Sir Thomas Bludworth (also spelt Bloodworth) is usually only remembered as the man who had the unfortunate job of being Lord Mayor of London when the Great Fire broke out in 1666. So, given the fire’s 350th anniversary this month, we thought it timely to take a more in-depth look at his life and career.
Sir Thomas Bludworth (also spelt Bloodworth) is usually only remembered as the man who had the unfortunate job of being Lord Mayor of London when the Great Fire broke out in 1666. So, given the fire’s 350th anniversary this month, we thought it timely to take a more in-depth look at his life and career.
Bludworth was born in London in February, in about 1620, the second surviving son of John Bludworth, master of the Vintner’s Company and a wealthy merchant. Trained to succeed his father – his elder brother having joined the clergy, Bludworth was himself admitted to the Vintner’s Company in the 1640s and joined the Levant Company in 1648.
First elected an alderman in 1658, he was discharged when he refused to serve as a sheriff and the following year served as the master of the Vintner’s Company. In 1660, he was briefly arrested along with 10 other members of City of London’s common council after the body refused to pay taxes until a representative parliament was convened.
Elected MP for Southwark later that year, Bludworth among city and parliamentary representatives who sailed to The Netherlands to attend the king, Charles II, in exile, and invite him to return to England. It was while attending the king in The Hague that he was knighted. Re-elected in 1661, he was an active parliamentarian who served in numerous different capacities.
Sir Thomas was twice married and had a number of children including a formidable daughter Anne who eventually married the historically unpopular George Jeffreys, (later King James II’s Lord Chief Justice and Lord Chancellor).
In mid-1662, he was once again made a City of London alderman and appointed one of two sheriffs for the following year. He became Lord Mayor of London in November, 1665, but apparently there was no pageant as was customary due to the plague.
During his year in the office – “the severest year any man had” – he faced both the plague and the Great Fire and his reputation has been largely formed out of his response to the latter thanks in large part his alleged response when woken and told of the fire as being: “Pish, a woman might piss it out!”.
Bludworth was heavily criticised at the time and over the years since his reaction to the fire – including not pulling down homes to create a firebreak and thus prevent the spread of the fire, but it should be noted that had he done so before he had received the king’s permission, he would have found himself personally liable.
Diarist Samuel Pepys’ who, following two encounters in the months before the fire had already described Bludworth as “mean man of understanding and despatch of any public business”, recorded that when he finally brought a message from the king ordering the creation of a firebreak, Sir Thomas seemed like “a man spent”.
“To the King’s message (to create a firebreak by pulling down houses), he cried, like a fainting woman, ‘Lord, what can I do? I am spent: people will not obey me. I have been pulling down houses, but the fire overtakes us faster than we can do it’.”
Another eyewitness describes him as looking like he was “frighted out of his wits” during the fire.
Sir Thomas’ own property at Gracechurch Street was among the casualties of the fire but he later built a new mansion in Maiden Lane.
He continued to serve as an MP after the fire and was, perhaps ironically, appointed to a committee working on a bill to provide “utensils” for the “speedy quenching of fire”. In the mid-1670s, he become one of the governing members of the Royal African Company.
Sir Thomas died on 12th May, 1682, aged around 60. He was apparently buried in Leatherhead.
 • From tonight (and across this weekend), museums all over Greater London will be opening their doors after usual closing time as part of the annual Museums at Night event. Among those institutions taking part in the event, produced by Culture24, are such well-known icons as the British Museum, Tower Bridge and The National Gallery as well as lesser known establishments like Queen Elizabeth’s Hunting Lodge in Chingford, Southside House on Wimbledon Common and the Grant Museum of Zoology in central London. The October event follows an earlier Museums at Night in May. For the full programme of events, see www.museumsatnight.org.uk.
• From tonight (and across this weekend), museums all over Greater London will be opening their doors after usual closing time as part of the annual Museums at Night event. Among those institutions taking part in the event, produced by Culture24, are such well-known icons as the British Museum, Tower Bridge and The National Gallery as well as lesser known establishments like Queen Elizabeth’s Hunting Lodge in Chingford, Southside House on Wimbledon Common and the Grant Museum of Zoology in central London. The October event follows an earlier Museums at Night in May. For the full programme of events, see www.museumsatnight.org.uk.
























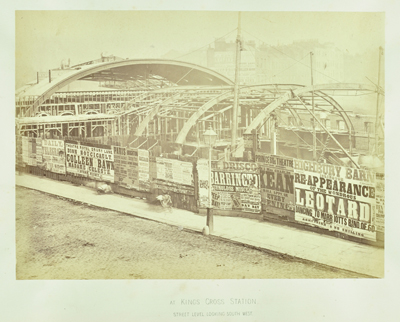
 Albury Street in Deptford, 1911. The image, taken by the London County Council, is just one of thousands which form part of a new free, online resource, Collage – The London Picture Archive. The world’s largest collection of images of London, the archive contains more than 250,000 images of London spanning the period from 1450 to the present day. It includes more than 8,000 historical photographs of life on the capital’s streets as well as major events – everything from the Great Fire of London in 1666 to the construction of Tower Bridge in the late 19th century. The photographs, maps, prints, paintings and films in the collection are all drawn from the collections of the City of London Corporation’s Guildhall Art Gallery and the London Metropolitan Archives in Clerkenwell. Other images shown here include (above right) ‘Street Life in London’, 1877 (taken by Adolphe Smith and John Thomson, this image was an early use of photography); (below) ‘Construction of the Metropolitan Railway (the first tube line)’, 1862 (taken at King’s Cross Station); and (far below), ‘The Construction of Tower Bridge’, 1891-1892 (taken from Tower Embankment). Collage – The London Picture Archive is free to access and available at
Albury Street in Deptford, 1911. The image, taken by the London County Council, is just one of thousands which form part of a new free, online resource, Collage – The London Picture Archive. The world’s largest collection of images of London, the archive contains more than 250,000 images of London spanning the period from 1450 to the present day. It includes more than 8,000 historical photographs of life on the capital’s streets as well as major events – everything from the Great Fire of London in 1666 to the construction of Tower Bridge in the late 19th century. The photographs, maps, prints, paintings and films in the collection are all drawn from the collections of the City of London Corporation’s Guildhall Art Gallery and the London Metropolitan Archives in Clerkenwell. Other images shown here include (above right) ‘Street Life in London’, 1877 (taken by Adolphe Smith and John Thomson, this image was an early use of photography); (below) ‘Construction of the Metropolitan Railway (the first tube line)’, 1862 (taken at King’s Cross Station); and (far below), ‘The Construction of Tower Bridge’, 1891-1892 (taken from Tower Embankment). Collage – The London Picture Archive is free to access and available at