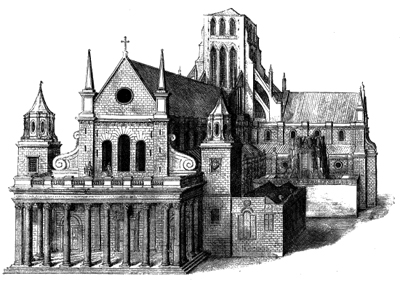
Founded in Clerkenwell in 1144, the Priory of the Order of St John of Jerusalem served as the order’s English headquarters.
The order, also known as the Knights Hospitaller, was founded in Jerusalem in 1080 to care for the sick and poor, and soon spread across Europe with the English ‘branch’ established on 10 acres just outside the City walls apparently by a knight, Jorden de Briset.
The original buildings – of which only the 12th century crypt (pictured above) survives complete with some splendid 16th century tomb effigies including that of the last prior, Sir William Weston – included a circular church, consecrated in 1185, and monastic structures including cloisters, a hospital, living quarters and a refectory or dining hall.
There are records of dignitaries staying at the priory as it grew in size and renown – among them was King John who in 1212, apparently stayed here for an entire month. There are also surviving accounts of Knights Hospitaller riding out in procession from the priory and through the City at the start of a journey to the Holy Land.
The priory and church were attacked during the Peasant’s Revolt of 1381, thanks to its connection with the hated Poll Tax (Prior Robert Hales was also the Lord High Treasurer and was beheaded during the revolt on Tower Hill).
The church was subsequently rebuilt as a rectangular-shaped building and then, in the early 16th century, enlarged when the site was significantly renovated. These renovations were still relatively new when the priory was dissolved in 1540 during the Dissolution of King Henry VIII.
The priory church, which survived the Great Fire of 1666, was later used as a parish church but was destroyed in an air raid in World War II. Subsequently rebuilt, it can be visited today along with the crypt below and the cloister garden, created in the 1950s as a memorial to St John’s Ambulance members from the London area (the original shape of the circular church is picked out in the paving here).
Perhaps the most famous building to survive is St John’s Gate which dates from the 16th century and was once the gatehouse entrance to the priory (added in the final renovations).
After the Dissolution it served various roles including as the office of the Master of Revels (where Shakespeare’s plays were licensed), the home of The Gentleman’s Magazine (Samuel Johnson was among contributors and worked on site), a coffee house (run by William Hogarth’s father) and a public house called the Old Jerusalem Tavern (yes, Charles Dickens was said to be a regular). It is now home to the recently renovated Museum of the Order of St John (you can see our earlier post on the museum here).
WHERE: Museum of the Order of St John, St John’s Gate (and nearby priory church), St John’s Lane, Clerkenwell (nearest Tube stations is Farringdon); WHEN: 10am to 5pm, Monday to Saturday (tours are held at 11am and 2.30pm on Tuesday, Friday and Saturday); COST: Free (a suggested £5 donation for guided tours); WEBSITE: www.museumstjohn.org.uk.
We’ll kick off a new Wednesday series next week…
 This bronze sculpture, located in Watling Street in the City of London, commemorates Ward of Cordwainer which in medieval times was home to London’s shoe-making industry.
This bronze sculpture, located in Watling Street in the City of London, commemorates Ward of Cordwainer which in medieval times was home to London’s shoe-making industry.