• This year marks the 150th anniversary of the transatlantic cable connecting Europe and America and in celebration of the event, the City of London Corporation’s Guildhall Art Gallery is holding an exhibition looking at the impact of cable telegraphy on people’s understanding of time, space and the speed of communication. Victorians Decoded: Art and Telegraphy, a collaboration between the gallery, King’s College London, The Courtauld Institute of Art and the Institute of Making at University College London, features never-before-seen paintings from the gallery’s collection as well as rare artefacts such as code books, communication devices, samples of transatlantic telegraph sales and ‘The Great Grammatizor’, a messaging machine that will enable the public to create a coded message of their own. It took nine years, four attempts and the then largest ship in the world, the Great Eastern, to lay the cable which stretched from Valentia Island in Ireland to Newfoundland in Canada and enabled same-day messaging across the continents for the first time. Displayed over four themed rooms – ‘Distance’, ‘Resistance’, ‘Transmission’ and ‘Coding’, the exhibition features works by artists including Edward John Pointer, Edwin Landseer, James Clarke Hook, William Logsdail, William Lionel Wyllie and James Tissot. The free exhibition, which runs until 22nd January, is accompanied by a series of special curator talks. For more information, see www.cityoflondon.gov.uk/victoriansdecoded. PICTURE: Commerce and Sea Power, William Lionel Wyllie/Courtesy Guildhall Art Gallery.
• The life of artist Sir James Thornhill – the painter behind the remarkable Painted Hall at the Old Royal Naval College in Greenwich, has opened at The Stephen Lawrence Gallery in Greenwich. A Great and Noble Design: Sir James Thornhill’s Painted Hall explores the story behind the commissioning of the Painted Hall, painted between 1708 and 1727, through a series of preparatory sketches made by the artist, including three newly-conserved original sketches by Thornhill. Also on show will be the results of new research undertaken into the paintings in the light of upcoming conservation work on the hall’s ceiling. The free exhibition runs at the centre at Stockwell Street until 28th October. For more, see www.ornc.org.
• The food served at the Foundling Hospital comes under scrutiny in a new show at The Foundling Museum in Bloomsbury. Based on new research, Feeding the 400 looks at the impact food and eating regimes had on children at the hospital between 1740 and 1950 through an examination of art, photographs, objects including tableware and the voices of former student captured in the museum’s extensive sound archive. Guest curated by Jane Levi, the exhibition also includes a newly commissioned sound work which evokes the experience of communal eating. A programme of events accompanies the exhibition which runs until the 8th January. Admission charge applies. For more, see www.foundlingmuseum.org.
Send all items for inclusion to exploringlondon@gmail.com.









 Albury Street in Deptford, 1911. The image, taken by the London County Council, is just one of thousands which form part of a new free, online resource, Collage – The London Picture Archive. The world’s largest collection of images of London, the archive contains more than 250,000 images of London spanning the period from 1450 to the present day. It includes more than 8,000 historical photographs of life on the capital’s streets as well as major events – everything from the Great Fire of London in 1666 to the construction of Tower Bridge in the late 19th century. The photographs, maps, prints, paintings and films in the collection are all drawn from the collections of the City of London Corporation’s Guildhall Art Gallery and the London Metropolitan Archives in Clerkenwell. Other images shown here include (above right) ‘Street Life in London’, 1877 (taken by Adolphe Smith and John Thomson, this image was an early use of photography); (below) ‘Construction of the Metropolitan Railway (the first tube line)’, 1862 (taken at King’s Cross Station); and (far below), ‘The Construction of Tower Bridge’, 1891-1892 (taken from Tower Embankment). Collage – The London Picture Archive is free to access and available at
Albury Street in Deptford, 1911. The image, taken by the London County Council, is just one of thousands which form part of a new free, online resource, Collage – The London Picture Archive. The world’s largest collection of images of London, the archive contains more than 250,000 images of London spanning the period from 1450 to the present day. It includes more than 8,000 historical photographs of life on the capital’s streets as well as major events – everything from the Great Fire of London in 1666 to the construction of Tower Bridge in the late 19th century. The photographs, maps, prints, paintings and films in the collection are all drawn from the collections of the City of London Corporation’s Guildhall Art Gallery and the London Metropolitan Archives in Clerkenwell. Other images shown here include (above right) ‘Street Life in London’, 1877 (taken by Adolphe Smith and John Thomson, this image was an early use of photography); (below) ‘Construction of the Metropolitan Railway (the first tube line)’, 1862 (taken at King’s Cross Station); and (far below), ‘The Construction of Tower Bridge’, 1891-1892 (taken from Tower Embankment). Collage – The London Picture Archive is free to access and available at 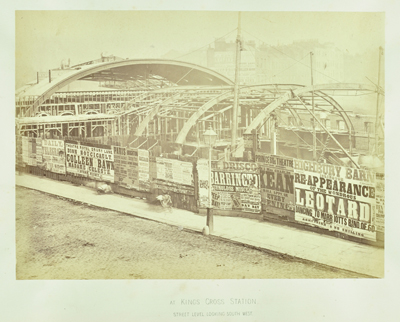






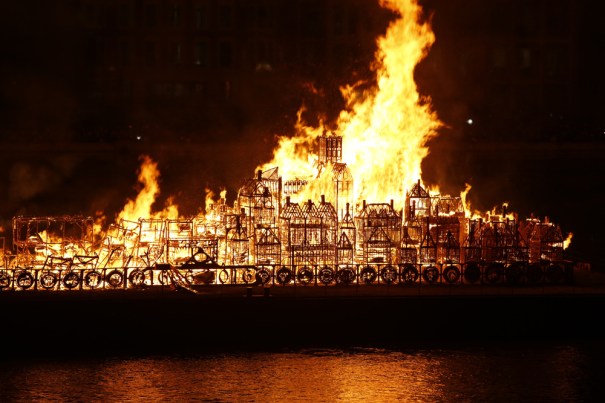
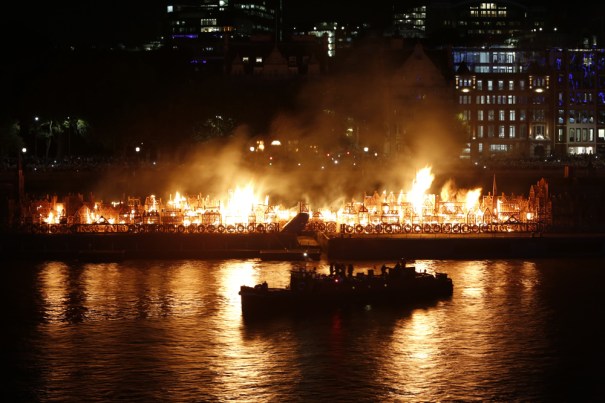
 Then only consisting of the central barrel and pump, it has been restored for the current exhibition, Fire! Fire!, being held to mark the 350th anniversary of the fire which wiped out much of the City of London.
Then only consisting of the central barrel and pump, it has been restored for the current exhibition, Fire! Fire!, being held to mark the 350th anniversary of the fire which wiped out much of the City of London.









