
• The glamour and opulence of the Edwardian era – and the two royal couples that exemplified it – is the subject of a new exhibition opening at The King’s Gallery at Buckingham Palace tomorrow. The Edwardians: Age of Elegance takes an in-depth look at the lives of King Edward VII and Queen Alexandra, and King George V and Queen Mary, exploring not only their family interactions but their glittering social circles, travel adventures and, of course, the royal events they attended. More than 300 items are on display in the exhibition – almost half on show for the first time – with highlights including Queen Mary’s ‘Love Trophy’ Collar necklace which is on display for the first time, a Cartier crystal pencil case set with diamonds and rubies, and, a blue enamel Fabergé cigarette case featuring a diamond-encrusted snake biting its own tail which was given to King Edward VII in 1908 by his favourite mistress as a symbol of eternal love. There’s also a never-before-seen photograph of Edward wearing fancy-dress as a knight of the Order of Malta as he attended a ball celebrating Queen Victoria’s 1897 Diamond Jubilee, a previously unseen study of Sleeping Beauty by the Pre-Raphaelite artist Sir Edward Burne-Jones, and, Charles Baugniet’s After the Ball which is on show for the first time in more than a century. Runs until 23rd November. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.rct.uk.
• More than 100,000 tulip bulbs are springing to life at Hampton Court Palace for its annual Tulip Festival. The display includes an installation of 10,000 tulips in the palace’s Fountain Court, floating tulip bowls in the Great Fountain, a vintage horse cart spilling tulips in the Clock Court, free-style planting, inspired by the tulip fields of the Netherlands, in the Kitchen Garden and rare, historic and specialist varieties of tulips in the Lower Orangery. There will be daily “tulip talks” in the palace’s wine cellar exploring the history of the flower and how Queen Mary II introduced them to the palace. Runs from Friday until 5th May. Included in general admission. For more, see www.hrp.org.uk.

• The first major exhibition in 30 years dedicated to Cartier jewels and watches opens at the V&A this Saturday. Cartier, which is being held in The Sainsbury Gallery, charts the rise of the globally recognised jewellery house and how it became known as “the jeweller of kings and the king of jewellers”. The display features more than 350 objects with highlights including the Williamson Diamond brooch which was commissioned by Queen Elizabeth II in 1953 and which features the rare 23.6 carat pink Williamson diamond; the Scroll Tiara commissioned in 1902 and worn to the coronation of Elizabeth II and later by Rihanna on the cover of W magazine in 2016; Grace Kelly’s engagement ring (1956) that she wore in her final film High Society; Mexican film star María Félix’s snake necklace (1968); and, a selection of Cartier timepieces that embody its pioneering approach to watchmaking, including the Crash wristwatch, designed by Cartier London (1967). The exhibition runs until 16th November. Admission charge applies. For more, see vam.ac.uk/exhibitions/cartier.
Send all items to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
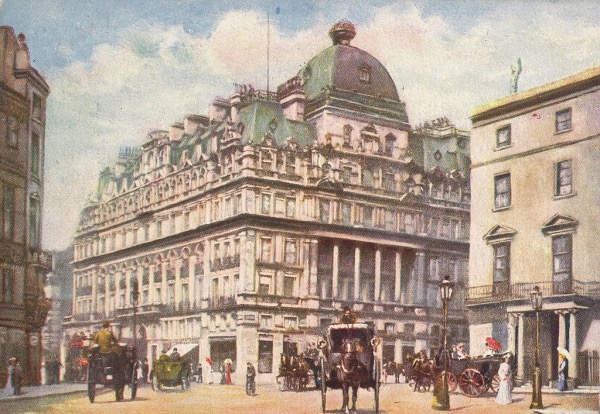
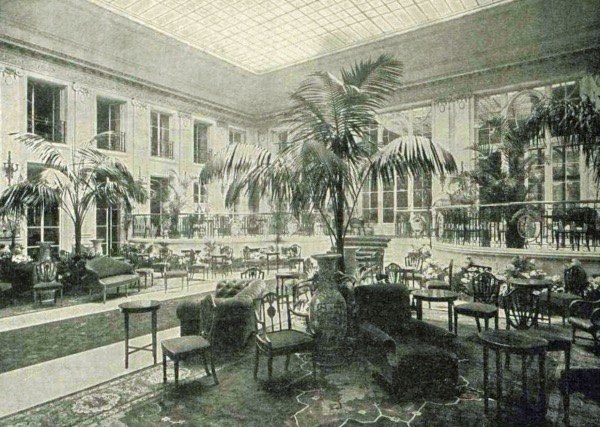





















 Another Drury Lane pub, the origins of this one go back to 1852 when it was established by Henry Wells on the site of what was once a potato warehouse.
Another Drury Lane pub, the origins of this one go back to 1852 when it was established by Henry Wells on the site of what was once a potato warehouse. 





