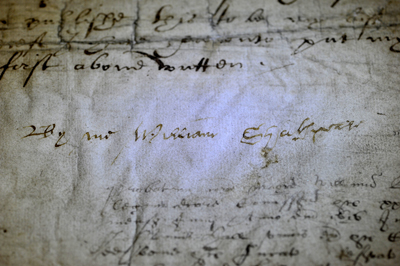Looking down Shaftesbury Avenue, the heart of London’s Theatreland, in the West End. PICTURE: Pedro Szekely/Flickr/CC BY-SA 2.0
West End
London Pub Signs – The Salisbury, St Martin’s Lane…
This popular Covent Garden pub lies in the heart of London’s Theatreland and is noted for its popularity with actors.
 Located at 90 St Martin’s Lane, the pub was built in the late 1800s on the site of an earlier public house which had been known under various different names including The Coach & Horses and Ben Caunt’s head (the latter after the famed bare knuckle fighter when the pub apparently hosted such bouts).
Located at 90 St Martin’s Lane, the pub was built in the late 1800s on the site of an earlier public house which had been known under various different names including The Coach & Horses and Ben Caunt’s head (the latter after the famed bare knuckle fighter when the pub apparently hosted such bouts).
It was first named the Salisbury Stores – an ‘SS’ motif can still be seen in some of the glasswork, with the origins of the name coming from the fact that the site was leased from Robert Cecil, Lord Salisbury, who was thrice PM in the late 19th and early 20th century, in about 1899.
The Cecil family’s coat-of-arms can be seen above the door on the corner of St Martin’s Lane and St Martin’s Court (Cecil Court is located nearby).
The now Grade II-listed Taylor Walker pub, which dropped the ‘Stores’ off its name in the 1960s, was restored in the mid-20th century and again at the end. It features original etched glass, hand-carved mahogany woodwork and art nouveau candelabra.
The pub, which, as well as its association with actors, has also long had an association with the gay community in London, has appeared in numerous films including Dirk Bogarde vehicle Victim and Travels With My Aunt as well as, in more recent times, The Boat That Rocked.
For more, see www.taylor-walker.co.uk/pub/salisbury-covent-garden/c3111/.
PICTURE: Garry Knight – Flickr/CC BY 2.0
This Week in London – Commemorating the Battle of the Somme; Transported by Design; and, Winifred Knights at Dulwich…
 • The Imperial War Museum in Lambeth is holding a free late night opening tonight featuring live music, film screenings, immersive theatre and poetry to mark the 100th anniversary of the Battle of the Somme. Highlights of Night Before the Somme, which runs from 8pm to midnight tonight, include slam poet Kat Francois’ critically acclaimed play Raising Lazarus, poet and broadcaster Ian McMillan’s show Magic Lantern Tales, and extracts from the immersive production Dr Blighty – which tells the story of the million Indians who travelled to fight in the war. Visitors will also have the chance to watch the film, The Battle of the Somme (filmed and screened in 1916, it was the first feature-length documentary about war), listen in to a series of Q&A’s with experts on the battle, and preview the major exhibition, Real to Reel: A Century of War Movies. Real to Reel, which officially opens on Friday, explores how film-makers have found inspiration in compelling personal stories and the real events of wars from the past century. As well as audio-visual installations, the display features film clips, costumes, props, scripts, sketches and designs from films such as The Dam Busters, Where Eagles Dare, Apocalypse Now, Battle of Britain, Das Boot, Casablanca, Jarhead, Atonement and War Horse along with original archival material and artefacts from the IWM collections. The exhibition, which is divided into five sections, runs until 8th January. Admission charges apply. See www.iwm.org.uk for more. PICTURE: © IWM (Q 70164. Staged scene from The Battle of the Somme film, 1916 British troops go ‘over the top’ into ‘No Man’s Land’. This scene was staged for the camera at a training school behind the lines.
• The Imperial War Museum in Lambeth is holding a free late night opening tonight featuring live music, film screenings, immersive theatre and poetry to mark the 100th anniversary of the Battle of the Somme. Highlights of Night Before the Somme, which runs from 8pm to midnight tonight, include slam poet Kat Francois’ critically acclaimed play Raising Lazarus, poet and broadcaster Ian McMillan’s show Magic Lantern Tales, and extracts from the immersive production Dr Blighty – which tells the story of the million Indians who travelled to fight in the war. Visitors will also have the chance to watch the film, The Battle of the Somme (filmed and screened in 1916, it was the first feature-length documentary about war), listen in to a series of Q&A’s with experts on the battle, and preview the major exhibition, Real to Reel: A Century of War Movies. Real to Reel, which officially opens on Friday, explores how film-makers have found inspiration in compelling personal stories and the real events of wars from the past century. As well as audio-visual installations, the display features film clips, costumes, props, scripts, sketches and designs from films such as The Dam Busters, Where Eagles Dare, Apocalypse Now, Battle of Britain, Das Boot, Casablanca, Jarhead, Atonement and War Horse along with original archival material and artefacts from the IWM collections. The exhibition, which is divided into five sections, runs until 8th January. Admission charges apply. See www.iwm.org.uk for more. PICTURE: © IWM (Q 70164. Staged scene from The Battle of the Somme film, 1916 British troops go ‘over the top’ into ‘No Man’s Land’. This scene was staged for the camera at a training school behind the lines.
• Don’t forget tonight’s vigil at Westminster Abbey to mark the 100th anniversary (as mentioned in last week’s entry here).
• Still on the centenary of the Battle of the Somme and a new exhibition opened at the Science Museum in South Kensington this week focusing on the innovations in medical practice and technologies developed as a result of the new kind of industrialised warfare seen in the battle. Wounded: Conflict, Casualties and Care has at its centre a collection of historic objects from the museum’s World War I medical collections including stretchers adapted for use in narrow trenches and made-to-measure artificial arms fitted to the wounded in British hospitals as well as lucky charms and personal protective items carried by frontline soldiers. There are also artworks from the period including Henry Tonk’s famous pastel drawings of facial injuries and a 1914 painting by John Lavery that depicts the arrival of the first British wounded soldiers at the London hospital. Admission is free and the exhibition can be seen until early 2018. For more, see www.sciencemuseum.org.uk.
• Regent Street will be transformed on Sunday, 3rd July, with the Transported by Design Festival featuring transport designs which have shaped and will shape London. The festival, which will stretch from Piccadilly Circus to Oxford Circus Tube stations, will see the street divided into three zones – past, present and future. Among the objects on show in ‘past’ section will be a horse-drawn bus and other heritage buses, a 1927 train carriage and an exhibition of classic advertising posters and signage while the ‘present’ section will feature ‘Cycle Spin Fun’ by Santander Cycles, Moquette Land – a showcase of fabric used across the transport network, and, a ‘design a bus’ competition, and the ‘future’ section will feature a range of technologies, including virtual reality headsets, exploring what transport could look like in 2040. The free festival, part of the ‘Summer Streets’ program which sees Regent Street closed to traffic on Sundays over summer, runs from noon to 6pm. For more, see www.tfl.gov.uk/campaign/transported-by-design/event-calendar?intcmp=40582.
• The work of artist Winifred Knights, the first British woman to win the Prix de Rome scholarship, is the subject of a recently-opened exhibition at the Dulwich Picture Gallery. The display, the first major retrospective of the work of Knights (1899-1947), brings together more than 70 preparatory studies and her most ambitious works including The Deluge (1920), The Potato Harvest (1918) and Leaving the Munitions Works (1919). Winifred Knights (1899-1947) runs until 18th September. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.dulwichpicturegallery.org.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
Lost London – Exeter/Essex House…
Located on the south side of the Strand, the then-named Exeter House was built in the 1300s as the London palace of the Bishops of Exeter on land which had previously been occupied by the Knights Templar.
 It was Bishop Walter Stapledon who had the palace constructed – as well as being Bishop of Exeter, he was Lord High Treasurer to the unpopular King Edward II, a role which eventually led to him being dragged from his horse in the City of London and murdered.
It was Bishop Walter Stapledon who had the palace constructed – as well as being Bishop of Exeter, he was Lord High Treasurer to the unpopular King Edward II, a role which eventually led to him being dragged from his horse in the City of London and murdered.
King Henry VIII gave the property to his Secretary of State, William, Lord Paget, and, in the late 16th century, it came into the hands of Robert Dudley, the 1st Earl of Leicester. He rebuilt it and renamed it Leicester House which it remained until, following his death in 1588, it was inherited by his stepson, Robert Devereux, the 2nd Earl of Essex and a favourite of Queen Elizabeth I, and renamed Essex House.
The house was rather large and in 1590 was reported as having as many as 42 bedrooms as well as a picture gallery, a banqueting suite and chapel.
Devereux ended up beheaded for treason on Tower Hill in 1601 but his son, also Robert Devereux, became a distinguished general for the Parliamentarians during the Civil War. He received a delegation from the House of Commons at the property to offer their congratulations after the Battle of Newbury in 1643 and was laid out in state there in 1646 (insatiable diarist Samuel Pepys, then a 13-year-old boy, was among those who saw the body).
After the Civil War, the family’s debts resulted into the property passing into the hands of other families. The main part of the house was eventually demolished in the 1670s and part of the property sold to developer Nicholas Barbon. He built Essex Street, which still stands in the area, was built on the site.
The remaining part of the house, meanwhile, was used to house the Cotton Library before, in 1777, it too was demolished.
The mansion’s chapel, meanwhile, became a dissenters meeting house, known as the Essex Street Chapel, which became the birthplace of Unitarianism in England. The denomination’s headquarters, named Essex Hall, still stands on the site.
The pub The Devereux (pictured above), named for Robert Devereux, is among the buildings which now stand on the site (for more on the pub, see our earlier post here).
What’s in a name?…Fitzrovia…
 This West End district, located between Bloomsbury, Marylebone and Soho, probably owes its name to the Fitzroy Tavern, a public house which in turn is believed to owe its name to the Dukes of Grafton, whose family name was Fitzroy.
This West End district, located between Bloomsbury, Marylebone and Soho, probably owes its name to the Fitzroy Tavern, a public house which in turn is believed to owe its name to the Dukes of Grafton, whose family name was Fitzroy.
The Fitzroys (the name derives from a Norman-French phrase and was typically associated with base-born royal sons), owned land in the area until the end of the 1800s.
The family first become associated with the area after the Manor of Tottenham (more on that name in an upcoming post) came into the possession of Henry Fitzroy, an illegitimate son of King Charles II who became the Earl of Euston and later Duke of Grafton.
Incidentally, the grand Fitzroy Square, developed by the duke’s great-grandson, and Fitzroy Street are both also named after the family as are numerous other locations in the area including Grafton Street.
Fashionable as a residential area in the 1700s, the houses were gradually transformed into workshops – the area was noted for furniture-makers in particular – or cheap tenements and it’s during this period in the early 1800s that artists like John Constable were living in the area.
The name Fitzrovia apparently became popularised for the district which in the inter-war years, due to the community of artists and writers that met at the pub; it is said to have first appeared in print in the 1940s. Among those who were associated with the area during this period were the likes of writers Dylan Thomas and George Orwell and artists like Roger Fry and Augustus John.
More recently the area has become home to numerous media companies, particularly TV-related companies, and still hosts ample pubs, restaurants and cafes.
Notable buildings in the area include the BT Tower, a communications tower completed in 1964 which was until 1980, the tallest building not only in London but in the UK (and from where panoramic views could once be had – sadly it’s been long closed to the public).
Fitzrovia is also home to the quirky Pollock’s Toy Museum.
PICTURE: David Castor (caster)/Wikipedia
Correction: Fitzroy Square was developed by the great grandson of the 1st Duke of Grafton, not grandson as was originally stated.
LondonLife – Celebrating International Women’s Day…
It’s International Women’s Day, so we’re celebrating by remembering two heroic women immortalised in statues in central London. Above is Edith Cavell, a British nurse who was trapped in Brussels by advancing German armies in 1914 and then subsequently arrested for aiding French and British soldiers to escape before being executed by firing squad on 12th October, 1915 – an event widely condemned around the world. The marble statue, located in St Martin’s Place at the intersection of Charing Cross Road and St Martin’s Lane, is by George Frampton and was erected in 1920. Below, meanwhile, is a bust of Violette Szabo which tops a memorial to the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Szabo, who was posthumously awarded the George Cross and the Croix de Guerre after she was captured and eventually executed by the German Army in early 1945, was among 117 SOE agents who did not return from their missions to France. Located on Albert Embankment, the statue – which is the work of Karen Newman – was unveiled in 2009.

Treasures of London – William Shakespeare’s last will and testament…
Recently conserved by the National Archives, Shakespeare’s last will and testament is at the heart of a new exhibition on show at Somerset House.
By Me William Shakespeare: A Life In Writing, the first joint exhibition of the National Archives and King’s College London, features four of the six known signatures of Shakespeare still in existence and, along with his last will and testament, shows some of the most significant Shakespeare-related documents in the world tracking his existence as everything from a London citizen, businessman, family man, servant to possibly even a thief and subversive.
But back to the will. While not written in the Bard’s hand, the will is signed by him in three places and indicates the wealth and status he had garnered by the time of his death on 23rd April, 1616.
Evidence shows that Shakespeare revised his will as his estate changed, and just before his death, he added personal bequests including that a silver bowl be given to his second eldest daughter Judith, memorial rings to actor friends in London and his second best bed to his wife Anne. He left most of his property to his eldest daughter, Susanna, although his will, according to the National Archives, indicates that he had hoped to establish a male legacy.
Other beneficiaries named in the will include his sister Joan and her sons and his grand-daughter Elizabeth Hall while Susanna and her husband John Hall were named as his executors.
The exhibition, which is being held in the Inigo Jones Rooms in Somerset House’s East Wing as part of the series of events being held to mark the 400th anniversary of Shakespeare’s death, runs until 29th May. Admission charge applies.
Other documents featured in the display – all of which are registered with UNESCO – include accounts listing the grant of four-and-half yards of red cloth to Shakespeare by King James I for participation in his coronation procession in 1604, accounts from the Master of Revels showing when plays were performed at court (useful for helping to date when Shakespeare wrote particular plays), and a document recording testimony Shakespeare gave in court when his landlord, Christopher Mountjoy, failed to provide his son-in-law with a dowry for his daughter’s hand (Shakespeare is likely to have played a role in arranging the marriage).
For more on the exhibition, see www.bymewilliamshakespeare.org.
This Week in London – John Dee’s library; Botticelli and Dante; and, women in war at the IWM…
• John Dee (1527-1609), the enigmatic Elizabethan “mathematician, magician, astronomer, astrologer, imperialist, alchemist and spy”, is the subject of an exhibition currently running at the Royal College of Physicians Museum in Regent’s Park. Scholar, courtier, magician: the lost library of John Dee explores his life through remnants of his personal library and features mathematical, astronomical and alchemical texts, many of which he elaborately annotated and even illustrated. The texts are drawn from the collection of the college library which has more than 100 of the doctor’s volumes and which forms the largest collection of Dee’s books in the world. The books represent only a fraction of the more than 3,000 books and 1,000 manuscripts he claimed to own before his library was, so Dee claimed, sold off illicitly by his brother-in-law Nicholas Fromond after he gave them into his care when he travelled to Europe in the 1580s. Many of them apparently fell into the hands of Nicholas Saunder, possibly a former student of Dee’s and later passed into the hands of book collector Henry Pierrepont, the Marquis of Dorchester, whose family gave his entire library to the Royal College of Physicians after his death in 1680. The free exhibition runs until 29th July. For more, see www.rcplondon.ac.uk.
 • Botticelli’s drawings for Dante’s epic poem, the Divine Comedy, are at the heart of a new exhibition which opened earlier this month at the Courtauld Gallery in Somerset House. Botticelli and Treasures from the Hamilton Collection, which is being run in collaboration with the Kuperferstichkabinett (Prints and Drawings Museum) in Berlin, features treasures which were sold to Berlin by the 12th Duke of Hamilton in 1882 despite efforts by Queen Victoria to prevent the transaction. They include a selection of 30 of Botticelli’s drawings – which date from about 1480-95 – as well as illuminated manuscripts including the Hamilton Bible. Said to be one of the most important illuminated manuscripts in the world, it is being returned to the UK for the first time since 1882. The exhibition, which coincides with Botticelli Reimagined opening at the V&A next month, runs until 15th May. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.courtauld.ac.uk. PICTURE: Sandro Botticelli – Beatrice explains to Dante the order of the cosmos (Divine Comedy, Paradiso II), around 1481-1495/© Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Kupferstichkabinett/Philipp Allard.
• Botticelli’s drawings for Dante’s epic poem, the Divine Comedy, are at the heart of a new exhibition which opened earlier this month at the Courtauld Gallery in Somerset House. Botticelli and Treasures from the Hamilton Collection, which is being run in collaboration with the Kuperferstichkabinett (Prints and Drawings Museum) in Berlin, features treasures which were sold to Berlin by the 12th Duke of Hamilton in 1882 despite efforts by Queen Victoria to prevent the transaction. They include a selection of 30 of Botticelli’s drawings – which date from about 1480-95 – as well as illuminated manuscripts including the Hamilton Bible. Said to be one of the most important illuminated manuscripts in the world, it is being returned to the UK for the first time since 1882. The exhibition, which coincides with Botticelli Reimagined opening at the V&A next month, runs until 15th May. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.courtauld.ac.uk. PICTURE: Sandro Botticelli – Beatrice explains to Dante the order of the cosmos (Divine Comedy, Paradiso II), around 1481-1495/© Staatliche Museen zu Berlin, Kupferstichkabinett/Philipp Allard.
• The stories of women in times of war form the heart of a new display on show at the Imperial War Museum in Lambeth. Eleven Women Facing War features photographs and films taken by award-winning British photographer and film-maker Nick Danziger. He first photographed the 11 women, who all lived in conflict zones, in 2001 for an International Committee of the Red Cross study documenting the needs of women facing war before setting out 10 years later to find each of the women and see what had become of their lives. The exhibition features 33 photographs and 11 short films from conflict zones including Bosnia, Kosovo, Israel, Gaza, Hebron (West Bank), Sierra Leone, Colombia and Argentina. Among the stories told are those of Mah Bibi, a 10-year-old orphan who was begging for food for herself and two brothers when first photographed in Afghanistan and who, 10 years later, had vanished and is believed to have died in 2006. Another is that of Mariatu, who was struggling to rebuild her life in Sierra Leone after her hands had been forcibly amputated by guerrilla soldiers at the age of 13 when she was photographed in 2001 and who 10 years later had moved to Canada. The exhibition runs until 24th April. Admission is free. For more, see www.iwm.org.uk.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
This Week in London – Behind the scenes at London’s (and New York’s) theatres; Leonardo da Vinci’s mechanical talents; and, deeper inside the Queen’s wardrobe…
 • London’s West End “Theatreland” and New York’s Broadway are jointly the subject of a new exhibition which opened at the V&A this week. Curtain Up: Celebrating 40 Years of Theatre in London and New York takes visitors on an immersive, behind the scenes look at how award-winning plays, musicals and productions are made as well as the history of theatrical awards and life on the red carpet. Objects – taken from the V&A collection and that of The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts at Lincoln Centre – on display include Maria Bjornson’s original costume designs from The Phantom of the Opera (1986), one of the longest-running West End musicals and the longest running Broadway production in history as well as a selection of golden top hats from A Chorus Line which won both the Tony Award and the inaugural Olivier Award for Best New Musical in 1976, a tunic worn by Rudolf Nureyev in Romeo and Juliet, winner of the Olivier Award in 1977, and a dress designed by Bob Crowley and worn by Dame Helen Mirren in The Audience, a production which earned the actress both an Olivier award in 2013 and a Tony Award in 2015. The free exhibition, organised in partnership with the Society of London Theatre as part of a year long celebration of 40 years of the Olivier Award, runs until 31st August in the V&A’s Theatre and Performance Galleries before touring to The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts at Lincoln Centre later this year. For more, see www.vam.ac.uk/curtainup. PICTURE: © Victoria and Albert Museum.
• London’s West End “Theatreland” and New York’s Broadway are jointly the subject of a new exhibition which opened at the V&A this week. Curtain Up: Celebrating 40 Years of Theatre in London and New York takes visitors on an immersive, behind the scenes look at how award-winning plays, musicals and productions are made as well as the history of theatrical awards and life on the red carpet. Objects – taken from the V&A collection and that of The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts at Lincoln Centre – on display include Maria Bjornson’s original costume designs from The Phantom of the Opera (1986), one of the longest-running West End musicals and the longest running Broadway production in history as well as a selection of golden top hats from A Chorus Line which won both the Tony Award and the inaugural Olivier Award for Best New Musical in 1976, a tunic worn by Rudolf Nureyev in Romeo and Juliet, winner of the Olivier Award in 1977, and a dress designed by Bob Crowley and worn by Dame Helen Mirren in The Audience, a production which earned the actress both an Olivier award in 2013 and a Tony Award in 2015. The free exhibition, organised in partnership with the Society of London Theatre as part of a year long celebration of 40 years of the Olivier Award, runs until 31st August in the V&A’s Theatre and Performance Galleries before touring to The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts at Lincoln Centre later this year. For more, see www.vam.ac.uk/curtainup. PICTURE: © Victoria and Albert Museum.
• A visually stunning exhibition highlighting the talents of Leonardo da Vinci opened at the Science Museum in South Kensington yesterday. Leonardo da Vinci: The Mechanics of Genius takes a look at some of the unique mechanical concepts dreamt up by one of “history’s greatest minds”. The display features 39 historical models of designs da Vinci drew – including those of flying machines, diving apparatus and weapons – which were made in Milan in 1952 to mark the 500th anniversary of his birth. Runs until 4th September. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.sciencemuseum.org.uk/leonardo.
• Kensington Palace is taking you even further into the wardrobes of Queen Elizabeth II, Princess Margaret and Diana, Princess of Wales, in a new display of dresses as part of the Fashion Rules exhibition. The new display continues the exhibitions exploration of how each of the three women have navigated the fashion ‘rules’ defined by their royal duties in their own unique style. Among the dresses on display is a candy-striped dress in the “Parisian style” created by Norman Hartnell in the late 1940s for Princess Margaret – on show for the first time at the palace, as well as formal dresses worn by the Queen on state visits to France and the Middle East, and a bottle green silk velvet halterneck worn by Diana which was later made famous in images by photographer Mario Testino. The new display goes on show today. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.hrp.org.uk/kensingtonpalace.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
LondonLife – Through the archway at Covent Garden…
 A quiet moment in one of Covent Garden’s covered arcades. For more on the history of Covent Garden, see our earlier post here.
A quiet moment in one of Covent Garden’s covered arcades. For more on the history of Covent Garden, see our earlier post here.
Famous Londoners – Joseph Grimaldi…
 The most renowned of English clowns, Joseph Grimaldi rose to the heights of fame in early 19th century London despite a private life characterised by hardships and pain.
The most renowned of English clowns, Joseph Grimaldi rose to the heights of fame in early 19th century London despite a private life characterised by hardships and pain.
Grimaldi was born in Clare Market, London on 18th December, 1778, the son of actor and clown Joseph Giuseppe Grimaldi (known simply as the “Signor”), and Londoner Rebecca Brooker, a dancer who was more than 50 years younger than Grimaldi when she become one of a string of mistresses.
 Joe was groomed for the stage by his father from an early age and made his debut at Sadler’s Wells Theatre in late 1780. He was soon also working at Drury Lane Theatre, running between the two to make performances (at the same time, he did attend a theatrical academy in Putney known for educating the children of performers).
Joe was groomed for the stage by his father from an early age and made his debut at Sadler’s Wells Theatre in late 1780. He was soon also working at Drury Lane Theatre, running between the two to make performances (at the same time, he did attend a theatrical academy in Putney known for educating the children of performers).
Joe’s father died when he was just nine-years-old and he became the family’s main breadwinner and while he was still able to work at both Sadler’s Wells and Drury Lane, his pay was cut after his father’s death meaning the family had to move out of their home in Holborn and into the slum of St Giles where they took lodgings in Great Wild Street.
In 1799, having met three years before, he married Maria Hughes, the eldest daughter of Richard Hughes, the proprietor of Sadler’s Wells Theatre. The newlyweds moved to a home at 37 Penton Street in Pentonville. It was not to be a long-lasting marriage – Maria died during childbirth on 18th October, 1800.
Further hardship was to come soon after when, while performing at Drury Lane Theatre, he accidentally shot himself in his foot and was forced to bed to recover. But there was a silver lining – his mother employed a dancer, Mary Bristow, to look after him during his rehabilitation and they formed a bond which led to them being married on 24th December, 1801.
After recovering from his injury, meanwhile, he had resumed his hectic schedule at London theatres as well as country venues and it was during this period that he redesigned the way in which he painted his face – adopting a white face design still used by many clowns today – and created the iconic clown which he named simply ‘Joey’.
In 1802, his only child was born – Joseph Samuel, known simply as ‘JS’ – and from the age of 18 months, he was introduced to the theatre, making his own acting debut at Sadler’s Wells in 1814.
In 1806, Joe played what is arguably his most famous roles – as both Bugle and the Clown in Thomas Dibdin’s Harlequin and Mother Goose, which opened at the Covent Garden Theatre on 29th December, 1806, and ran for the next two years.
Financial need saw him continue to take on roles in London and elsewhere but finally, in 1823, ill health – the consequence of his many years of physically abusing his body for his act – forced him into retirement. In 1828, two farewell benefit performances were held in which he had a limited role, his last was at Drury Lane on 27th June.
The last years of his life were marked with tragedy – relations which his son were strained (and they spent years estranged) before JS died on 11th December, 1832, at just the age of 30 while his wife died in 1834.
Grimaldi spent the last years of his life living alone in Southampton Street, Islington, before he was found dead in his bed by his housekeeper on 1st June, 1837. He was buried in St James’s churchyard, Pentonville, on 5th June, 1837 – the area is now Joseph Grimaldi Park and features, as well as his grave, a coffin-shaped memorial (pictured, top) that plays musical notes when danced upon (it’s apparently possible to play his signature song, Hot Codlins when “dancing upon his grave”).
Described as being the pre-eminent entertainer of his day, Grimaldi is credited with transforming the role of the Clown in pantomime and ushering in a whole new era in the art of clowning. His legacy – still remembered by clowns everywhere – received a boost when after his death, Charles Dickens edited his memoirs in 1838.
He is remembered in an annual service held on the first Sunday in February every year in Holy Trinity Church, Hackney (the Sunday just past), an event which is attended by clowns in full get-up.
For a detailed look at the life of Grimaldi, see Andrew McConnell Stott’s The Pantomime Life of Joseph Grimaldi: Laughter, Madness and the Story of Britain’s Greatest Comedian.
This Week in London – Norway on show at Dulwich; Bruegel the Elder at the Courtauld; and, Kew Gardens celebrates the orchid…
 • The first UK show dedicated to the works of Norwegian landscape painter and printmaker, Nikolai Astrup, opens at the Dulwich Picture Gallery tomorrow. Painting Norway: Nikolai Astrup (1880-1928) features more than 120 paintings, woodcuts and archive material – many of public display for the first time. Astrup is described as one of Norway’s finest 20th century artists and long with Munch, expanded the possibilities of woodcuts to capture the wild landscapes and traditional way of life in his western Norway home. Works on show include everything from the woodcut A Clear Night in June (1905-07), the many coloured masterpiece A Night in June in the Garden (1909), and the celebratory Midsummer Eve Bonfire (1915). Runs until 15th May. Admission charges apply. The gallery is also hosting a series of related events. For more, head to www.dulwichpicturegallery.org.uk. PICTURE: Marsh Marigold Night, c.1915 – The Savings Bank Foundation DNB/The Astrup Collection/KODE Art Museums of Bergen. Photo © Dag Fosse/KODE.
• The first UK show dedicated to the works of Norwegian landscape painter and printmaker, Nikolai Astrup, opens at the Dulwich Picture Gallery tomorrow. Painting Norway: Nikolai Astrup (1880-1928) features more than 120 paintings, woodcuts and archive material – many of public display for the first time. Astrup is described as one of Norway’s finest 20th century artists and long with Munch, expanded the possibilities of woodcuts to capture the wild landscapes and traditional way of life in his western Norway home. Works on show include everything from the woodcut A Clear Night in June (1905-07), the many coloured masterpiece A Night in June in the Garden (1909), and the celebratory Midsummer Eve Bonfire (1915). Runs until 15th May. Admission charges apply. The gallery is also hosting a series of related events. For more, head to www.dulwichpicturegallery.org.uk. PICTURE: Marsh Marigold Night, c.1915 – The Savings Bank Foundation DNB/The Astrup Collection/KODE Art Museums of Bergen. Photo © Dag Fosse/KODE.
• Bruegel the Elder’s only three surviving grisaille paintings have been brought together in a new exhibition opening at the Courtauld Gallery at Somerset House today. The works, painted in shades of grey, include the Courtauld’s Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery as well as The Death of the Virgin (brought from the National Trust-managed Upton House) and Three Soldiers (borrowed from the Frick Collection in New York. They’re among the less than 40 works attributed to the artist (c1525-1569) and while The Death of the Virgin was owned by his friend, map-maker Abraham Ortelius, Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery was one of few paintings kept by the artist himself. The exhibition Bruegel in Black and White: Three Grisailles Reunited also includes replicas made by Bruegel’s sons as well as other grisailles while other works by Bruegel from the Courtauld’s collection will be displayed in the Butler Drawings Gallery. Runs until 8th May. Admission charges apply. For more, see www.courtauld.ac.uk.
• Head to Kew Gardens for a splash of colour as the annual Orchid Festival kicks off in the Princess of Wales Conservatory on Saturday. And, following the success of last year’s events, the conservatory will once again throw its doors open after dark on the 11th, 18th and 25th February and 3rd March for Orchid Lates at Kew Gardens (there’s also a special Valentine’s Late at Kew Gardens on 13th February). Admission charges apply. For more, head to www.kew.org.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
LondonLife – London in a different light…
Last weekend saw London transformed in a blaze of colour and light as the city hosted its first Lumiere light festival. More than a million people hit the streets over the four nights of the event – developed by creative producers Artichoke and supported by the Mayor of London – to take in the 30 artworks. Above are some of images of British screen stars and directors which were projected on 195 Piccadilly in an installation by Newcastle-based studio NOVAK. Below are some more images from the rather spectacular event. For more on the event, check out www.visitlondon.com/lumiere.
Above is Les Voyageurs (The Travellers) by French artist Cédric Le Borgne (located in St James) while below is Litre of Light by Mick Stephenson and Central Saint Martin’s students in Kings Cross.
Above is binaryWaves by LAB[au] while below is Ron Haselden’s Diver depicting an illuminated figure plunging into the water of the King’s Cross Pond Club.
What’s in a name?…Savile Row
Famous around the world as the home of bespoke tailoring in London, Savile Row owes its name – like so many other streets in Mayfair – to landowner Richard Boyle, the 3rd Earl of Burlington.
 Burlington (1612-98) resided at Burlington House (now home of the Royal Academy of Arts) on Piccadilly and after his death the land around his former home was developed and the streets named for Burlington and members of his family.
Burlington (1612-98) resided at Burlington House (now home of the Royal Academy of Arts) on Piccadilly and after his death the land around his former home was developed and the streets named for Burlington and members of his family.
Among them was his wife, Lady Burlington, née Lady Dorothy Savile, after whom Savile Row was named. Laid out in 1695, the street was actually located on the site of the former kitchen gardens of Burlington House and was given its name (originally Savile Street) in the 1730s.
The first to reside here were apparently mostly military and politicians (these included PM William Pitt the Younger) and it was only in the early 19th century that the first tailors started to set up shop here. With clients including society dandy Beau Brummell (see our our earlier post here) and the Prince Regent (later King George IV), the street’s fame grew rapidly and continued into the 20th century when customers included some of the biggest names in Hollywood – Cary Grant, Bing Crosby and Frank Sinatra among them.
Among the famous tailoring firms still operating in Savile Row are Anderson & Sheppard (at number 30, it’s where the Prince of Wales has his suits made), Henry Poole (at number 15, Victorian-era owner Henry Poole is credited as the inventor of the tuxedo), and Hardy Amies.
Headquartered at number 14 (with a shop at number 8), Amies gained an international reputation when appointed dressmaker to Queen Elizabeth II in 1955/the address was previously owned by the playwright Richard Brinsley Sheridan and was also the address Jules Vernes gave Phileas Fogg in Around the World in Eighty Days).
One last tailor worth a particular mention is that of Tommy Nutter, who set up shop at number 35 in the late Sixties with a nameplate out front simply reading Nutters and shocked traditionalists with his modern take on tailoring – this modern approach continues among some tailors in the street even today.
The street also has a famous claim in the story of the Beatles – the moved their company Apple Corps Company into number 3 in July, 1968, and it was on the roof of this building that they played their last live gig on 3rd January, 1969.
This Week in London – London illuminated; commemorating Shakespeare’s death; and, of bees and pollination…
 • The biggest ever light festival to hit London opens tonight. Lumber London, produced by Artichoke with the support of the Mayor of London and visitlondon.com, will see a host of international artists transform a series of iconic buildings and locations in four areas across the city – Piccadilly, Regent Street and St James’s, Trafalgar Square and Westminster, Mayfair and King’s Cross. The 30 installations include French collective TILT’s Garden of Light featuring giant illuminated plants in Leicester Square, Patrice Warrener’s The Light of the Spirit which envelopes the west front of Westminster Abbey in colour and light, Deepa Mann-Kler’s Neon Dogs – a collection of 12 neon dogs inspired by the balloon dogs seen at children’s parties, this sits near Trafalgar Square, and, Pipette, a colourful installation by Miriam Gleeman (of The Cross Kings) and Tom Sloan (of Tom Sloan Design) which sits in the pedestrian subway, the King’s Cross Tunnel. Other highlights include Julian Opie’s work Shaida Walking, 2015 which will be permanently located in Broadwick Street, Soho, and Janet Echelon’s enormous net sculpture 1.8 London which is strung between buildings at Oxford Circus. The festival runs from 6.30pm to 10.30pm over the next four nights. You can download a free map on the installations or use the free London Official City Guide app to locate them. For more information – including the full programme – see www.visitlondon.com/lumiere.
• The biggest ever light festival to hit London opens tonight. Lumber London, produced by Artichoke with the support of the Mayor of London and visitlondon.com, will see a host of international artists transform a series of iconic buildings and locations in four areas across the city – Piccadilly, Regent Street and St James’s, Trafalgar Square and Westminster, Mayfair and King’s Cross. The 30 installations include French collective TILT’s Garden of Light featuring giant illuminated plants in Leicester Square, Patrice Warrener’s The Light of the Spirit which envelopes the west front of Westminster Abbey in colour and light, Deepa Mann-Kler’s Neon Dogs – a collection of 12 neon dogs inspired by the balloon dogs seen at children’s parties, this sits near Trafalgar Square, and, Pipette, a colourful installation by Miriam Gleeman (of The Cross Kings) and Tom Sloan (of Tom Sloan Design) which sits in the pedestrian subway, the King’s Cross Tunnel. Other highlights include Julian Opie’s work Shaida Walking, 2015 which will be permanently located in Broadwick Street, Soho, and Janet Echelon’s enormous net sculpture 1.8 London which is strung between buildings at Oxford Circus. The festival runs from 6.30pm to 10.30pm over the next four nights. You can download a free map on the installations or use the free London Official City Guide app to locate them. For more information – including the full programme – see www.visitlondon.com/lumiere.
• A property deed signed by playwright William Shakespeare and one of the most complete first folios of his works have gone on show in the London Heritage Gallery at the Guildhall Art Gallery. Alongside the two documents which dates from 1613 and 1623, the Shakespeare and London exhibition marks the 400th anniversary of Shakespeare’s death – to be commemorated on 23rd April this year – will also display other documents related to the story of London’s playhouses. The property deed – which relates to a property in Blackfriars – is only one of six surviving documents to bear the playwrights authenticated signature while the first folio is one of five of the most complete copies in existence and is apparently usually only brought out for consultation by Shakespearean scholars and actors. The exhibition runs until 31st March. Admission is free. For more on it and other events being run to commemorate the Bard’s death, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/shakespeare400. For more on other events this year, check out www.shakespeare400.org.
• See your art featured in an upcoming exhibition on the importance of bees and pollination by attending a drop-in workshop at Victoria Tower Gardens next to the Houses of Parliament next week. The workshop, which will be held from 10am to 2pm on 20th January, will see participants create their own 3D flowers based on famous paintings by Vincent Van Gogh and Jan Van Huysum currently in The National Gallery’s collection – all as part of a focus looking at what plants bees are attracted to. The art created in the workshop will be seen in an exhibition A Right Royal Buzz which is the result of a collaboration between The Royal Parks, The National Gallery and Mall Galleries and will be seen across all three venues (Victoria Tower Gardens representing the Royal Parks) from 17th t0 20th February. For more, head to this link.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
LondonLife – Australia House’s holy well…
 News this week that scientists have confirmed an ancient sacred well beneath Australia House in the Strand (on the corner of Aldwych) contains water fit to drink. The well, believed to be one of 20 covered wells in London, is thought to be at least 900 years old and contains water which is said to come from the now-subterranean Fleet River. Australia’s ABC news was recently granted special access to the well hidden beneath a manhole cover in the building’s basement and obtained some water which was tested and found to be fit for drinking. It’s been suggested that the first known mention of the well – known simply as Holywell (it gave its name to a nearby street now lost) – may date back to the late 12th century when a monk, William FitzStephen, commented about the well’s “particular reputation” and the crowds that visited it (although is possible his comments apply to another London well). Australia House itself, home to the Australian High Commission, was officially opened in 1918 by King George V, five years after he laid the foundation stone. The Prime Minister of Australia, WM “Billy” Hughes, was among those present at the ceremony. The interior of the building has featured in the Harry Potter movies as Gringott’s Bank. PICTURE: © Martin Addison/Geograph.
News this week that scientists have confirmed an ancient sacred well beneath Australia House in the Strand (on the corner of Aldwych) contains water fit to drink. The well, believed to be one of 20 covered wells in London, is thought to be at least 900 years old and contains water which is said to come from the now-subterranean Fleet River. Australia’s ABC news was recently granted special access to the well hidden beneath a manhole cover in the building’s basement and obtained some water which was tested and found to be fit for drinking. It’s been suggested that the first known mention of the well – known simply as Holywell (it gave its name to a nearby street now lost) – may date back to the late 12th century when a monk, William FitzStephen, commented about the well’s “particular reputation” and the crowds that visited it (although is possible his comments apply to another London well). Australia House itself, home to the Australian High Commission, was officially opened in 1918 by King George V, five years after he laid the foundation stone. The Prime Minister of Australia, WM “Billy” Hughes, was among those present at the ceremony. The interior of the building has featured in the Harry Potter movies as Gringott’s Bank. PICTURE: © Martin Addison/Geograph.
This Week in London – Celts at the British Museum; the Fallen Woman at the Foundling; and Ai Weiwei…
 • The story of the Celts and their culture is being explored in a new exhibition which opens at the British Museum in Bloomsbury today. Celts: Art and Identity, being run in partnership with National Museums Scotland, is the first British exhibition on the Celts in 40 years. Highlights of the display include a hoard of four gold torcs found at Blair Drummond in Stirling in 2009, Christian artefacts including iron handbells used to call people to prayer, elaborately illustrated Gospels, carved stone crosses and, a gilded bronze processional cross which, dating from 700-800 AD and coming from Tully Lough in Ireland, will be on show for the first time in Britain. Also present will be the Gundestrup cauldron, which dates from 100 BC-1 AD and comes from Denmark (pictured), London artefacts such as the Waterloo helmet and Battersea shield, and works created more recently which reflect on an often mythical Celtic past such as George Henry and Edward Atkinson Homel’s 1890 painting The Druids: Bringing in the Mistletoe. Runs until 31st January in the Sainsbury Exhibition Gallery (Room 30). Admission charge applies. For more, see www.britishmuseum.org. PICTURE: © The National Museum of Denmark.
• The story of the Celts and their culture is being explored in a new exhibition which opens at the British Museum in Bloomsbury today. Celts: Art and Identity, being run in partnership with National Museums Scotland, is the first British exhibition on the Celts in 40 years. Highlights of the display include a hoard of four gold torcs found at Blair Drummond in Stirling in 2009, Christian artefacts including iron handbells used to call people to prayer, elaborately illustrated Gospels, carved stone crosses and, a gilded bronze processional cross which, dating from 700-800 AD and coming from Tully Lough in Ireland, will be on show for the first time in Britain. Also present will be the Gundestrup cauldron, which dates from 100 BC-1 AD and comes from Denmark (pictured), London artefacts such as the Waterloo helmet and Battersea shield, and works created more recently which reflect on an often mythical Celtic past such as George Henry and Edward Atkinson Homel’s 1890 painting The Druids: Bringing in the Mistletoe. Runs until 31st January in the Sainsbury Exhibition Gallery (Room 30). Admission charge applies. For more, see www.britishmuseum.org. PICTURE: © The National Museum of Denmark.
• A new exhibition exploring the myth and reality of the ‘fallen woman’ in Victorian Britain opens at the Foundling Museum in Bloomsbury tomorrow. The Fallen Woman features works by artists including Dante Gabriel Rossetti, Richard Redgrave, George Frederic Watts and George Cruikshank, displayed alongside stereoscopes and depictions of the fallen woman in the era’s popular media. It also looks at the petitions of women applying to the Foundling Hospital, bringing to life the real ‘fallen women’ of the period through a specially-commissioned sound installation by artist and musician Steve Lewinson. The exhibition runs until 3rd January. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.foundlingmuseum.org.uk.
• The London Transport Museum’s Depot in Acton hosts its autumn open days this weekend. The day includes the chance to see the original printing blocks used for the Johnston font – London Transport’s iconic typeface, expert talks on transport vehicles, a chance to see how the moquette – the seat covering on the tube – is made and film screenings from the LTM archive. From 11am to 5pm Saturday and Sunday. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.ltmuseum.co.uk.
• The Worshipful Company of Woolmen will be holding their annual sheep drive across London bridge this Sunday. The event, free to watch, kicks off at 10am and runs until 5pm. For more, see www.woolmen.com.
• On Now: Ai Weiwei. This landmark exhibition at the Royal Academy of Arts in Piccadilly celebrates the work of Honorary Royal Academician and leading Chinese artist Ai Weiwei with significant works from 1993 onwards and new, site specific installations. Among the key exhibits is Straight (2008-12), a body of work related to the Sichuan earthquake of 2008, fabricated from 90 tonnes of bent and twisted rebar which was collected by the artist and straightened by hand. Runs until 13th December. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.royalacademy.org.uk.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
What’s in a name?…Carnaby Street…
Renowned as the heart of the UK’s fashion industry in the 1960s, Carnaby Street’s origins go back to a mansion built here known as Karnaby House (with a ‘k’, although the street always apparently started with a ‘c’).
 The house was built in 1683 although who it was built for remains something of a mystery. It was apparently was demolished within 50 years or so when the east side of the street, which had been laid out in the late 1600s, was recorded as the site of a series of “pest” (plague) houses.
The house was built in 1683 although who it was built for remains something of a mystery. It was apparently was demolished within 50 years or so when the east side of the street, which had been laid out in the late 1600s, was recorded as the site of a series of “pest” (plague) houses.
The street was later home an abbatoir and while tailors had moved in during the late 19th century, it wasn’t until the middle of the 20th century that it began to attract a reputation for fashion, becoming the epicentre of Swinging London during the 1960s.
Boutiques included John Stephen’s pioneering men’s boutique His Clothes – which attracted high profile customers including members of The Small Faces, The Rolling Stones and The Who – as well as Lady Jane, Lord John, and the wonderfully named I was Lord Kitchener’s Valet.
The street – which was pedestrianised in 1973 – is still home to a large number of fashion boutiques. It’s numerous pop-culture references include its appearance in U2’s video for the 1992 song Even Better Than The Real Thing and it being named as the location of the flat of ‘spy’ Austin Powers. In recent years it’s also has its own stage show: Carnaby Street: The Musical.
For more on Carnaby Street today, check out www.carnaby.co.uk.
This Week in London – Animals in the British Library; Gladiators at Guildhall; and celebrating “pocket parks”…
 • From Peter Rabbit to Aesop’s Fables, animals and their appearance in some of the classics of literature are the subject of a new exhibition which opened at the British Library in St Pancras yesterday. Animal Tales explores the role animals have played in traditional tales around the world along with their importance in the development of children’s literature, and their use in allegorical stories such as CS Lewis’ The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe as well as literary transformations between man and beast (this last in a nod to the fact it’s the centenary of Franz Kafka’s The Metamorphosis). Highlights in the exhibition include one of the first children’s picture books – the 1659 edition of Comenius’ Orbis sensualism pictus, an 18th century woodblock edition of Wu Cheng’en’s Journey to the West, and a soundscape installation drawn from the library’s world leading collection of natural history recordings along with other animal tales from the sound archive. The exhibition, which runs until 1st November, will be accompanied by a series of events. Entry is free (and the display includes a children’s reading area and a family trail brochure). For more, see www.bl.uk. PICTURE: The title page from the 1950 London edition of CS Lewis’ The Lion, the witch and the wardrobe. © CS Lewis Pte Ltd.
• From Peter Rabbit to Aesop’s Fables, animals and their appearance in some of the classics of literature are the subject of a new exhibition which opened at the British Library in St Pancras yesterday. Animal Tales explores the role animals have played in traditional tales around the world along with their importance in the development of children’s literature, and their use in allegorical stories such as CS Lewis’ The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe as well as literary transformations between man and beast (this last in a nod to the fact it’s the centenary of Franz Kafka’s The Metamorphosis). Highlights in the exhibition include one of the first children’s picture books – the 1659 edition of Comenius’ Orbis sensualism pictus, an 18th century woodblock edition of Wu Cheng’en’s Journey to the West, and a soundscape installation drawn from the library’s world leading collection of natural history recordings along with other animal tales from the sound archive. The exhibition, which runs until 1st November, will be accompanied by a series of events. Entry is free (and the display includes a children’s reading area and a family trail brochure). For more, see www.bl.uk. PICTURE: The title page from the 1950 London edition of CS Lewis’ The Lion, the witch and the wardrobe. © CS Lewis Pte Ltd.
• Gladiators will battle it out on the former site of London’s open air Roman amphitheatre in Guildhall Yard this weekend. The shows – which will recreate what gladiatorial games were like in Roman Londinium – will be presided over by an emperor with the crowd asked to pick its side. The ticketed event, being put on by the Museum of London, takes place Friday night from 7pm to 8pm and on Saturday and Sunday, from noon to 1pm and between 3pm and 4pm. Admission charges apply. To book, see www.museumoflondon.org.uk.
• A new International Visitors Victim Service has been launched in London to specifically help foreign nationals affected by crime in the city. The first of its kind in the UK, the service, which has been established by the Metropolitan Police working with independent charity Victim Support and embassies, already operates across the five central London boroughs and is now available through a mobile police kiosk located in the West End’s “impact zone”, an area which spans Leicester Square and Piccadilly Circus (alternatively they can contact the International Visitor Advocates by calling 0207 259 2424 or visit the West End Central Police Station at 27 Savile Row.
• The Mayor of London, Boris Johnson, has celebrated the creation of 100 new pocket parks across London’s 26 boroughs in a scheme which is now being adopted by other locations across the country. The parks range from a rain garden in Vauxhall to a dinosaur playground in Hornsey and have seen more than 25 hectares of community land converted into enhanced green areas. A free exhibition is running at City Hall until 28th August which focuses on the stories of 11 people involved in the creation of the parks. For more on London’s “great outdoors”, you can see an interactive map at www.london.gov.uk/outdoors.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.
This Week in London – London Festival of Architecture’s ‘Work in Progress’; objects and sestudes at the Foundling Museum; and, sculpting Sir Tim Berners-Lee…
 • The month-long London Festival of Architecture is underway with this year’s theme ‘Work in Progress’. Highlights of this year’s programme – which includes 220 exhibitions, installations, talks and tours – include a discussion at this year’s Serpentine Gallery (pictured) by architects SelgasCano, access to development sites including Olympic Park, Goodman’s Fields, and Nine Elms, a London Transport Museum tour of London’s first skyscraper, an installation exploring the role of coffee shop as workspace by the Not to Scale Collective, and a Routemaster tour of the West End. For more, including a downloadable PDF of the programme, see www.londonfestivalofarchitecture.org.
• The month-long London Festival of Architecture is underway with this year’s theme ‘Work in Progress’. Highlights of this year’s programme – which includes 220 exhibitions, installations, talks and tours – include a discussion at this year’s Serpentine Gallery (pictured) by architects SelgasCano, access to development sites including Olympic Park, Goodman’s Fields, and Nine Elms, a London Transport Museum tour of London’s first skyscraper, an installation exploring the role of coffee shop as workspace by the Not to Scale Collective, and a Routemaster tour of the West End. For more, including a downloadable PDF of the programme, see www.londonfestivalofarchitecture.org.
• A series of 26 ‘sestudes’ – texts exactly 62 words long – are being displayed along with the objects that inspired them in a new exhibition, 26 Pairs of Eyes, at The Foundling Museum in Bloomsbury. The sestudes have been written by the likes of former Poet Laureate Sir Andrew Motion in a bid cast new light on the objects, which are all from the museum’s collection and which range from a pencil which once belonged to Hospital Secretary John Brownlow to George Frideric Handel’s will. The display, which opens today, is on show until 6th September. Meanwhile the museum is also hosting another exhibition, Lines of Beauty, which explores the tradition of decorative plasterwork including the restored Rococo splendour of the hospital’s Court Room (donated by William Wilton in the 1740s and saved when the Foundling Hospital building was demolished in the 1920s). Admission charges apply. For more, see www.foundlingmuseum.org.uk.
• A new portrait of the inventor of the World Wide Web, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, has been unveiled at the National Portrait Gallery. The work of Sean Henry, the painted bronze sculpture depicts a two-thirds life size Berners-Lee carrying the leather rucksack in which he keeps his laptop. It was commissioned to mark Sir Tim’s 60th birthday and is the gallery’s first commissioned portrait sculpture for seven years. On display in Room 40. Admission is free. For more, see www.npg.org.uk.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.