 Described as the first dedicated Indian restaurant in Britain, the Hindoostanee (also spelt Hindoostane) Coffee House was established by Dean Mahomet (later Sheikh or ‘Sake’ Dean Mahomet), an Indian who served with the East India Company Army before coming to Britain.
Described as the first dedicated Indian restaurant in Britain, the Hindoostanee (also spelt Hindoostane) Coffee House was established by Dean Mahomet (later Sheikh or ‘Sake’ Dean Mahomet), an Indian who served with the East India Company Army before coming to Britain.
Accompanying East India Company man Godfrey Baker to Ireland, he lived initially with the Baker family before meeting and marrying a young woman while learning English and subsequently establishing his own household in Cork.
In 1794, he published a book, The Travels of Dean Mahomet, which, written as a series of letters to an imaginary friend, described his own life and Indian customs. It is credited as the first book to be written and published in English by an Indian.
Around 1807, he and his wife and son moved to London where he initially found employment with Sir Basil Cochrane at a “vapour spa” Sir Basil had established in Portman Square. While Mahomet introduced Indian innovations such as “shampooing” to the spa, he was given little credit for his work, however, and so decided to break out on his own.
In 1810, he set-up the coffee house at 34 George Street, Portman Square, just behind Sir Basil’s house.
The establishment was aimed at Anglo-Indians who had spent time in India and offered them Indian-style foods – such as curries and spiced dishes – along with other reminders of the sub-Continent such as a room set up for the use of the hookah with “real Chilm tobacco” – all in an Indian-style setting.
Sadly, the establishment was only rather short-lived and, despite taking on a partner, Mahomet was forced to declare bankruptcy in 1812. But he did go on to establish a very successful Indian-style baths in Brighton, Mahomet’s Baths (and later even opened a second branch in St James’s London which would be managed by his son).
A plaque was erected by the City of Westminster close to the site of the former coffee house in 2005.
PICTURE: Simon Harriyott from Uckfield, England [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons.


 4. Number four is another in our current series on London battlefields – this time looking at the site where Queen Boudicca is believed to have been defeated by the Romans –
4. Number four is another in our current series on London battlefields – this time looking at the site where Queen Boudicca is believed to have been defeated by the Romans –  7. At number seven is a post we published in February as part of our ongoing Lost London series. In it we looked at the later history of the fortification known as Baynard’s Castle –
7. At number seven is a post we published in February as part of our ongoing Lost London series. In it we looked at the later history of the fortification known as Baynard’s Castle – 


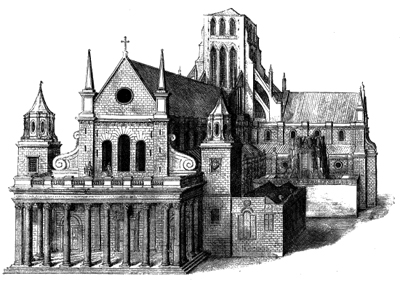




 The first was in Holborn, located between the northern end of Chancery Lane and Staple Inn, and was known as the ‘Old Temple’ after which, in the latter years of the 12th century, the Templars moved their headquarters to the new site – ‘New Temple’ or
The first was in Holborn, located between the northern end of Chancery Lane and Staple Inn, and was known as the ‘Old Temple’ after which, in the latter years of the 12th century, the Templars moved their headquarters to the new site – ‘New Temple’ or 
