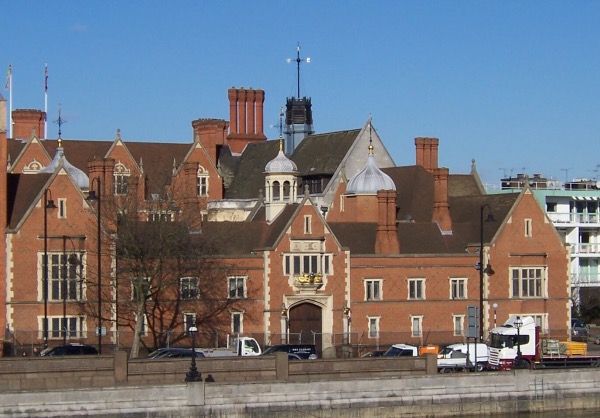
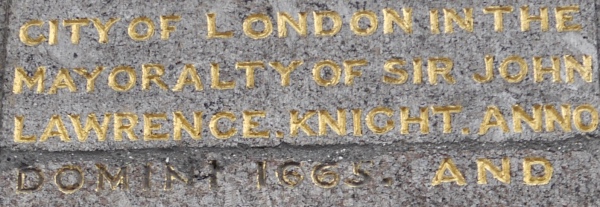This hall was originally constructed in Bishopsgate as the great hall at the heart Crosby Place, the mansion of wealthy merchant and courtier Sir John Crosby.
Built over the decade from 1466 to 1475 on land which had previously been part of St Helen’s Convent, the property became famous for royal connections.
Richard, Duke of Gloucester, had apparently acquired the property from Sir John’s widow by 1483 and it was one of his homes when the Princes in the Tower – Edward V and his younger brother Richard – were murdered, leading to his coronation as King Richard III (as a result the hall is the setting for several scenes in Shakespeare’s Richard III).
 Catherine of Aragon, meanwhile, resided in the hall with her retinue after she arrived from Spain on her way to marry Prince Arthur, King Henry VII’s eldest son and then heir (and King Henry VIII’s older brother).
Catherine of Aragon, meanwhile, resided in the hall with her retinue after she arrived from Spain on her way to marry Prince Arthur, King Henry VII’s eldest son and then heir (and King Henry VIII’s older brother).
The property was later – in the 1530s – owned by Sir Thomas More (although he probably never lived here), and subsequently, from about 1576 to 1610 by Sir John Spencer, a Lord Mayor of London (Queen Elizabeth I was apparently among his guests) while Sir Walter Raleigh had lodgings here in 1601.
It served as head office of the East India Company from 1621 to 1638 and, having survived the Great Fire of London, was used in various capacities including as a Presbyterian Meeting House and for various commercial uses, including as a warehouse and restaurant.
In 1908, it was bought by the Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China who wanted to build new offices on the site. The hall was saved from demolition and in 1910 moved stone-by-stone and, under the eye of Walter Godfrey, reconstructed on its present location in Cheyne Walk in Chelsea, a Thames-side site which had formerly been part of Sir Thomas More’s Chelsea garden which was provided by the London County Council.
Having been used to house Belgian refugees during World War I, it was formerly opened by Elizabeth, Duchess of York (later the Queen Mother), in 1926.
Around that time, the property was leased by the British Federation of University Women which had WH Godfrey build a tall Arts and Crafts residential block at right angles to the great hall (the residential block has subsequently bene adapted to appear Jacobean to fit with the hall).
The now Grade II*-listed hall – which, although not complete, is the only surviving example of a City of London medieval merchant’s house – was purchased by philanthropist and businessman Sir Christopher Moran in 1988 and is now part of an expansive private residence designed with the hall as its centrepiece (recent visitors have included Prime Minister Boris Johnson).
PICTURES: Top – sarflondondunc (licensed under CC BY-ND-NC 2.0/Image cropped); Right- Matt Brown (CC BY 2.0/Image cropped)