights include an 1,800-year-old ancient wax tablet, early 19th century Burmese tattooing instruments, the final diary entry of Antarctic explorer Captain Robert Falcon Scott, James Joyce’s notes for Ulysses, Caxton’s 1476-7 printing of The Canterbury Tales – the first book printed in England, and the personal notebooks of Elizabethan explorer Sir Walter Raleigh (pictured). There’s also a 60,000 signature petition from 1905 protesting the first partition of Bengal, Mozart’s catalogue of his complete works from 1784-1791 featuring his handwriting and musical notation, and Alexander Fleming’s notebook in which he recorded his discovery of penicillin in 1928. A programme of events accompanies the exhibition which runs until 27th August. Admission charge applies. For more see www.bl.uk. PICTURE: © British Library.
• Carved stone inscriptions, medieval manuscripts and early printed works are among items on display in a new exhibition looking at the act of writing and its impact on human civilisation at the British Library. Writing: Making Your Mark spans five millennia and five continents and includes writing examples from more than 30 writing systems including Greek, Chinese and Arabic. Highlights include an 1,800-year-old ancient wax tablet, early 19th century Burmese tattooing instruments, the final diary entry of Antarctic explorer Captain Robert Falcon Scott, James Joyce’s notes for Ulysses, Caxton’s 1476-7 printing of The Canterbury Tales – the first book printed in England, and the personal notebooks of Elizabethan explorer Sir Walter Raleigh (pictured). There’s also a 60,000 signature petition from 1905 protesting the first partition of Bengal, Mozart’s catalogue of his complete works from 1784-1791 featuring his handwriting and musical notation, and Alexander Fleming’s notebook in which he recorded his discovery of penicillin in 1928. A programme of events accompanies the exhibition which runs until 27th August. Admission charge applies. For more see www.bl.uk. PICTURE: © British Library.
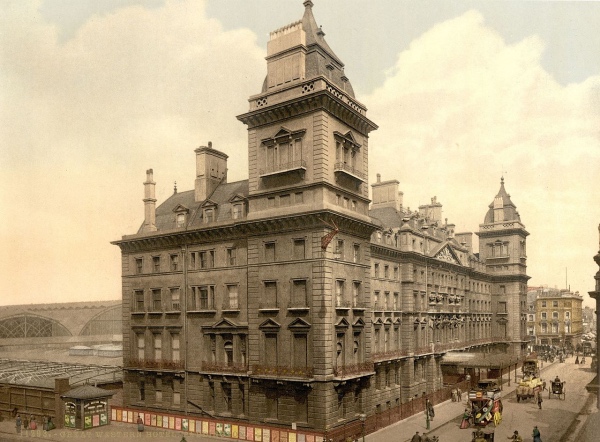
• London’s forgotten rivers, tunnels, sewers, deep shelters, and the world’s first subterranean railway are all explored in a new free exhibition at the London Metropolitan Archives in Clerkenwell. Under Ground London in part celebrates the 200th anniversary of the birth of Victorian engineer Sir Joseph Bazalgette – who designed the scheme to overhaul the city’s sewers in the 19th century. As well as Bazalgette’s landmark work, the exhibition explores the legend of a cobbled street buried beneath today’s Oxford Street and tells the story of the Thames Tunnel which, when it opened in 1843, was the world’s first tunnel under a river. There’s also information on London’s ‘ghost stations’, including Strand and King William Street; and the Metropolitan Railway – the world’s first underground railway as well as images of the River Fleet, displayed for the first time. The display can be seen until 31st October. For more, follow this link.
• Women artists working in Britain in the past 60 years are being celebrated in a new display at the Tate Britain in Millbank. Sixty Years features about 60 works spanning painting, photography, sculpture, drawing and film and includes many recent acquisitions. Artists whose works are on show include Mona Hatoum, Sarah Lucas, Bridget Riley, Mary Martin and Anthea Hamilton. Highlights include Gillian Wearing’s film Sacha and Mum (1996), Susan Hiller’s large scale multimedia installation Belshazzar’s Feast, the Writing on Your Wall (1983-84), and two new mixed media works by Monster Chetwynd – Crazy Bat Lady (2018) and Jesus and Barabbas (Odd Man Out 2011) (2018). For more, see www.tate.org.uk/visit/tate-britain.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.






 • The first exhibition to examine the work of Dutch artist Vincent van Gogh through his relationship with Britain has opened at Tate Britain this week. Van Gogh and Britain includes more than 40 works by the artist including L’Arlésienne (1890), Starry Night on the Rhone (1888), and Sunflowers (1888). The exhibition will also feature later works by Van Gogh including two he painted while in the Saint-Paul asylum – At Eternity’s Gate (1890 – pictured) and Prisoners Exercising (1890). The exhibition shows how Van Gogh, who lived in London between 1873 and 1876 working as a trainee art dealer, responded to works by artists like John Constable and John Everett Millais and his love of British writers like William Shakespeare, Christina Rossetti and, particularly, Charles Dickens (L’Arlésienne features one of Dickens’ favourite books in the foreground). The show runs until 11th August and is being accompanied by a series of talks and other events. Admission charge applies. For more, see
• The first exhibition to examine the work of Dutch artist Vincent van Gogh through his relationship with Britain has opened at Tate Britain this week. Van Gogh and Britain includes more than 40 works by the artist including L’Arlésienne (1890), Starry Night on the Rhone (1888), and Sunflowers (1888). The exhibition will also feature later works by Van Gogh including two he painted while in the Saint-Paul asylum – At Eternity’s Gate (1890 – pictured) and Prisoners Exercising (1890). The exhibition shows how Van Gogh, who lived in London between 1873 and 1876 working as a trainee art dealer, responded to works by artists like John Constable and John Everett Millais and his love of British writers like William Shakespeare, Christina Rossetti and, particularly, Charles Dickens (L’Arlésienne features one of Dickens’ favourite books in the foreground). The show runs until 11th August and is being accompanied by a series of talks and other events. Admission charge applies. For more, see